Question
Scroll Down options for Beginning of Requirement 2: 1) Higher, Lower 2) Higher-Cost current-period units, higher-cost prior-period units, lower-cost current-period units, lower-cost prior-period units 3)

 Scroll Down options for Beginning of Requirement 2:
Scroll Down options for Beginning of Requirement 2:
1) Higher, Lower
2) Higher-Cost current-period units, higher-cost prior-period units, lower-cost current-period units, lower-cost prior-period units
3) Higher-Cost current-period units, higher-cost prior-period units, lower-cost current-period units, lower-cost prior-period units
4) Creates a greatly higher cost per equivalent unit, smooths out costs per equivalent unit
5) More of the higher cost units, only a few of the higher cost units
6) None of the lower cost units, some of the lower cost units
7) Higher, Lower
8) Higher, Lower
Scroll Down options for End of Requirement 2:
1) Be indifferent between the two methods, choose the FIFO method, choose the weighted-average method
2) Increases, lower
3) Higher, lower
4) Separate the costs of the current period from costs incurred in the previous periods, smooth the cost per equivalent unit
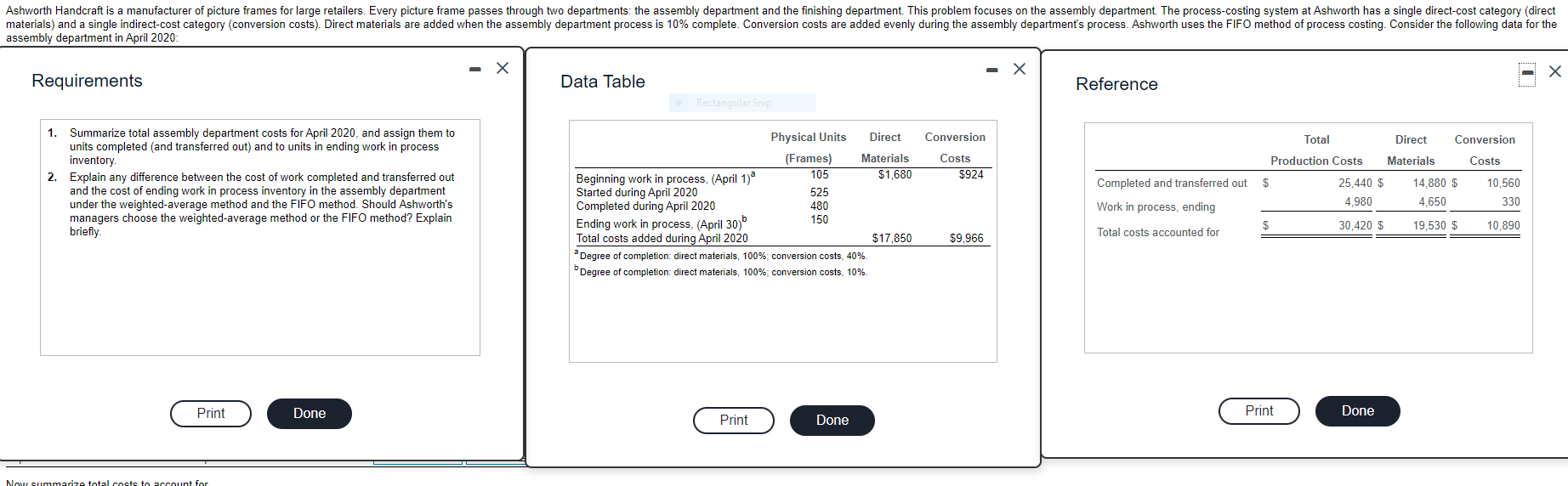
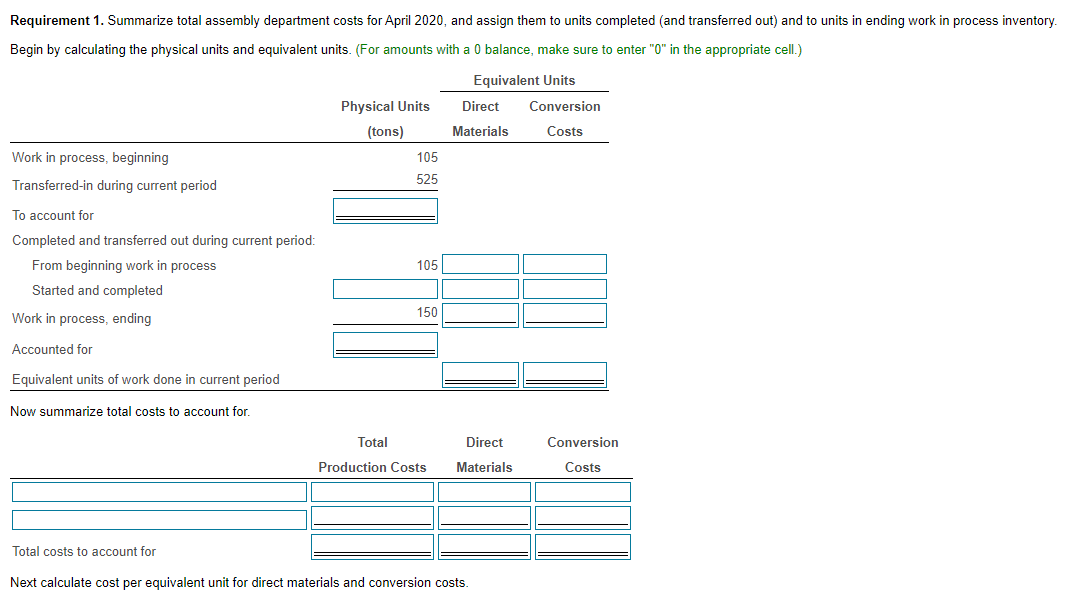
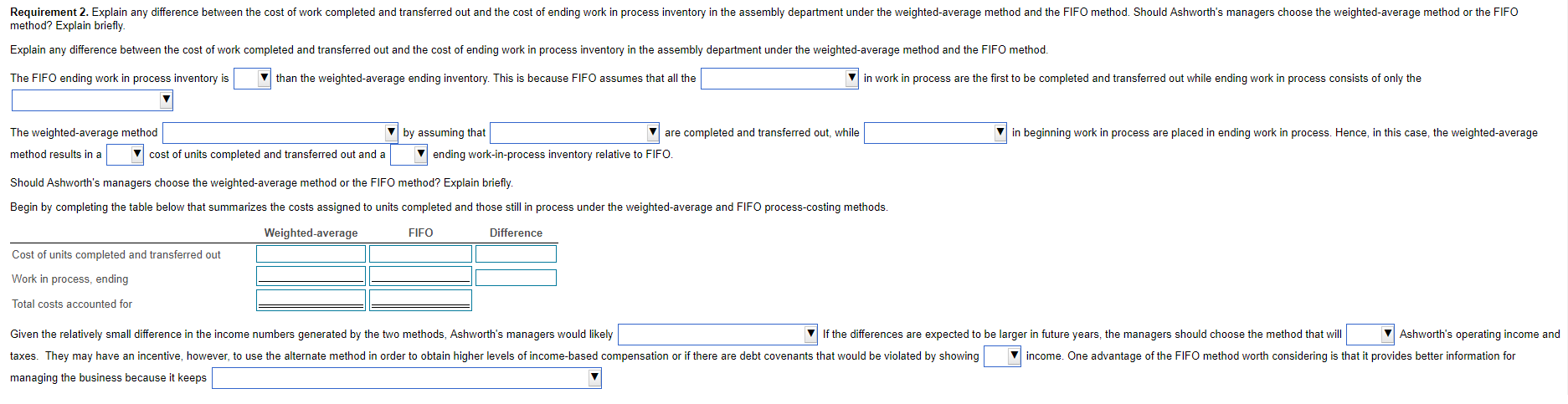
Ashworth Handcraft is a manufacturer of picture frames for large retailers. Every picture frame passes through two departments: the assembly department and the finishing department. This problem focuses on the assembly department. The process-costing system at Ashworth has a single direct-cost category (direct materials) and a single indirect-cost category (conversion costs). Direct materials are added when the assembly department process is 10% complete. Conversion costs are added evenly during the assembly department's process. Ashworth uses the FIFO method of process costing. Consider the following data for the assembly department in April 2020: X Requirements Data Table Reference Rectangular Ship Conversion Total Direct Conversion Production Costs Materials Costs Costs $924 1. Summarize total assembly department costs for April 2020, and assign them to units completed (and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process