

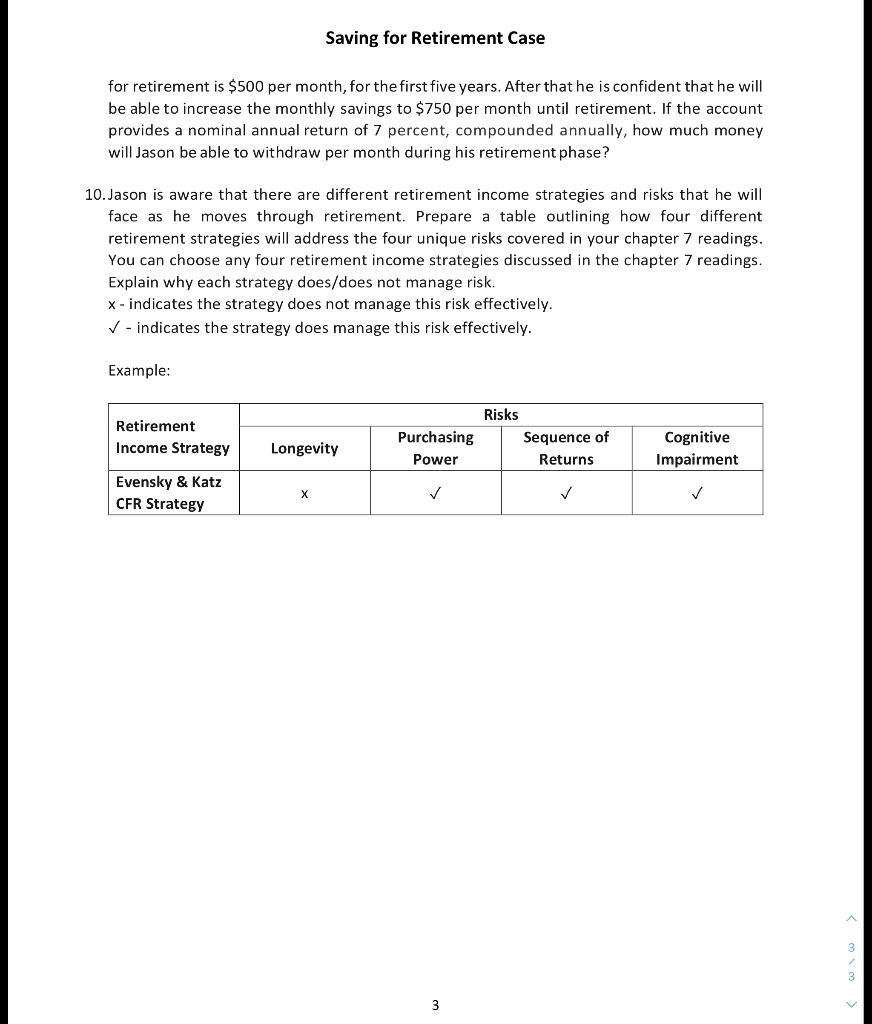
Saving for Retirement Case "Boy, this is all so confusing," said Jason as he stared at the papers on his desk. "If only I had taken the advice of my finance instructor, I would not be in such a predicament today." Jason Welch, aged 27, graduated five years ago with a degree in food marketing and is currently employed as a middle-level manager for a fairly successful grocery chain. His current annual salary of $75 000 has increased at an average rate of 3% per year (the inflation rate) and is projected to increase at least at that rate for the foreseeable future. The firm has a voluntary retirement savings program in place, whereby employees are allowed to contribute up to 11% of their gross annual salary, on a monthly basis, (up to a maximum of $12 000 per year) and the company matches every dollar that the employee contributes. Unfortunately, like many other young people who start out in their first "real" job, Jason has not yet taken advantage of the retirement savings program. He opted instead to buy a fancy car, rent an expensive apartment, and consume most of his income. However, with wedding plans on the horizon, Jason has finally come to the realization that he had better start putting away some money for the future. His fianc, Jillian, of course, had a lot to do with giving him this reality check. Jillian reminded Jason that besides retirement, there were various other large expenses that would be forthcoming and thatit would be wise for him to design a comprehensive savings plan, keeping in mind the various cost estimates and timelines involved. Jason figures that the two largest expenses down the road would be those related to the wedding and a down payment on a house. He estimates that the wedding, which will take place in 12 months, should cost about $22 000 in today's dollars. Furthermore, he plans to move into a $300 000 house (in today's terms) after five years and would need 20% for a down payment. Jason is aware that his cost estimates are in current terms and would need to be adjusted for inflation. Moreover, he knows that an automatic payroll deduction is probably the best way to go because he is not a very disciplined investor. Jason is really not sure how much money he should put away each month, given the inflation effects, the differences in timelines, and the salary increases that would be forthcoming. All this number crunching seems overwhelming, and the objectives seem insurmountable. If only he had started planning and saving five years ago, his financial situation would have been so much better. But, as the saying goes, "It's better late than never!" Saving for Retirement Case 1. What was Jason's starting salary? How much could he have contributed to the voluntary savings plan in his first year of employment? HINT: Jason has been with the employer for 5 years, so his starting salary is not $75 000. 2. Had Jason taken advantage of the company's voluntary retirement plan up to the maximum every year for the past five years, how much money would he currently have accumulated in his retirement account, assuming a nominal rate of return of 7 percent, compounded annually? How much more would his investment value have been worth had he opted for a higher risk alternative (.e., 100% in common stocks), which was expected to yield an average compound rate of return of 12 percent, compounded annually? HINT: Provide your answer in real dollars by calculating the real rate of return using a 3 percent rate of inflation. 3. If Jason starts his monthly retirement savings plan from January of next year by contributing the maximum allowable amount into the firm's voluntary retirement savings program and continuing each year up until his retirement, how much money will he have accumulated for retirement, in real dollars, assuming he retires at age 65? Assume that the rate of return on the account is 7 percent per year, compounded annually and that the maximum allowable contribution does not change. 4. How much would Jason have to save each month, starting from the end of the next month, in order to accumulate enough money for his wedding expenses, assuming that his investment fund is expected to yield a rate of return of 7 percent per year, compounded annually? 