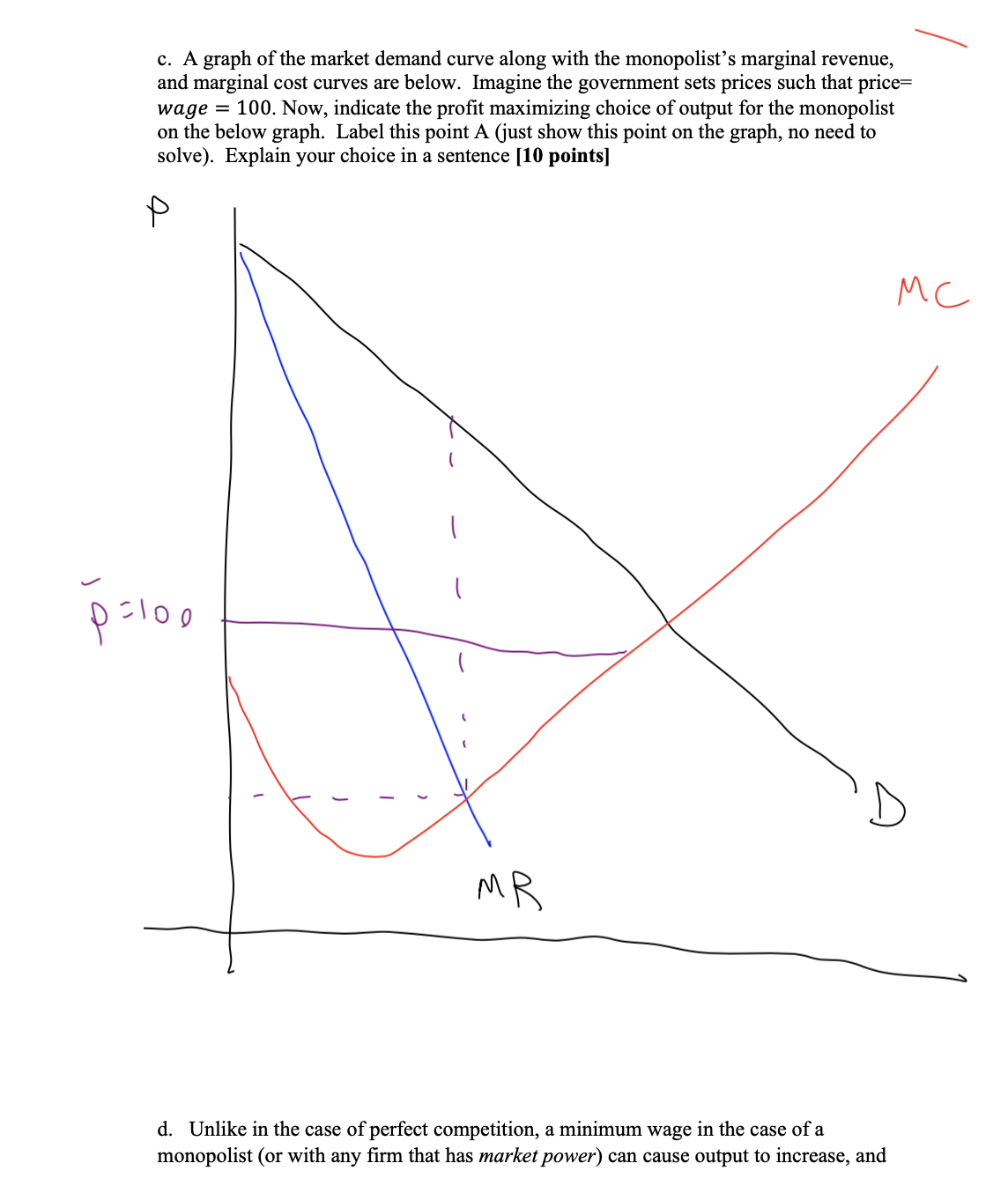
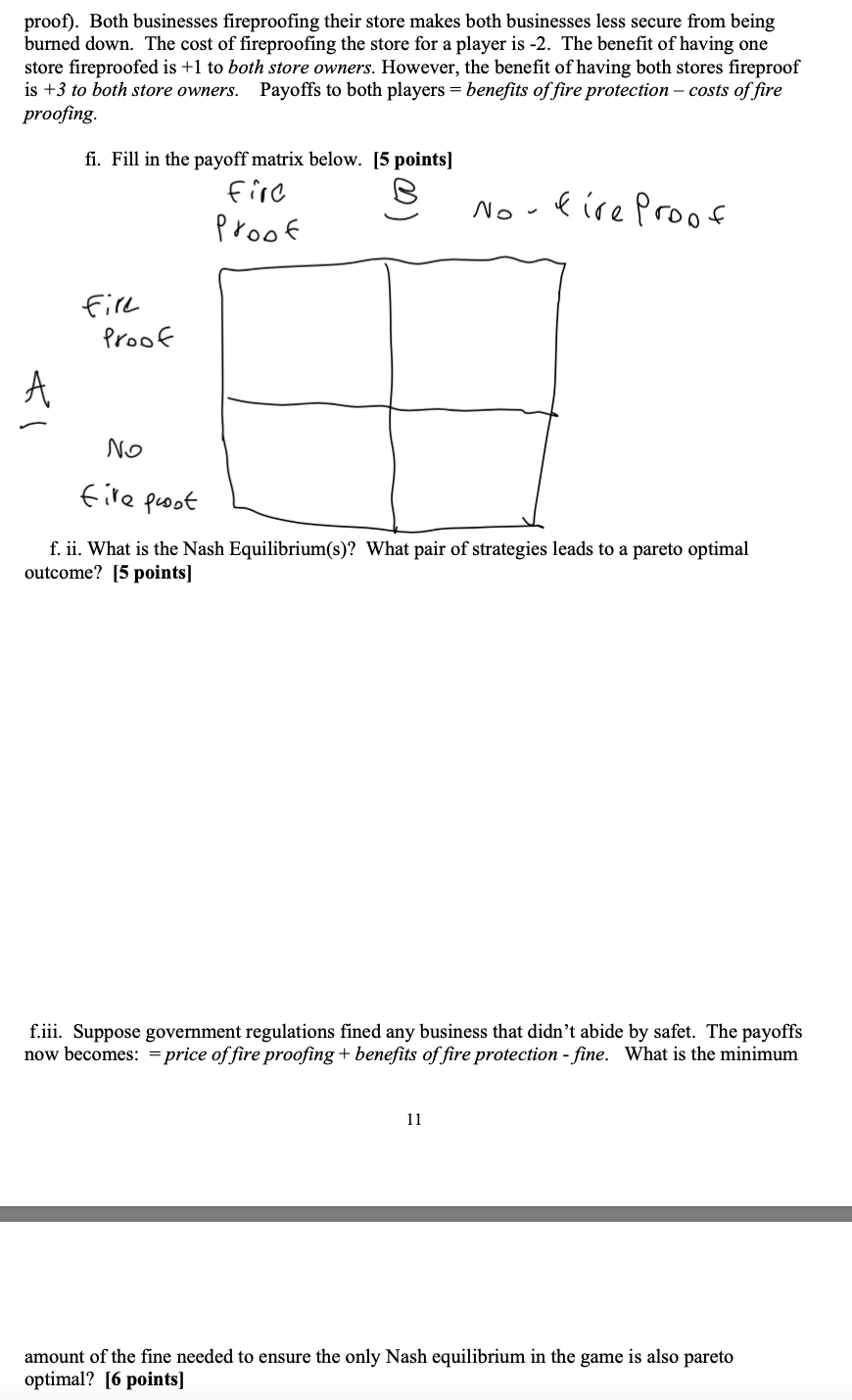
Short Answer 3: Market Failure. [50 points all together] A common result in models of perfect competition is that the wage controls leads to higher prices, reduced output and can cause a pareto tnez'cz'ent outcome. In this problem we will investigate that model and see if the results hold when a rm has market power. Consider the following setup: a rm hires workers to produce output (y) which it sells for revenue. The rm's production function is such that their only marginal cost is the wage they pay workers. In a model of perfect competition, competition with many other rms forces the following to hold wage =marginal costs=prce of the output. A minimum wage serves as a price oor, because employers are required to spend more on workers forcing prices higher. We are going to simplify this to assume the government directly sets wages above the marginal cost of production. First, let's assume the model of perfect competition holds: Below is a demand and supply graph in the perfectly competitive case. Draw a horizontal line for the wage control (remember minimum wage: price), outside of equilibrium, such that this mandated minimum wage increase prices and reduces the quantity supplied. Label this line, \"government set price.\" Indicate on the graph the quantity demanded, the quantity supplied, and the amount of the shortage. [4 points] g i\" Q' CK a. Next, we will allow the rm to be a monopolist, with market power to arbitrarily raise prices above the marginal cost. Being more explicit: the monopolist faces the following demand curve from consumers: 1901) = 150 y, and has the following total cost curve: ix3 %x2 + 3x+ 10 i. Find the equation for the marginal revenue curve. [4 points] ii. Find the equation for marginal costs 4 points] iii. Set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost and solve for the prot maximizing level of output (y), and associated marked-up prot maximizing level of price. 