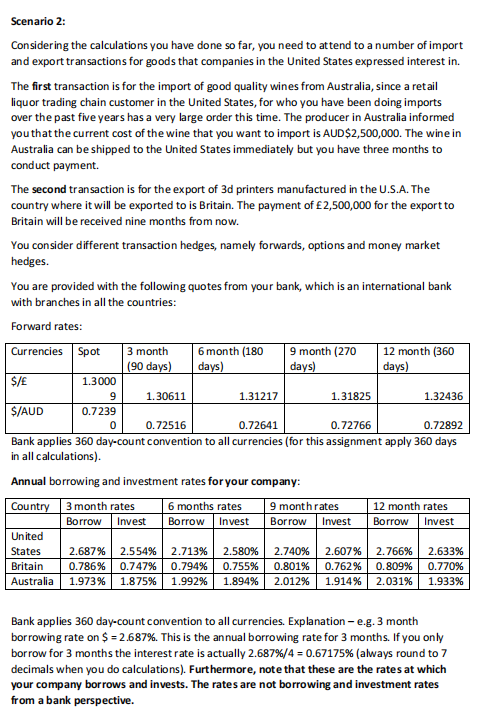
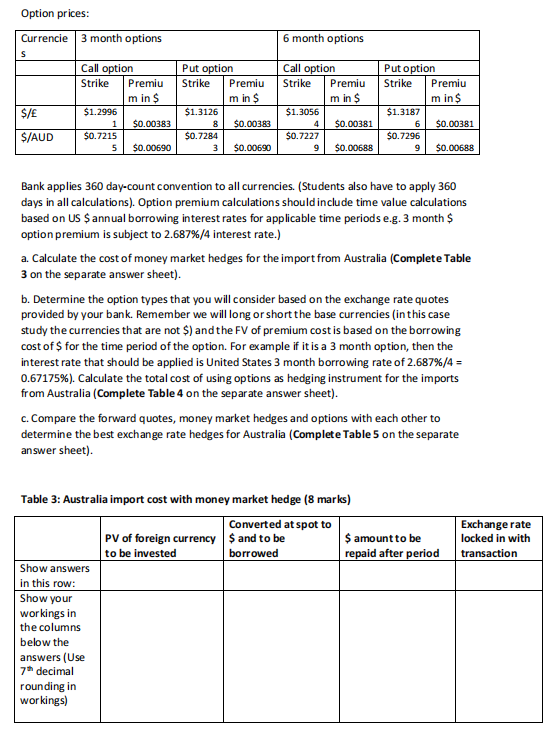
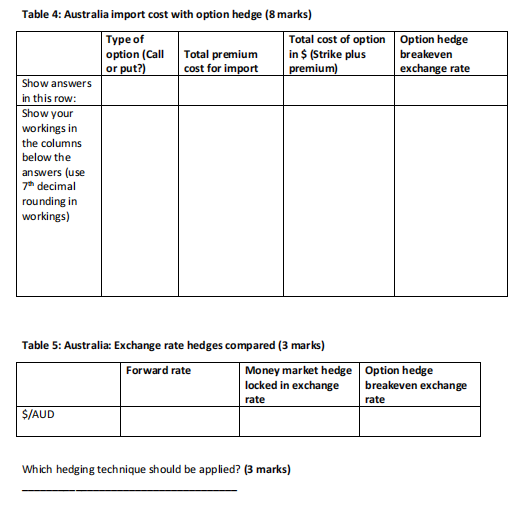
Scenario 2: Considering the calculations you have done so far, you need to attend to a number of import and export transactions for goods that companies in the United States expressed interest in. The first transaction is for the import of good quality wines from Australia, since a retail liquor trading chain customer in the United States, for who you have been doing imports over the past five years has a very large order this time. The producer in Australia informed you that the current cost of the wine that you want to import is AUD$2,500,000. The wine in Australia can be shipped to the United States immediately but you have three months to conduct payment The second transaction is for the export of 3d printers manufactured in the U.S.A. The country where it will be exported to is Britain. The payment of 2,500,000 for the export to Britain will be received nine months from now. You consider different transaction hedges, namely forwards, options and money market hedges. You are provided with the following quotes from your bank, which is an international bank with branches in all the countries: Forward rates: Currencies Spot 3 month 6 month (180 9 month (270 12 month (360 (90 days) days) days) days) $/ 1.3000 1.30611 1.31217 1.31825 1.32436 S/AUD 0.7239 0.72766 0.72892 Bank applies 360 day-count convention to all currencies (for this assignment apply 360 days in all calculations). Annual borrowing and investment rates for your company: Country 3 month rates 6 months rates 9 month rates 12 month rates Invest Borrow Invest Borrow Borrow United 2.687% 2.554% 2.713% 2.580% 2.607% 2.766% 2.633% 0.786% 0.747% 0.755% 0.801% 0.762% 0.809% 0.770% Australia 1.973% 1.875% 1.992% 1.894% 2.012% 1.914% 2.031% 9 0 0.72516 0.72641 Borrow Invest Invest 2.740% States Britain 0.794% 1.933% Bank applies 360 day-count convention to all currencies. Explanation - e.g. 3 month borrowing rate on $ = 2.687%. This is the annual borrowing rate for 3 months. If you only borrow for 3 months the interest rate is actually 2.687%/4 = 0.67175% (always round to 7 decimals when you do calculations). Furthermore, note that these are the rates at which your company borrows and invests. The rates are not borrowing and investment rates from a bank perspective. Option prices: Currencie 3 month options 6 month options S $/ Call option Strike Premiu min $ $1.2996 1 $0.00383 $0.7215 5 $0.00690 Put option Strike Premiu m in $ $1.3126 $0.00383 $0.7284 3 $0.00690 Call option Strike Premiu m in $ $1.3056 4 $0.00381 $0.7227 9 $0.00688 Put option Strike Premiu min $ $1.3187 6 $0.00381 $0.7296 9 $0.00688 8 $/AUD Bank applies 360 day-count convention to all currencies. (Students also have to apply 360 days in all calculations). Option premium calculations should include time value calculations based on US $ annual borrowing interest rates for applicable time periods e.g.3 month $ option premium is subject to 2.687%/4 interest rate.) a. Calculate the cost of money market hedges for the import from Australia (Complete Table 3 on the separate answer sheet). b. Determine the option types that you will consider based on the exchange rate quotes provided by your bank. Remember we will long or short the base currencies (in this case study the currencies that are not $) and the FV of premium cost is based on the borrowing cost of $ for the time period of the option. For example if it is a 3 month option, then the interest rate that should be applied is United States 3 month borrowing rate of 2.687%/4 = 0.67175%). Calculate the total cost of using options as hedging instrument for the imports from Australia (Complete Table 4 on the separate answer sheet). C. Compare the forward quotes, money market hedges and options with each other to determine the best exchange rate hedges for Australia (Complete Table 5 on the separate answer sheet). Exchange rate locked in with transaction Table 3: Australia import cost with money market hedge (8 marks) Converted at spot to PV of foreign currency $ and to be $ amount to be to be invested borrowed repaid after period Show answers in this row: Show your workings in the columns below the answers (Use 7 decimal rounding in workings) Table 4: Australia import cost with option hedge (8 marks) Type of Total cost of option Option hedge option (Call Total premium in $ (Strike plus breakeven or put?) cost for import premium) exchange rate Show answers in this row: Show your workings in the columns below the answers (use 7 decimal rounding in workings) Table 5: Australia: Exchange rate hedges compared (3 marks) Forward rate Money market hedge Option hedge locked in exchange breakeven exchange rate rate $/AUD Which hedging technique should be applied









