Question: Several months ago, you started working at a large public accounting firm as an IT staff auditor. You are currently working on your first assignment,
Several months ago, you started working at a large public accounting firm as an IT staff auditor. You are currently working on your first assignment, an ITGC review of the Foods Fantastic Company (FFC) as part of the 2021 audit of the financial statements. FFC is a publicly traded, regional grocery store chain, headquartered in Mason, Maryland, and includes 50 stores located in the mid-Atlantic area. The centralized data center is in Mason. FFC relies on an integrated suite of application programs that include state-of-the-art software to manage merchandise replenishment, store-level sales forecasting, and point-of-sale data. For example, FFC relies on bar-code scanners, and credit/debit card readers. To maintain its competitive edge in its market area, FFC recently implemented a fingerprint bio-coding payment system in all of its stores. The implementation of This new system required that FFC change several of its general-ledger application programs, in particular, those related to its cash receipts processing. FFC does not use any outside service organizations to provide its IT services.
Sophie Ewing, the audit senior who heads up your team, noted that because of FFCs complex and sophisticated IT processing, an IT General Control (ITGC) review is mandatory to meet the requirements of AS 2201. You know that an ITGC review is very important because ITGCs provide the foundation for reliance on any financial information FFCs systems produce. Your evaluation will affect your assessment of FFCs ICFR and also impact the extent of testing you perform on the ITACs (IT Application controls) and the extent of substantive testing you will perform. In short, your audit strategy will be impacted. At your first team meeting, Sophie announced that your firms network security specialists would review the technical issues related to FFCs internal controls (eg. hardware controls). They will evaluate FFCs operating systems, its telecommunications software, and its network configuration and firewalls. Sophie noted that she believes that FFC has strong ITGCs the CIO and CFO both indicated to her that their tests of controls did not reveal any MW in IT controls . She did acknowledge that her initial assessment may be biased because of the respect she has for the CFO and CIO at FFC. Their system also seems very similar to one that another of her clients uses and thus she does not anticipate any significant issues.
In preparation for the meeting, Sophie encouraged you to review the key provisions included in AS 2201, as well as your firms internal guidance (summarized below), which groups ITGCs into the following five areas: IT management, program development, data security/access to programs & data controls, change management, and business continuity planning (BCP). You note that the firm separates out IT management and BCP which you were taught are typically included as part of Computer Operations. Sophie points out that your firm prefers to highlight these separately.
IT Management
IT managements key concepts include ITs position within the organization, whether IT goals are aligned with the organizations strategic goals, the use of an IT steering committee, and whether the IT departments structure promotes proper segregation of duties to protect the organizations assets. Your primary concerns are:
- Does FFC have an IT strategic plan? Is the CIO involved in strategic decision? Is the IT dept sufficiently resourced?
- To whom does the Chief Information Officer (CIO) report?
- What key responsibility areas report to the CIO? Is there proper segregation of duties between critical roles?
- Does FFC have an IT steering committee? Is so, who are the members?
Program/Systems Development
The key concepts within systems development include the existence of a new systems implementation methodology, project management, pre- and post-implementation reviews, quality control, adequate testing, and demonstrated compliance with the selected implementation methodology. Based on this understanding, your teams primary concerns are:
- Does FFC design, develop, and implement systems in a logical fashion?
- Does the organization consider internal controls as an integral part of systems design or does it retrofit them after implementation?
- To what extent is FFCs Internal Audit department involved in systems development activities? Is it part of the project review team? Is it a voting member of the team?
- In particular, how well did FFC manage the development and implementation of its new fingerprint bio-coding payment system?
Data Security (Access to programs and data controls)
The critical concepts within data security include adherence to an established information security policy, access approval on a need-to-know basis, periodic rotation or change of access controls, monitoring, exception reporting, and incident response. Data security has both physical and logical aspects. On the physical side, data security includes physical access and environmental controls over the data center computer room. On the logical side, data security included policies related to password configuration, change, and history restrictions. Logical security also includes prompt review, modification, or removal of access due to personnel transfers, promotions, and terminations. Your teams primary concerns are:
- How well does FFC control physical access to its data center computer room?
- Is FFCs computer room adequately protected against environmental dangers, such as fire?
- Does FFC control logical access to its information systems? In particular, how does it control the logical access of terminated or transferred employees?
