Question
SG Concrete has a division specializing in precast and prefabricated products. Precast concrete walls are moulded to the specification, size and form required by customers
SG Concrete has a division specializing in precast and prefabricated products. Precast concrete walls are moulded to the specification, size and form required by customers at SG Concretes factory and then lifted and transported to the building site for assembling and installation. The process requires large equipment and machinery and skilled personnel. Each project is complex and diverse, requiring different sizes, dimensions and designs. As such, SG Concrete uses job order costing.
In addition, SG Concrete uses a normal costing system and closes off all overhead variances to the cost of goods sold at the end of each year. Its budgeted factory and non-manufacturing overhead expenses for the year were estimated to be $74,880,000 and $31,200,000 respectively. The budgeted direct labour hours (DLH) for the year were 624,000 hours in total. Direct labour hours have been used as the basis for overheads application since the company was first founded.
Jobs 201, 202 and 207 were completed during the year. Job 201 was invoiced in September and subsequently fully paid before the year end. Job 207 was invoiced in December and its payment was not settled as at the year-end. Job 202 was just completed but various administrative documents and certifications were outstanding at year end, and therefore, the invoice could not be issued.
(a) Compute the predetermined overhead rate for the normal costing purpose.
(b) Use available information to compute the value of the ending work in process and finished goods at the year end, and the cost of goods sold balance after all required adjustments. Clearly show your supporting computations.
(c) Write a journal entry to close the overhead variance.
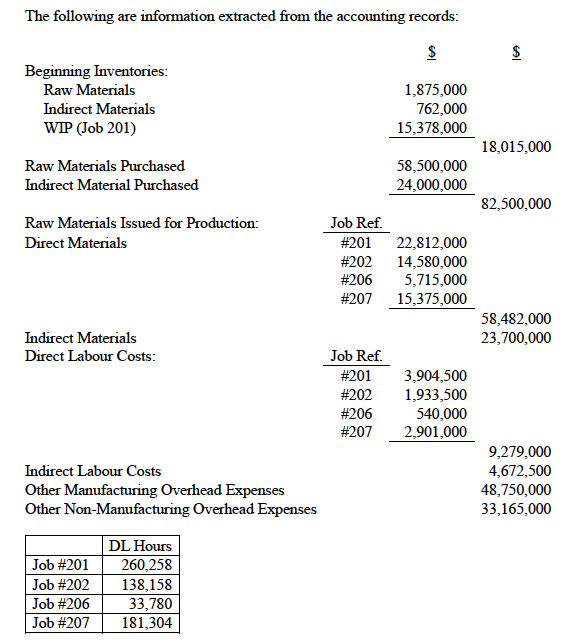
The following are information extracted from the accounting records: Beginning Inventories: Raw Materials Indirect Materials WIP (Job 201) Raw Materials Purchased Indirect Material Purchased Raw Materials Issued for Production: Direct Materials Indirect Materials Direct Labour Costs: Indirect Labour Costs Other Manufacturing Overhead Expenses Other Non-Manufacturing Overhead Expenses $ 1,875,000 762,000 15,378,000 18,015,000 58,500,000 24,000,000 82,500,000 Job Ref. #201#202#206#20722,812,00014,580,0005,715,00015,375,000 58,482,000 23,700,000 \begin{tabular}{cr} Job Ref. & \\ \cline { 1 - 2 } \#201 & 3,904,500 \\ \#202 & 1,933,500 \\ \#206 & 540,000 \\ \#207 & 2,901,000 \\ \cline { 2 - 2 } & \end{tabular} 9,279,000 4,672,500 48,750,000 33,165,000 \begin{tabular}{|l|r|} \hline & DL Hours \\ \hline Job \#201 & 260,258 \\ \hline Job \#202 & 138,158 \\ \hline Job \#206 & 33,780 \\ \hline Job \#207 & 181,304 \\ \hline \end{tabular}Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