5. If Jason starts saving immediately for the 20% down payment on his house, how much additional money will he have to save each month? Assume an investment rate of return of 7 percent per year, compounded annually. 6. If Jason wants to have a million dollars (in terms today's dollars) when he retires at age 65, how much should he save in equal monthly deposits from the end of the next month? Ignore the cost of the wedding and the down payment on the house. Assume his savings earn a rate of 7 percent per year, compounded annually. 7. If Jason saves up the million dollars (in terms of today's dollars) by the time of his retirement at age 65, how much can he withdraw each month (beginning one month after his retirement) in equal dollar amounts, if he figures he will live to the age of 85? Assume that his investment fund yields a nominal rate of return of 7 percent per year, compounded annually. 8. Referring to question 7, is it likely that Jason will withdraw equal dollar amounts from his account each month? Explain using supporting information from your chapter 7 readings. 2 9. After preparing a detailed budget, Jason estimates that the maximum he will be able to save 3 2 Saving for Retirement Case for retirement is $500 per month, for the first five years. After that he is confident that he will be able to increase the monthly savings to $750 per month until retirement. If the account provides a nominal annual return of 7 percent, compounded annually, how much money will Jason be able to withdraw per month during his retirement phase? 10. Jason is aware that there are different retirement income strategies and risks that he will face as he moves through retirement. Prepare a table outlining how four different retirement strategies will address the four unique risks covered in your chapter 7 readings. You can choose any four retirement income strategies discussed in the chapter 7 readings. Explain why each strategy does/does not manage risk. X - indicates the strategy does not manage this risk effectively. - indicates the strategy does manage this risk effectively. Example: Retirement Income Strategy Risks Sequence of Returns Purchasing Power Longevity Cognitive Impairment Evensky & Katz CFR Strategy X 3 3 Saving for Retirement Case "Boy, this is all so confusing," said Jason as he stared at the papers on his desk. "If only I had taken the advice of my finance instructor, I would not be in such a predicament today." Jason Welch, aged 27, graduated five years ago with a degree in food marketing and is currently employed as a middle-level manager for a fairly successful grocery chain. His current annual salary of $75 000 has increased at an average rate of 3% per year (the inflation rate) and is projected to increase at least at that rate for the foreseeable future. The firm has a voluntary retirement savings program in place, whereby employees are allowed to contribute up to 11% of their gross annual salary, on a monthly basis, (up to a maximum of $12 000 per year) and the company matches every dollar that the employee contributes. Unfortunately, like many other young people who start out in their first "real" job, Jason has not yet taken advantage of the retirement savings program. He opted instead to buy a fancy car, rent an expensive apartment, and consume most of his income. However, with wedding plans on the horizon, Jason has finally come to the realization that he had better start putting away some money for the future. His fianc, Jillian, of course, had a lot to do with giving him this reality check. Jillian reminded Jason that besides retirement, there were various other large expenses that would be forthcoming and thatit would be wise for him to design a comprehensive savings plan, keeping in mind the various cost estimates and timelines involved. Jason figures that the two largest expenses down the road would be those related to the wedding and a down payment on a house. He estimates that the wedding, which will take place in 12 months, should cost about $22 000 in today's dollars. Furthermore, he plans to move into a $300 000 house (in today's terms) after five years and would need 20% for a down payment. Jason is aware that his cost estimates are in current terms and would need to be adjusted for inflation. Moreover, he knows that an automatic payroll deduction is probably the best way to go because he is not