- Does FFC have a current IT security policy?
- Does FFC produce access violation reports?
- Do FFC IT personnel adhere to IT policy and follow IT procedures? For example, do appropriate personnel review any access violation reports and take the prescribed action?
Change Management
Change Managements key concepts include documented change procedures, user authorization and approval, separation of duties in implementing changes, management review, quality control, and adequate testing. Your audit teams primary concerns are:
- Does FFC have (and follow) formal change management procedures?
- In particular, did FFC follow these procedures when making any necessary changes to its current application programs because of the new bio-coding payment system? For example: Were the changes approved? Did the programmers adequately test the changes before putting them into production? Did the application programmer(s) that made the code changes, test the changes, and/or put them into production?
Computer Operations/Business Continuity Planning
Key concepts of BCP are managements expectations regarding a timely recovery of processing capabilities, the existence of a written plan, the currency of the plan, off-site storage of both the plan and data files, and testing of the plan. Your audit teams main concerns are:
- Does FFC have a written BCP plan? Is it current?
- When is the last time FFC tested its plan?
- Does FFC back-up its software and data? How often? Where do they store the back-ups?
- Did FFC need to recover its systems using its back-ups during the past fiscal year?
Information Collected During the ITGC Review
Under Sophie Ewings direction, you and other members of the audit team worked very diligently reviewing FFCs policies and procedures, interviewing FFC client personnel, and observing FFCs various operations and procedures related to its ITGCs. First, your team created an organization chart to document the FFCs management structure (see Exhibit 1). Exhibit 2 reflects the information your team collected from interviews, observations, and reviews of corroborating documentation related to FFCs ITGCs.
Case Requirements
Sophie Ewing assigned your team the following tasks (summarize your responses to questions 2-5 Exhibit 3):
- What types of audit procedures did the audit team use in their evaluation of ITGCs at FFC?
- For each ITGC area, identify the control issues and classify them as strengths or weaknesses.
- Determine the level of risk (High, Medium, or Low) that you believe is present in each of the 5 ITGC areas, given your analysis in part 1.
- Assess the overall risk of the organizations ITGCs, taking into consideration the five separate risk assessments that you just made (task #2 above), and their relative importance to internal controls over FFCs financial reporting. Provide a brief explanation for your assessment. How does your assessment compare to Sophies initial assessment? In what ways might Sophies assessment been biased (note the types of bias she may have been subject to.)
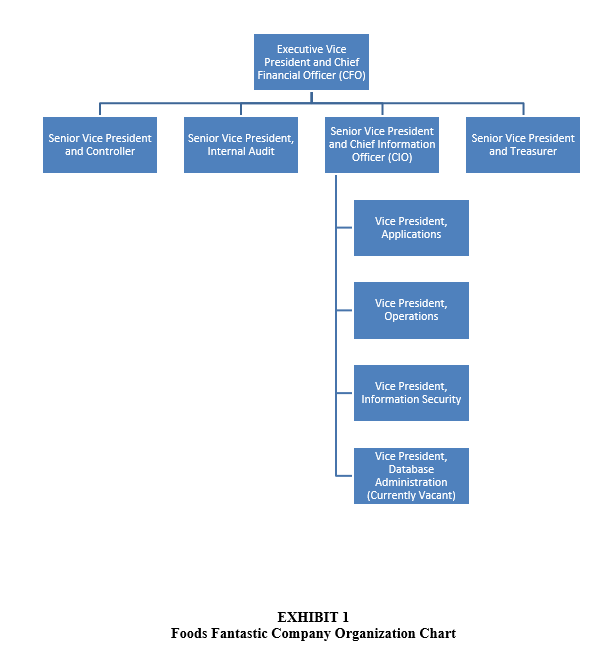






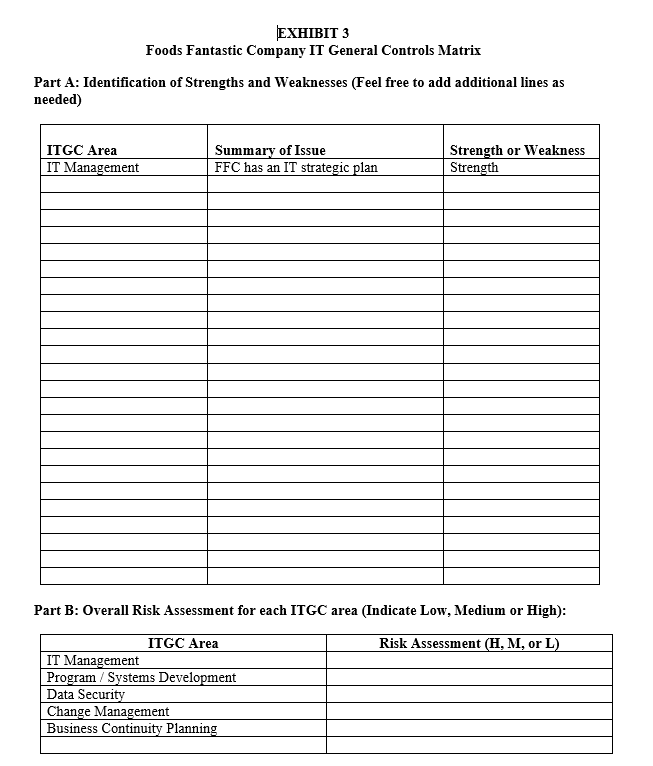

EXHIBIT 1 Foods Fantastic Company Organization Chart Foods Fantastic Company IT General Control (ITGC) Review Notes Notes from meetings with the Chief Financial Officer (CFO): - Foods Fantastic Company (FFC) implemented a new bio-coding payment system in all of its stores this past fiscal year. - FFC's IT Executive Steering Committee develops IT policies and reviews the overall operations of the IT department. The voting members of the committee are: 1. The Senior Vice President (SrVP) and Chief Information Officer (CIO) 2. The VP, Applications 3. The VP, Data Base Administration (DBA) 4. The VP, Operations 5. The VP, Information Security (IS) 6. The Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (CFO) 7. The SrVP, Internal Audit - The IT Executive Steering Committee revised FFC's security policy in 2019. The policy addresses all organizational security issues including IT. - FFC has no documented business continuity or disaster recovery plan. Management believes such a plan is cost-prohibitive for an organization of its size and FFC has never experienced any major business disruption. In case of disaster, the data center manager would retrieve the most recent backup tapes that are stored off-site. FFC would use these files to recover its systems. Notes from meetings with the Sr VP, Internal Audit: - FFC's Internal Audit Department is involved as a voting member of the project teams responsible for design, development, and implementation of new projects. Internal audit performs post-implementation reviews on all projects over $2 million. - The new bio-coding payment system was 25% over its initial time budget and 40% over its initial dollar budget. Notes from meetings with the CIO: - The VP, Applications is currently responsible for the DBA function. However, the CIO reviews the logs that show the actions of the Application VP's user ID. - FFC has an IT strategic plan, which is consistent with its corporate strategic plan. The IT strategic