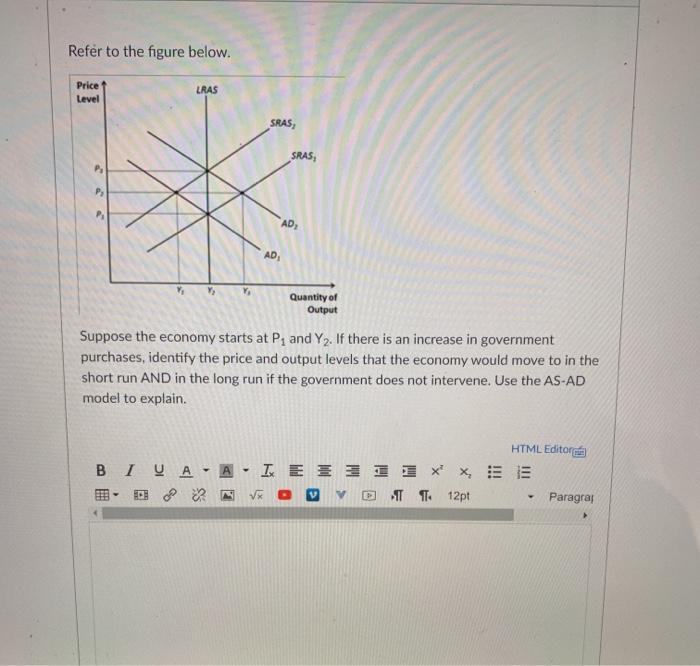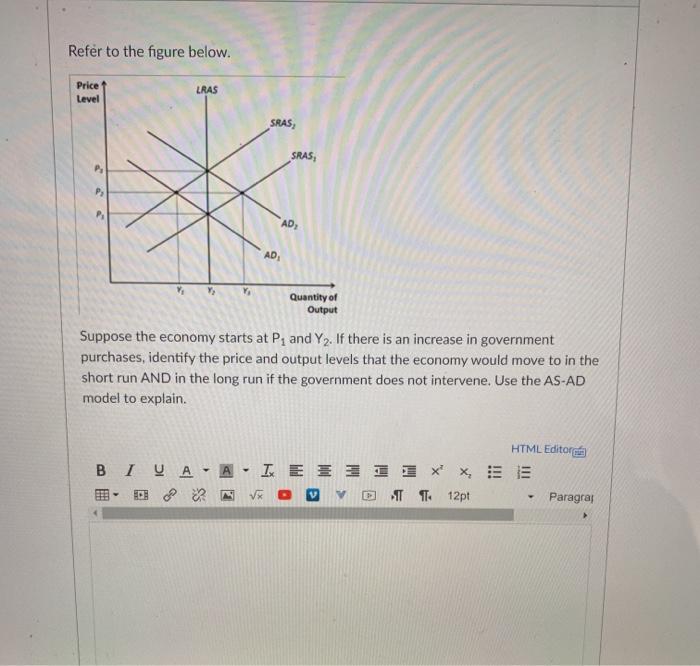

School of Computing, Information & Mathematical Sciences CS111: Introduction to Computing Science Assignment 3 Learning Outcome: 1. Apply programming concepts to computing problems 2. Identify the functionality of existing codes Weight: 20% Due Date: 17 June, 2020. Part 1: File Compression and multi-dimensional arrays Scenario A simple matrix could be used to store data about images by using 1's and O's to represent dark and light shades of color similar to a bitmap. You will find a file data.txt under your assignment 3 on Moodle. The file looks the image of an X drawn on a canvas. 0110000000000110 1000000000014 0011000000001100 0100000000140 0001100000011000 0000110000110000 0000011001100000 0000001111000000 0000000110000000 0000001111000000 0000011001100000 0000110000110000 0001100000011000 0011000000001100 07100000000110 0110000000000110 #1000000000017Question 29 O pts a. An economy is initially in equilibrium at the natural level. The central bank increases the money supply. Graphically illustrate and explain short-run monetary nonneutrality and long-run monetary neutrality using the AD-AS model. b. An economy is Initially in equilibrium at the natural level. The government increases the government spending. Graphically illustrate and explain short-run and long-run impacts using the AD-AS model. c. Related to our current economy, use the Ad-AS model to discuss the short-run and long-run impacts of current fiscal and monetary policies. Do you agree or disagree? Why?Refer to the figure below. Price LRAS Level SRAS, SRAS, AD, AD Quantity of Output Suppose the economy starts at P, and Y2. If there is an increase in government purchases, identify the price and output levels that the economy would move to in the short run AND in the long run if the government does not intervene. Use the AS-AD model to explain. HTML Editorme BIYA- ALEIX - 1 2 7 0 1 1 12p Paragral2. Consider a person with a current wealth of $100, 000 who faces a 25% chance of losing his automobile worth $20, 000. Her utility function is U(w) = log(w). a. Find the person's expected utility. b. What is the "actuarially fair" insurance premium and how much money will insurance cost? c. Up to how much money with the person be willing to pay to avoid the gamble (and thus live in a risk-free world)? Hint. The amount is a such that U (100, 000 -z) = expected utility from part a. d. How much money is the person saving by buying "actuarially fair" insurance?Karl-Heinz runs the BBQ place \"Fette San\" in Echo Park. His place is going reasOnably well but he is worried about a re that could ruin his inventory including the high-end sausages and the pork belly that he is selling. His wealth equals $1,000,000 and he gures that with 56.25 percent probability he loses inventory worth $640,000. His utility over wealth is given by U(W) = v\" W with, for example, U(1,000,000) = '/(1,000,000)=1,000 U(810,000) = 900 U{680,625) = 325 U(640,000) = 800 U(000,625) = 775 U(490,000) = 700 U(422,5D) = 050 U(350,000) = 600 U(302,500) = 550 U(250,000) = 500 1. What is Karl-Heinz's expected wealth? 'What is Karl-Heinz's expected utility? (20 Points) 2. Draw Karl-Heinz's utility niction in a diagram that has his wealth on the x-axis and his utility on the y-axis. Indicate his utilities in case of a re and in the absence of a re. Also indicate his expected utility and his expected wealth. Show graphically how the expected utility and the expected wealth depend on the loss probability. (20 points) 3. Karl-Heinz is considering buying an insurance that wordd cover his losses in the event of the re against a xed premium. What would be the \"fair\" premium? [20 points) 4. How much would Karl-Heinz be willing to pay for the insurance? Does it exceed the \"fair\" premium and if so why? Display Karl-Heine's willingness to pay for insurance graphically. (20 points)