a very disciplined investor. Jason is really not sure how much money he should put away each month, given the inflation effects, the differences in timelines, and the salary increases that would be forthcoming. All this number crunching seems overwhelming, and the objectives seem insurmountable. If only he had started planning and saving five years ago, his financial situation would have been so much better. But, as the saying goes, "It's better late than never!" Saving for Retirement Case 1. What was Jason's starting salary? How much could he have contributed to the voluntary savings plan in his first year of employment? HINT: Jason has been with the employer for 5 years, so his starting salary is not $75 000. 2. Had Jason taken advantage of the company's voluntary retirement plan up to the maximum every year for the past five years, how much money would he currently have accumulated in his retirement account, assuming a nominal rate of return of 7 percent, compounded annually? How much more would his investment value have been worth had he opted for a higher risk alternative (.e., 100% in common stocks), which was expected to yield an average compound rate of return of 12 percent, compounded annually? HINT: Provide your answer in real dollars by calculating the real rate of return using a 3 percent rate of inflation. 3. If Jason starts his monthly retirement savings plan from January of next year by contributing the maximum allowable amount into the firm's voluntary retirement savings program and continuing each year up until his retirement, how much money will he have accumulated for retirement, in real dollars, assuming he retires at age 65? Assume that the rate of return on the account is 7 percent per year, compounded annually and that the maximum allowable contribution does not change. 4. How much would Jason have to save each month, starting from the end of the next month, in order to accumulate enough money for his wedding expenses, assuming that his investment fund is expected to yield a rate of return of 7 percent per year, compounded annually? 5. If Jason starts saving immediately for the 20% down payment on his house, how much additional money will he have to save each month? Assume an investment rate of return of 7 percent per year, compounded annually. 6. If Jason wants to have a million dollars (in terms today's dollars) when he retires at age 65, how much should he save in equal monthly deposits from the end of the next month? Ignore the cost of the wedding and the down payment on the house. Assume his savings earn a rate of 7 percent per year, compounded annually. 7. If Jason saves up the million dollars (in terms of today's dollars) by the time of his retirement at age 65, how much can he withdraw each month (beginning one month after his retirement) in equal dollar amounts, if he figures he will live to the age of 85? Assume that his investment fund yields a nominal rate of return of 7 percent per year, compounded annually. 8. Referring to question 7, is it likely that Jason will withdraw equal dollar amounts from his account each month? Explain using supporting information from your chapter 7 readings. 2 9. After preparing a detailed budget, Jason estimates that the maximum he will be able to save 3 2 Saving for Retirement Case for retirement is $500 per month, for the first five years. After that he is confident that he will be able to increase the monthly savings to $750 per month until retirement. If the account provides a nominal annual return of 7 percent, compounded annually, how much money will Jason be able to withdraw per month during his retirement phase? 10. Jason is aware that there are different retirement income strategies and risks that he will face as he moves through retirement. Prepare a table outlining how four different retirement strategies will address the four unique risks covered in your chapter 7 readings. You can choose any four retirement income strategies discussed in the chapter 7 readings. Explain why each strategy does/does not manage risk. X - indicates the strategy does not manage this risk effectively. - indicates the strategy does manage this risk effectively. Example: Retirement Income Strategy Risks Sequence of Returns Purchasing Power Longevity Cognitive Impairment Evensky & Katz CFR Strategy X 3 3