plan outlines the objectives and strategies that the information systems group will implement to assist FFC in meeting its overall business objectives. - FFC adopted Structured Systems Analysis and Design Methodology (SSADM), an industry-recognized standard for systems development and project management. All projects (buy or build) follow the applicable SSADM phases. The CIO periodically reviews each project's required budget-to-actual reconciliation. - FFC's security policy states that the VP, IS is to conduct a user audit on a quarterly basis. The appropriate department manager reviews electronically submitted reports that list each user's profile, note changes on the reports, and return the reports to the VP, IS. The VP then makes the appropriate modifications based on the returned reports. The VP maintains the reports, and initials and dates the report after completing all modifications. Notes from meetings with the VP, Human Resources: - FFC is currently interviewing individuals to assume the DBA's responsibilities and hopes to hire someone within the next six to eight months. - Aside from the security policy, management does not provide any formalized security awareness programs related to data security. - Each month, the Human Resources department forwards a Transfers and Terminations report to the VP, IS. otes from meetings with the VP, Applications: - The VP, Applications assigns a project manager and develops an initial time and dollar budget for each new development project. - IT personnel adequately tested the new bio-coding payment system prior to its implementation. This testing included integration testing, stress testing, and user acceptance testing. User departments corroborated their testing and acceptance of the new system. - Application programmers do not have access to the computer room unless escorted by data center personnel (e.g., an operator). - FFC instituted formal procedures for change management. The VP, Applications is responsible for change management and maintains all documentation in a fireproof vault in his office. A Change Request form initiates all application software changes, including required software upgrades. A user completes the form, which the user's department manager approves. The user forwards the request form to the VP, Applications who logs each request in a Change Request Log. The VP performs an initial analysis and feasibility study and estimates the required development hours. The Change Request log is a listing of all requested changes and the status of the change request. The VP Applications uses this log to track open items and follow-up on changes not completed within the original time estimate. - The VP, Applications assigns the change request to an applications programmer and issues the current system's documentation to the programmer. The applications programmer copies the source code from the system's production region to its development region and makes the change. The programmer works in the systems development region using test data. The programmer tests the change first within the affected module and then within the entire application. Changes are never tested against production data. The programmer updates the necessary system's documentation. - The applications programmer migrates the code to the system's test region. A second programmer performs systems integration testing, volume testing, and user acceptance testing, again using test files. The second programmer then performs a quality review of the change, including a source-compare analysis, and reviews the updated systems documentation. - Upon completion of testing, the user who requested the change and the appropriate department manager review the test results and accept the change by signing the original request form. The VP, Applications reviews the user-approved request form on which the department manager has indicated that s/ he is satisfied that the program is ready for implementation. The VP, Applications also reviews the documentation prior to implementing any new or changed program to ensure that the documentation is adequate. - The VP, Applications approves the change, initials the change request form, and transfers the change to the VP, Operations, who officially accepts the change. The VP, Applications then updates the Change Request log and returns the revised systems documentation to the fireproof vault. Notes from meetings with the VP, Operations: - FFC's computer room, within its data center, is locked at all times. All outside contractors or visitors must first contact the data center manager for entry into the computer room. Each must bring an official picture ID, sign a visitors' log, and be escorted at all times by data center personnel during the visit. - In 2017, FFC installed video cameras on all doors entering the computer room to record activity 24/7. Building management staff, who report to the facilities manager, are responsible for maintaining these tapes. The VP, Operations has not needed to review these tapes for at least six months since no unauthorized access attempts