Question
Seek Time Optimization Algorithms for HDD access Overview Accessing data in traditional, electromechanical hard disk drives is the slowest of all data access inside a
Seek Time Optimization Algorithms for HDD access Overview Accessing data in traditional, electromechanical hard disk drives is the slowest of all data access inside a computer. There are multiple factors that contribute to the delay or access time calculation in case of HDDs. One of the file access time factors is seek time. Seek time is the slowest of all these factors. It is the time taken to position the read/write head on the right track. There are some device handler algorithms for optimizing on seek strategies that can be used to minimize seek time. The goals of these scheduling algorithms are to minimize arm movement, mean response time, and variance in response time. The simplest of these algorithms is the First-come, first-served (FCFS) algorithm. It gets the list of sectors/clusters that the requested file is stored in and then traverses across the disk tracks in the same sequence as received. The algorithm is easy to implement, although on average, it does not meet the three seek strategy goals and comes with the disadvantage of extreme arm movement. Another algorithm is Shortest seek time first (SSTF) that reads in the full list of sectors/clusters to be serviced and then optimizes the list of requests by moving to the track closest to one being served. This algorithm minimizes the overall seek time and postpones traveling to out of way tracks, buffering the information and sequencing it up in the right order later. This project requires the students to understand and implement the two mentioned algorithms above - FCFS and SSTF. Learning Objectives The focus of this assignment is on the following learning objectives: ?Be able to allow the disk scheduler program to accept a list that contains the cylinder values for the file which is being read from the hard disk drive or being written into the disk. ?Be able to allow the disk scheduler program to choose from a list of algorithms and compare between them. ?According to the chosen algorithm, the disk arm movement is affected and total arm travel in the number of cylinders moved across, for the list. ?Report the sequence of cylinder travel and the total number of cylinders traveled. Create one for FCFS and SSTF algorithms. Prerequisites
?An understanding of the material presented in class and the numerical examples worked in the class ?An understanding of the material covered in the textbook. Problem Description You are to implement a program that would solve questions like the one below: On a traditional magnetic hard disk drive with 300 cylinders, a file transfer requires access to the cylinders in the following fashion: 121, 37, 98, 122, 89, 14, 156, 201, 67, 288 Indicate the head travel sequence in the order of cylinders covered for FCFS and SSTF algorithms. Also report the total head movement for all the algorithms, assuming that the head is over cylinder 132 at the start and going towards cylinder 299. The list of requirements are as follows: General requirements for the program: 1. The program then asks the initial cylinder location of the arm containing the read/write head assembly. 2. The program next asks for and accepts a list containing cylinder numbers (expected to be in a non-sorted, random order, dictated by the geographical distribution of parts of a file) of any length. You should not assume a fixed number of cylinders. These number of cylinders should be variable. 3. Your program should NOT ask the user about the number of entries in the list of cylinders. You should figure out some other technique to find out the number of entries. 4. The program then offers a menu to the user with three choices: FCFS algorithm, SSTF algorithm and Quit. The program should keep coming back to this menu until the 'Quit' option is chosen. 5. If the FCFS algorithm is chosen, the program runs the algorithm and reports the sequence of cylinders traversed and the total number of cylinders traveled. 6. If the SSTF algorithm is chosen, the program runs the algorithm and reports the sequence of cylinders traversed and the total number of cylinders traveled.
Why won't my code work?
