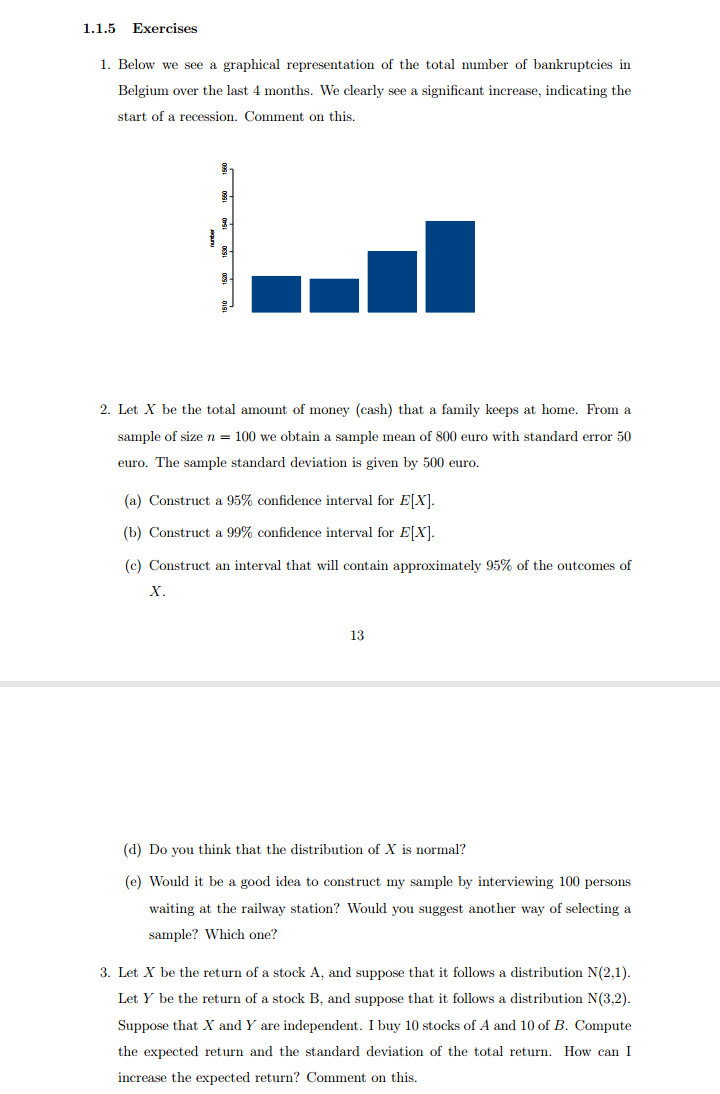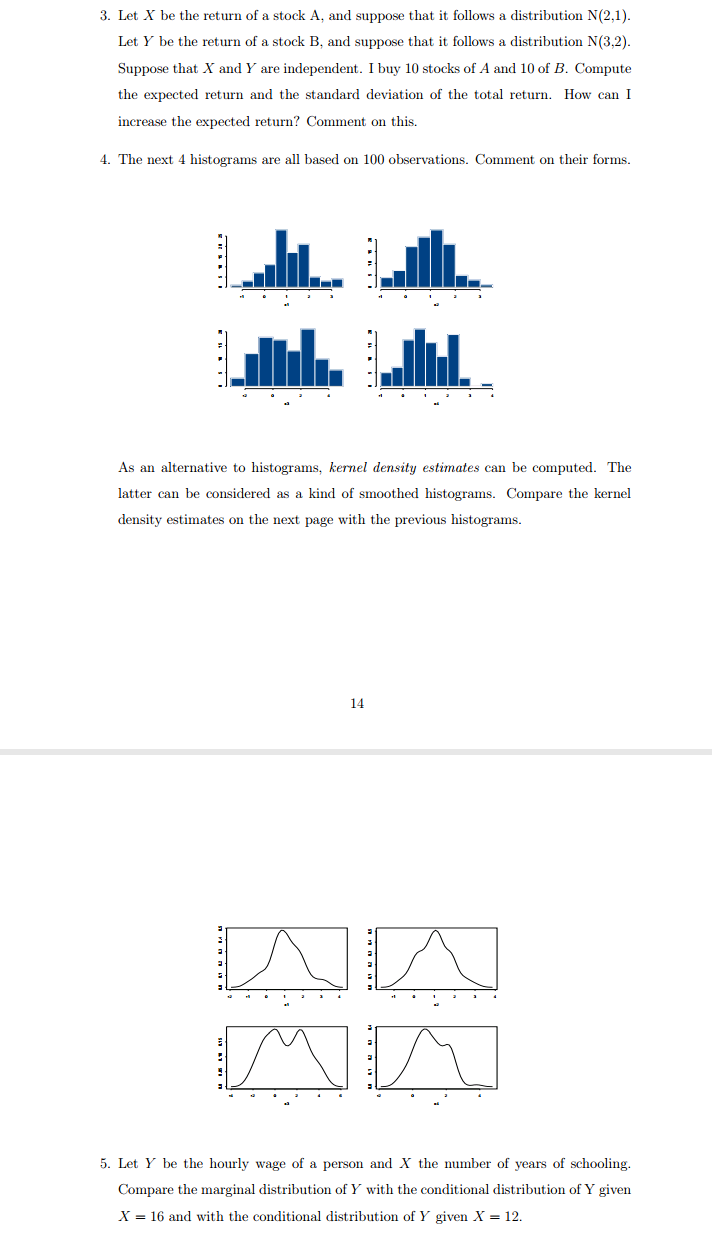