have been reported. - Environmental controls are in place in the computer room (i.e., temperature controls, uninterrupted power supply, a backup generator, fire-extinguishing equipment, and raised floor). Appropriate maintenance staff tests these controls semi-annually. - FFC backs up all of its data each day. It stores its most recent daily backup once a week at a company-owned off-site location, along with the most recent version of its software. FFC did not test backup tapes during the past year and has no plan to test these tapes in the future. - The VP, Operations assigns IT operations personnel the task of placing new or changed applications programs into production after VP, Applications has approved the work. Notes from meetings with the VP, Information Security: - The VP, IS grants key-card access to the computer room. The VP, IS receives a key-card access report for the computer room on a monthly basis. The VP, IS determines if an unauthorized access attempt into the computer room has occurred. - Passwords are not displayed on terminals or reports. Password standards are enforced by security software. FFC requires a minimum password length of six alphanumeric or special characters and a maximum length of nine alphanumeric or special characters. The software prevents the same character from being used more than once in a password and prevents numbers from being used next to each other in a password. The security software forces users to change their passwords twice each year. The security software maintains a history of two previous passwords and does not permit employees to reuse their two most recent passwords. The security software does not display statistics regarding employees' sign-on information. For example, there is no information regarding a user's sign-on attempts (such as date and time of last sign-on), number of invalid sign-on attempts since last successful sign-on, or number of days prior to password expiration. - The system allows three access attempts. If the third attempt is unsuccessful, the user ID is automatically disabled. The user must contact the VP, IS to reset the user ID. The system generates a logical access violation report on a daily basis. - User access is limited to workstations within the corresponding responsibility area. For example, users with access to the Accounts Payable module can only log in from workstations located in the Accounts Payable area. A workstation can stand idle for up to 60 minutes before the user is logged off. - The VP, IS is responsible for maintaining user profiles and authorization lists. - The VP grants access to the system to new hires. The appropriate department manager completes a computerized form that specifies the proper level of access. The VP reviews the request form for proper approvals and then either approves or denies the request. If approved, the VP issues the necessary ID and initial password with the requested access via encrypted e-mail. - Normal users may have multiple IDs. Each user ID can logon to one sign-on session at a time. The VP, IS, who has unlimited access, can log in from any workstation and have multiple sign-on sessions. - The VP, IS is responsible for modifying and/or disabling user IDs for personnel whose job duties change because of promotions, transfers, and/or terminations based on the Transfers and Terminations report. The VP maintains the report, and initials and dates the report when the VP has made all of the modifications. Notes from meeting with the facilities manager, who reports to the VP, Human Resources: - According to the facilities manager, no one asked to view the computer room video tapes during the past six months. Specific Observations of the audit team: - Documentation of the systems development process for the new bio-coding payment system confirms that the VP of Applications complied with SSADM requirements when implementing this new system. - The data center is on the first floor of FFC's building. The data center manager reports to the VP, Operations. - Company policy requires the VP, IS to review the key-card access report at least once per quarter and initial the report. During the past six months, the VP has not reviewed the report for any unauthorized access attempts. - The team observed no instances in which application programmers were in the computer| room without a proper escort. - The team observed no instances in which visitors or outside contractors were in the computer room without a proper escort. - Documentation of the computer room environment controls test results for the last 18 months shows no irregularities. These files are in the CIO's office. - If someone attempts to enter the computer room without authorization, company policy requires that the VP, Operations review the video tapes from the computer room cameras within 24 hours. - The FFC security policy requires each employee to sign an acknowledgment that s/he read the current policy. A review of the personnel files of a sample of employees found no exceptions. - A review of the selected user profiles and passwords revealed