5 points] \\ c. A graph of the market demand curve along with the monopolist's marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves are below. Imagine the government sets prices such that price= wage = 100. Now, indicate the prot maximizing choice of output for the monopolist on the below graph. Label this point A (just show this point on the graph, no need to solve). Explain your choice in a sentence [10 points] P d. Unlike in the case of perfect competition, a minimum wage in the case of a monopolist (or with any rm that has market power) can cause output to increase, and leads to a pareto optimal outcome. Explain in a few sentences, why government set prices in the model above correct for the market failure, leading to a pareto efficient outcome. [ 4 points] .e Another market failure we learned about is an externality. Provide an example of a negative externality. [ 3 points] f. Below is an example of the payoff matrix from a two player (players A and B) simultaneous game. Both players are small business owners whose retail stores are located next to each other. Both players can choose to fire-proof their stores or not (stratagies are fire-proof or not-fire-proof). Both businesses fireproofing their store makes both businesses less secure from being burned down. The cost of fireproofing the store for a player is -2. The benefit of having one store fireproofed is +1 to both store owners. However, the benefit of having both stores fireproof is +3 to both store owners. Payoffs to both players = benefits of fire protection - costs of fire proofing. fi. Fill in the payoff matrix below. [5 points] fire proof No - fireproof fill Proof No fire pwoot f. ii. What is the Nash Equilibrium(s)? What pair of strategies leads to a pareto optimal outcome? [5 points] f.iii. Suppose government regulations fined any business that didn't abide by safet. The payoffs now becomes: = price of fire proofing + benefits of fire protection - fine. What is the minimum 11 amount of the fine needed to ensure the only Nash equilibrium in the game is also pareto optimal? [6 points]