inventory 2. Explain any difference between the cost of work completed and transferred out and the cost of ending work in process inventory in the assembly department under the weighted average method and the FIFO method. Should Ashworth's managers choose the weighted average method or the FIFO method? Explain briefly Completed and transferred out $ 25.440 $ 4.980 14.880 $ 4.650 10,560 330 Physical Units Direct (Frames) Materials Beginning work in process, (April 1) a 105 $1.680 Started during April 2020 525 Completed during April 2020 480 Ending work in process, (April 30) 150 Total costs added during April 2020 $17,850 Degree of completion: direct materials, 100%; conversion costs, 40% Degree of completion direct materials, 100%; conversion costs, 10% Work in process, ending $ 30,420 $ 19.530 $ 10,890 $9.966 Total costs accounted for Print Done Print Done Print Done Now summarize total costs to account for Requirement 1. Summarize total assembly department costs for April 2020, and assign them to units completed and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process inventory. Begin by calculating the physical units and equivalent units. (For amounts with a 0 balance, make sure to enter "0" in the appropriate cell.) Equivalent Units Direct Conversion Physical Units (tons) Materials Costs Work in process, beginning Transferred-in during current period 105 525 To account for Completed and transferred out during current period: From beginning work in process Started and completed Work in process, ending 105 150 Accounted for Equivalent units of work done in current period Now summarize total costs to account for. Total Direct Conversion Production Costs Materials Costs Total costs to account for Next calculate cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs. Direct Conversion Materials Costs Divide by Cost per equivalent unit Assign total costs to units completed and transferred out) and to units in ending work in process inventory. Begin by calculating the total from beginning inventory, then calculate the total costs accounted for. Total Direct Conversion Production Costs Materials Costs Completed and transferred out Total from beginning inventory Total costs of