the following: Note: The acronym QSECOFR looks familiar. Remember to review A Beginner's Guide to Auditing the AS/400 Operating System (Bines 2002). - During the past six months, the dates of the modifications were about three weeks after the VP, IS received the HR's Transfers and Terminations report. - The VP, IS performed the most recent user audit eight months ago. - Company policy requires the VP, IS to review the unauthorized system access report on a monthly basis to check for unusual activity (e.g., multiple violations, changes to the authorization lists, etc.). During the past six months, the VP, IS has not reviewed the report for any unauthorized access attempts. - The audit team verified that FFC followed its approved change management procedures when making the bio-code-payment-related changes to its cash receipts processing and other financial reporting application programs. - In the past fiscal year, no incidents occurred that required FFC to recover its systems using its back-up tapes. EXHIBIT 3 Foods Fantastic Company IT General Controls Matrix Part A: Identification of Strengths and Weaknesses (Feel free to add additional lines as needed) Part B: Overall Risk Assessment for each ITGC area (Indicate Low, Medium or High): Part C: Conclusion: Complete the statement below regarding your overall risk assessment of ITGC's at FFC. I set FFC's assessed level of ITGC risk as (Low, Medium or High) because of (briefly explain -ie in a few sentences the primary reasons that contributed to your assessment.) EXHIBIT 1 Foods Fantastic Company Organization Chart Foods Fantastic Company IT General Control (ITGC) Review Notes Notes from meetings with the Chief Financial Officer (CFO): - Foods Fantastic Company (FFC) implemented a new bio-coding payment system in all of its stores this past fiscal year. - FFC's IT Executive Steering Committee develops IT policies and reviews the overall operations of the IT department. The voting members of the committee are: 1. The Senior Vice President (SrVP) and Chief Information Officer (CIO) 2. The VP, Applications 3. The VP, Data Base Administration (DBA) 4. The VP, Operations 5. The VP, Information Security (IS) 6. The Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (CFO) 7. The SrVP, Internal Audit - The IT Executive Steering Committee revised FFC's security policy in 2019. The policy addresses all organizational security issues including IT. - FFC has no documented business continuity or disaster recovery plan. Management believes such a plan is cost-prohibitive for an organization of its size and FFC has never experienced any major business disruption. In case of disaster, the data center manager would retrieve the most recent backup tapes that are stored off-site. FFC would use these files to recover its systems. Notes from meetings with the Sr VP, Internal Audit: - FFC's Internal Audit Department is involved as a voting member of the project teams responsible for design, development, and implementation of new projects. Internal audit performs post-implementation reviews on all projects over $2 million. - The new bio-coding payment system was 25% over its initial time budget and 40% over its initial dollar budget. Notes from meetings with the CIO: - The VP, Applications is currently responsible for the DBA function. However, the CIO reviews the logs that show the actions of the Application VP's user ID. - FFC has an IT strategic plan, which is consistent with its corporate strategic plan. The IT strategic plan outlines the objectives and strategies that the information systems group will implement to assist FFC in meeting its overall business objectives. - FFC adopted Structured Systems Analysis and Design Methodology (SSADM), an industry-recognized standard for systems development and project management. All projects (buy or build) follow the applicable SSADM phases. The CIO periodically reviews each project's required budget-to-actual reconciliation. - FFC's security policy states that the VP, IS is to conduct a user audit on a quarterly basis. The appropriate department manager reviews electronically submitted reports that list each user's profile, note changes on the reports, and return the reports to the VP, IS. The VP then makes the appropriate modifications based on the returned reports. The VP maintains the reports, and initials and dates the report after completing all modifications. Notes from meetings with the VP, Human Resources: - FFC is currently interviewing individuals to assume the DBA's responsibilities and hopes to hire someone within the next six to eight months. - Aside from the security policy, management does not provide any formalized security awareness programs related to data security. - Each month, the Human Resources department forwards a Transfers and Terminations report to the VP, IS. otes from meetings with the VP, Applications: - The VP, Applications assigns a project manager and develops an initial time and dollar budget for each new development project. - IT personnel adequately tested the new bio-coding payment system prior to its