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void resort(float aTime[50],float bTime[50],float tTime[50],float wTime[50],int info[50],int n)
{
for(int i=0;i { for(int j=0;j { if(info[j]>info[j+1]) { int temp1=info[j]; info[j]=info[j+1]; info[j+1]=temp1; float temp2=tTime[j]; tTime[j]=tTime[j+1]; tTime[j+1]=temp2; float temp3=wTime[j]; wTime[j]=wTime[j+1]; wTime[j+1]=temp3; float temp4=aTime[j]; aTime[j]=aTime[j+1]; aTime[j+1]=temp4; float temp5=bTime[j]; bTime[j]=bTime[j+1]; bTime[j+1]=temp5; } } } } void bandwTime(float aTime[50],float bTime[50],float wTime[50],float tTime[50],float gcTime[2][102],int n,int m){ int i=0,k=0; float extra[50]; while(i if(gcTime[1][k]==0){ extra[i]=gcTime[0][k+1]; i++; k+=2; } else{ extra[i]=gcTime[0][k]; i++; k++; } } for(int i=0;i tTime[i]=abs(extra[i]-aTime[i]); wTime[i]=abs(tTime[i]-bTime[i]); } } int gangChart(float gcTime[2][102],float bTime[50],float aTime[50],int PID[50],int n) { int i=0,k=0; if(aTime[0]!=0){ gcTime[0][0]=aTime[0]; gcTime[1][0]=0; gcTime[0][1]=gcTime[0][0]+bTime[0]; gcTime[1][1]=PID[0]; i++; k+=2; } else{ gcTime[0][0]=bTime[0]; gcTime[1][0]=PID[0]; i++; k++; } while(i if(gcTime[0][k-1] float IT=aTime[i]-gcTime[0][k-1]; gcTime[0][k]=gcTime[0][k-1]+IT; gcTime[1][k]=0; k++; } gcTime[0][k]=gcTime[0][k-1]+bTime[i]; gcTime[1][k]=PID[i]; i++; k++; } return k; } void sorting(float aTime[50],float bTime[50],int PID[50],int n) { for(int i=0;i { for(int j=0;j { if(aTime[j]>aTime[j+1]) { float temp1=aTime[j]; aTime[j]=aTime[j+1]; aTime[j+1]=temp1; float temp2=bTime[j]; bTime[j]=bTime[j+1]; bTime[j+1]=temp2; int temp3=PID[j]; PID[j]=PID[j+1]; PID[j+1]=temp3; } } } } int main(){ float aTime[50],bTime[50],wTime[50],tTime[50],gcTime[2][102]; int n,PID[50]; cout cout cout cout cout cout cout cout cout cout cin>>n; cout for(int i=0;i cin>>bTime[i]; } cout for(int i=0;i cin>>aTime[i]; } for(int i=0;i PID[i]=i+1; } sorting(aTime,bTime,PID,n); int m=gangChart(gcTime,bTime,aTime,PID,n); bandwTime(aTime,bTime,wTime,tTime,gcTime,n,m); float sum1=0,sum2=0,avgTT,avgWT; for(int i=0;i sum1+=tTime[i]; sum2+=wTime[i]; } avgTT=sum1; avgWT=sum2; int info[50]; int i=0,k=0; while(i if(gcTime[1][k]==0){ k++; } info[i]=gcTime[1][k]; i++; k++; } resort(aTime,bTime,tTime,wTime,info,n); cout for(int i=0;i cout } cout cout return 0; } What is wrong with my makefile? output: project3.o g++ project3.output project3.o: project3.cpp g++ -c main.cpp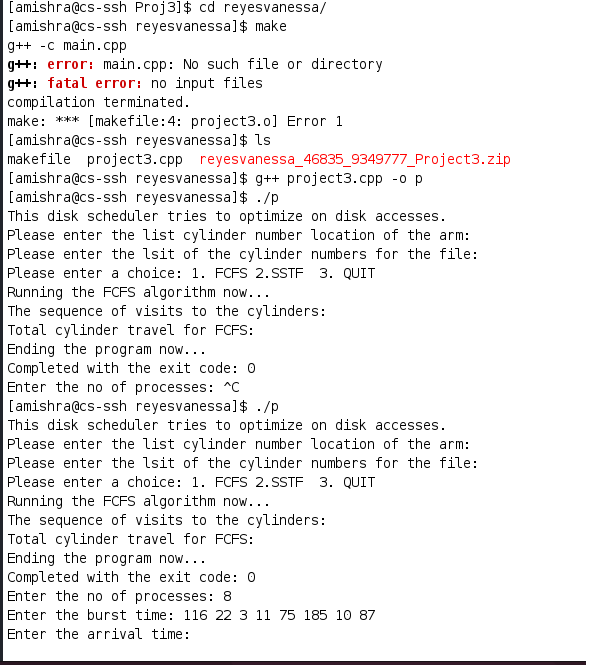
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