units completed and transferred out Total costs accounted for Requirement 2. Explain any difference between the cost of work completed and transferred out and the cost of ending work in process inventory in the assembly department under the weighted-average method and the FIFO method. Should Ashworth's managers choose the weighted-average method or the FIFO method? Explain briefly. Explain any difference between the cost of work completed and transferred out and the cost of ending work in process inventory in the assembly department under the weighted-average method and the FIFO method. The FIFO ending work in process inventory is than the weighted average ending inventory. This is because FIFO assumes that all the in work in process are the first to be completed and transferred out while ending work in process consists of only the in beginning work in process are placed in ending work in process. Hence, in this case, the weighted-average The weighted-average method method results in a cost of units completed and transferred out and a by assuming that V are completed and transferred out, while ending work-in-process inventory relative to FIFO. Should Ashworth's managers choose the weighted-average method or the FIFO method? Explain briefly. Begin by completing the table below that summarizes the costs assigned to units completed and those still in process under the weighted average and FIFO process-costing methods. Weighted average FIFO Difference Cost of units completed and transferred out Work in process, ending Total costs accounted for Given the relatively small difference in the income numbers generated by the two methods, Ashworth's managers would likely If the differences are expected to be larger in future years, the managers should choose the method that will Ashworth's operating income and taxes. They may have an incentive, however, to use the alternate method in order to obtain higher levels of income-based compensation or if there are debt covenants that would be violated by showing income. One advantage of the FIFO method worth considering is that it provides better information for managing the business because it keepsStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