implementation. This testing included integration testing, stress testing, and user acceptance testing. User departments corroborated their testing and acceptance of the new system. - Application programmers do not have access to the computer room unless escorted by data center personnel (e.g., an operator). - FFC instituted formal procedures for change management. The VP, Applications is responsible for change management and maintains all documentation in a fireproof vault in his office. A Change Request form initiates all application software changes, including required software upgrades. A user completes the form, which the user's department manager approves. The user forwards the request form to the VP, Applications who logs each request in a Change Request Log. The VP performs an initial analysis and feasibility study and estimates the required development hours. The Change Request log is a listing of all requested changes and the status of the change request. The VP Applications uses this log to track open items and follow-up on changes not completed within the original time estimate. - The VP, Applications assigns the change request to an applications programmer and issues the current system's documentation to the programmer. The applications programmer copies the source code from the system's production region to its development region and makes the change. The programmer works in the systems development region using test data. The programmer tests the change first within the affected module and then within the entire application. Changes are never tested against production data. The programmer updates the necessary system's documentation. - The applications programmer migrates the code to the system's test region. A second programmer performs systems integration testing, volume testing, and user acceptance testing, again using test files. The second programmer then performs a quality review of the change, including a source-compare analysis, and reviews the updated systems documentation. - Upon completion of testing, the user who requested the change and the appropriate department manager review the test results and accept the change by signing the original request form. The VP, Applications reviews the user-approved request form on which the department manager has indicated that s/ he is satisfied that the program is ready for implementation. The VP, Applications also reviews the documentation prior to implementing any new or changed program to ensure that the documentation is adequate. - The VP, Applications approves the change, initials the change request form, and transfers the change to the VP, Operations, who officially accepts the change. The VP, Applications then updates the Change Request log and returns the revised systems documentation to the fireproof vault. Notes from meetings with the VP, Operations: - FFC's computer room, within its data center, is locked at all times. All outside contractors or visitors must first contact the data center manager for entry into the computer room. Each must bring an official picture ID, sign a visitors' log, and be escorted at all times by data center personnel during the visit. - In 2017, FFC installed video cameras on all doors entering the computer room to record activity 24/7. Building management staff, who report to the facilities manager, are responsible for maintaining these tapes. The VP, Operations has not needed to review these tapes for at least six months since no unauthorized access attempts have been reported. - Environmental controls are in place in the computer room (i.e., temperature controls, uninterrupted power supply, a backup generator, fire-extinguishing equipment, and raised floor). Appropriate maintenance staff tests these controls semi-annually. - FFC backs up all of its data each day. It stores its most recent daily backup once a week at a company-owned off-site location, along with the most recent version of its software. FFC did not test backup tapes during the past year and has no plan to test these tapes in the future. - The VP, Operations assigns IT operations personnel the task of placing new or changed applications programs into production after VP, Applications has approved the work. Notes from meetings with the VP, Information Security: - The VP, IS grants key-card access to the computer room. The VP, IS receives a key-card access report for the computer room on a monthly basis. The VP, IS determines if an unauthorized access attempt into the computer room has occurred. - Passwords are not displayed on terminals or reports. Password standards are enforced by security software. FFC requires a minimum password length of six alphanumeric or special characters and a maximum length of nine alphanumeric or special characters. The software prevents the same character from being used more than once in a password and prevents numbers from being used next to each other in a password. The security software forces users to change their passwords twice each year. The security software maintains a history of two previous passwords and does not