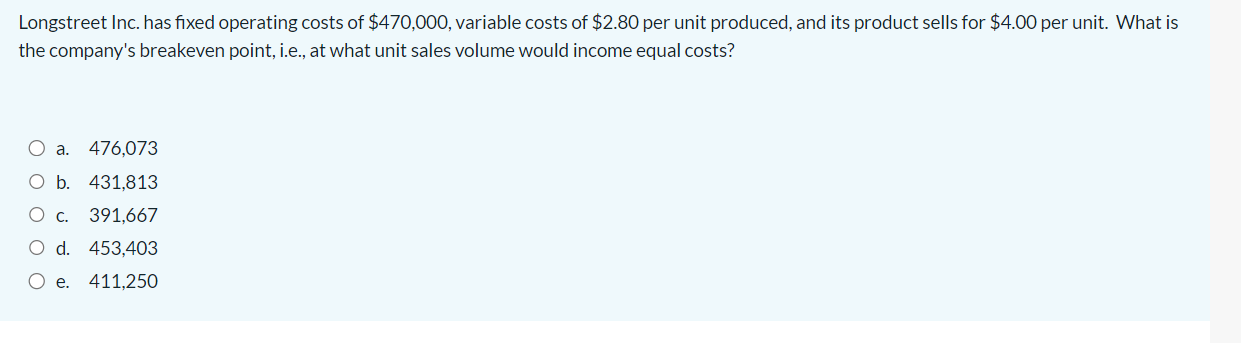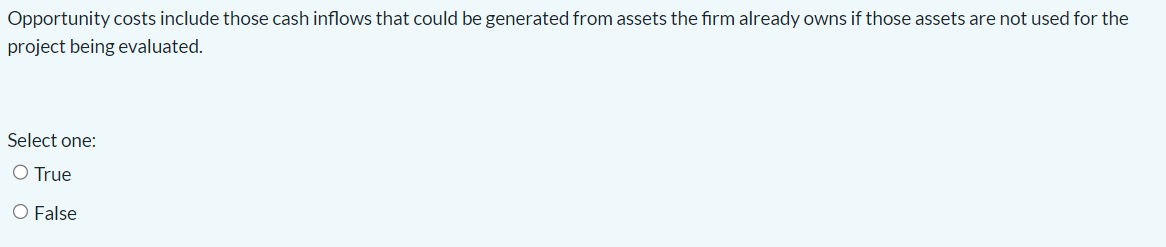
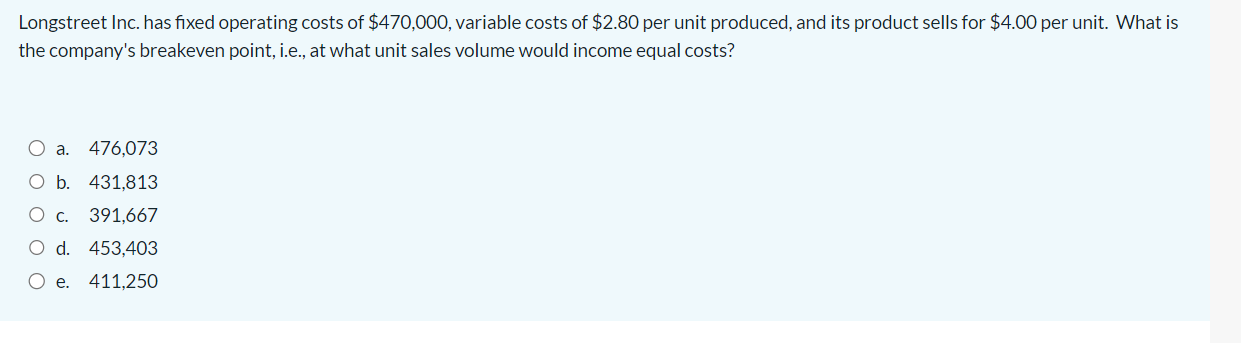

Sheehan Inc. is deciding whether to invest in a project today or to postpone the decision until next year. The project has a positive expected NPV, but its cash flows might turn out to be lower than expected, in which case the NPV could be negative. No competitors are likely to invest in a similar project if the firm decides to wait. Which of the following statements best describes the issues that the firm faces when considering this investment timing option? a. Since the project has a positive expected NPV today, this means that its expected NPV will be even higher if the firm chooses to wait a year. b. Waiting would probably reduce the project's risk. c. The more uncertainty about the future cash flows, the more logical it is to go ahead with this project today. d. Since the project has a positive expected NPV today, this means that it should be accepted in order to lock in that NPV. e. The investment timing option would not affect the cash flows and therefore would have no impact on the project's risk. Opportunity costs include those cash inflows that could be generated from assets the firm already owns if those assets are not used for the project being evaluated. Select one: True False Longstreet Inc. has fixed operating costs of $470,000, variable costs of $2.80 per unit produced, and its product sells for $4.00 per unit. What is the company's breakeven point, i.e., at what unit sales volume would income equal costs? a. 476,073 b. 431,813 c. 391,667 d. 453,403 e. 411,250 Which of the following statements is CORRECT? a. A good example of a sunk cost is a situation where Home Depot opens a new store, and that leads to a decline in sales of one of the firm's existing stores. b. Sunk costs were formerly hard to deal with, but once the NPV method came into wide use, it became possible to simply include sunk costs in the cash flows and then calculate the PV. c. A sunk cost is any cost that must be expended in order to complete a project and bring it into operation. d. A sunk cost is a cost that was incurred and expensed in the past and cannot be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project. e. A sunk cost is any cost that was expended in the past but can be recovered if the firm decides not to go forward with the project