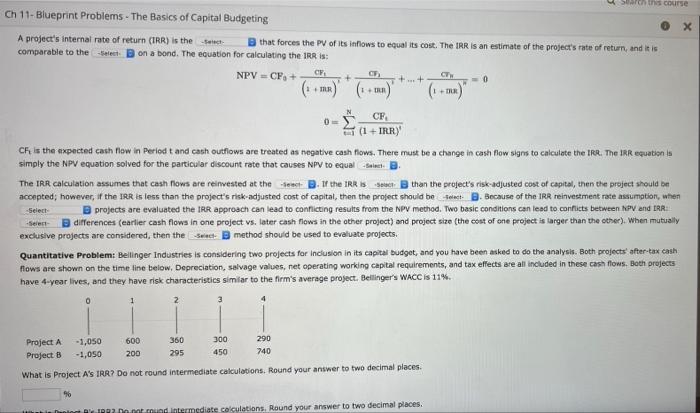
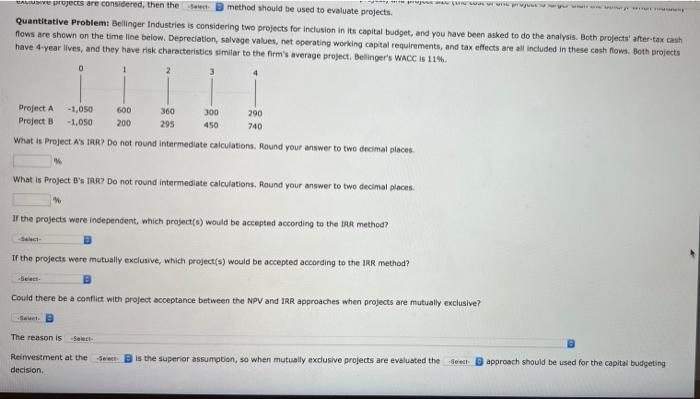
ser cone Ch 11- Blueprint Problems - The Basics of Capital Budgeting X A project's internal rate of return (IRR) is the elect that forces the PV of its inflows to equal its cost. The IRR is an estimate of the project's rate of return, and it is comparable to the select on a bond. The equation for calculating the IRR IS: NPV = CF,+ CIFE CW + ... + =0 TUR (1 ++x) RR + + N 0= CF (1 + IRRY Che is the expected cash flow in Period t and cash outflows are treated as negative cash flows. There must be a change in cash flow signs to calculate the IRR. The IRR equation is simply the NPV equation solved for the particular discount rate that causes NPV to equal - B The IRR calculation assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the sec B. If the IRR IS Seach than the project's risk-adjusted cost of capital, then the project should be accepted, however, if the IRR is less than the project's risk-adjusted cost of capital, then the project should be select 2. Because of the IRR reinvestment rate assumption, when -Select projects are evaluated the IRR approach can lead to conflicting results from the NPV method. Two basic conditions can lead to conflicts between NPV and ERR B differences (earlier cash flows in one project vs. later cash flows in the other project) and project size (the cost of one project is targer than the other). When mutually exclusive projects are considered, then the Sac method should be used to evaluate projects. Quantitative Problem: Bellinger Industries is considering two projects for inclusion in its capital budget, and you have been asked to do the analysis. Both projects after-tax cash flows are shown on the time line below, Depreciation, salvage values, net operating working capital requirements, and tax effects are all included in these cash flows. Both projects have 4-year lives, and they have risk characteristies similar to the firm's average project. Bellinger's WACC is 11% 0 1 2 Project A Project B -1,050 -1,050 600 200 350 295 300 450 290 740 What is Project A's IRR? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. 996 Do not und intermediate calculations, Round your answer to two decimal places. . LAUWE projects are considered, then the method should be used to evaluate projects. Quantitative Problem: Bellinger Industries is considering two projects for inclusion in its capital budget, and you have been asked to do the analysis. Both projects' after-tax cash nows are shown on the time line below. Depreciation, salvage values, net operating working capital requirements, and tax effects are all included in these cash flows. Both projects have 4-year lives, and they have risk characteristics similar to the firm's average project, Belinger's WACC IS 11% 0 Project A -1,050 600 360 300 290 Project B - 1.050 200 295 450 740 What is Project A's TAR? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places What is Project B's 1AR? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places If the projects were independent, which project(e) would be accepted according to the tak method? If the projects were mutually exclusive, which project(s) would be accepted according to the IRR method? Could there be a conflict with project acceptance between the NPV and IRR approaches when projects are mutually exclusive? surt. B The reason is Select Reinvestment at the Set decision is the superior assumption, so when mutually exclusive projects are evaluated the end approach should be used for the capital budgeting