permit employees to reuse their two most recent passwords. The security software does not display statistics regarding employees' sign-on information. For example, there is no information regarding a user's sign-on attempts (such as date and time of last sign-on), number of invalid sign-on attempts since last successful sign-on, or number of days prior to password expiration. - The system allows three access attempts. If the third attempt is unsuccessful, the user ID is automatically disabled. The user must contact the VP, IS to reset the user ID. The system generates a logical access violation report on a daily basis. - User access is limited to workstations within the corresponding responsibility area. For example, users with access to the Accounts Payable module can only log in from workstations located in the Accounts Payable area. A workstation can stand idle for up to 60 minutes before the user is logged off. - The VP, IS is responsible for maintaining user profiles and authorization lists. - The VP grants access to the system to new hires. The appropriate department manager completes a computerized form that specifies the proper level of access. The VP reviews the request form for proper approvals and then either approves or denies the request. If approved, the VP issues the necessary ID and initial password with the requested access via encrypted e-mail. - Normal users may have multiple IDs. Each user ID can logon to one sign-on session at a time. The VP, IS, who has unlimited access, can log in from any workstation and have multiple sign-on sessions. - The VP, IS is responsible for modifying and/or disabling user IDs for personnel whose job duties change because of promotions, transfers, and/or terminations based on the Transfers and Terminations report. The VP maintains the report, and initials and dates the report when the VP has made all of the modifications. Notes from meeting with the facilities manager, who reports to the VP, Human Resources: - According to the facilities manager, no one asked to view the computer room video tapes during the past six months. Specific Observations of the audit team: - Documentation of the systems development process for the new bio-coding payment system confirms that the VP of Applications complied with SSADM requirements when implementing this new system. - The data center is on the first floor of FFC's building. The data center manager reports to the VP, Operations. - Company policy requires the VP, IS to review the key-card access report at least once per quarter and initial the report. During the past six months, the VP has not reviewed the report for any unauthorized access attempts. - The team observed no instances in which application programmers were in the computer| room without a proper escort. - The team observed no instances in which visitors or outside contractors were in the computer room without a proper escort. - Documentation of the computer room environment controls test results for the last 18 months shows no irregularities. These files are in the CIO's office. - If someone attempts to enter the computer room without authorization, company policy requires that the VP, Operations review the video tapes from the computer room cameras within 24 hours. - The FFC security policy requires each employee to sign an acknowledgment that s/he read the current policy. A review of the personnel files of a sample of employees found no exceptions. - A review of the selected user profiles and passwords revealed the following: Note: The acronym QSECOFR looks familiar. Remember to review A Beginner's Guide to Auditing the AS/400 Operating System (Bines 2002). - During the past six months, the dates of the modifications were about three weeks after the VP, IS received the HR's Transfers and Terminations report. - The VP, IS performed the most recent user audit eight months ago. - Company policy requires the VP, IS to review the unauthorized system access report on a monthly basis to check for unusual activity (e.g., multiple violations, changes to the authorization lists, etc.). During the past six months, the VP, IS has not reviewed the report for any unauthorized access attempts. - The audit team verified that FFC followed its approved change management procedures when making the bio-code-payment-related changes to its cash receipts processing and other financial reporting application programs. - In the past fiscal year, no incidents occurred that required FFC to recover its systems using its back-up tapes. EXHIBIT 3 Foods Fantastic Company IT General Controls Matrix Part A: Identification of Strengths and Weaknesses (Feel free to add additional lines as needed) Part B: Overall Risk Assessment for each ITGC area (Indicate Low, Medium or High): Part C: Conclusion: Complete the statement below regarding your overall risk assessment of ITGC's at FFC. I set FFC's assessed level of ITGC risk as (Low, Medium or High) because of (briefly explain -ie in a few sentences the primary reasons that contributed to your assessment.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