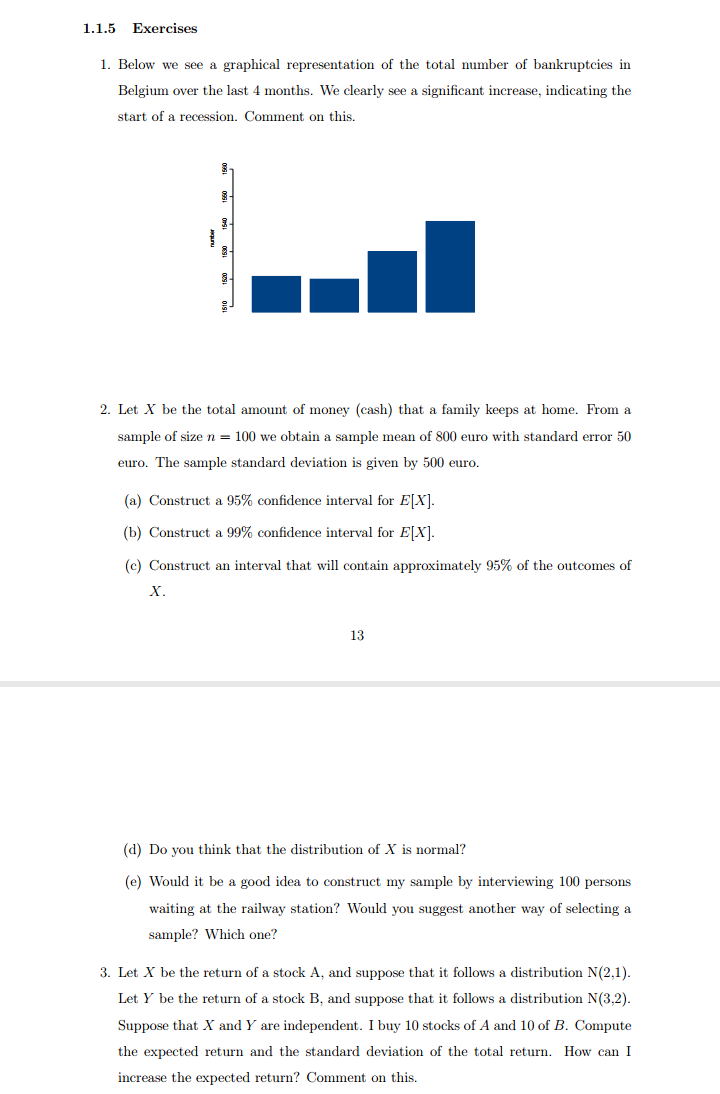
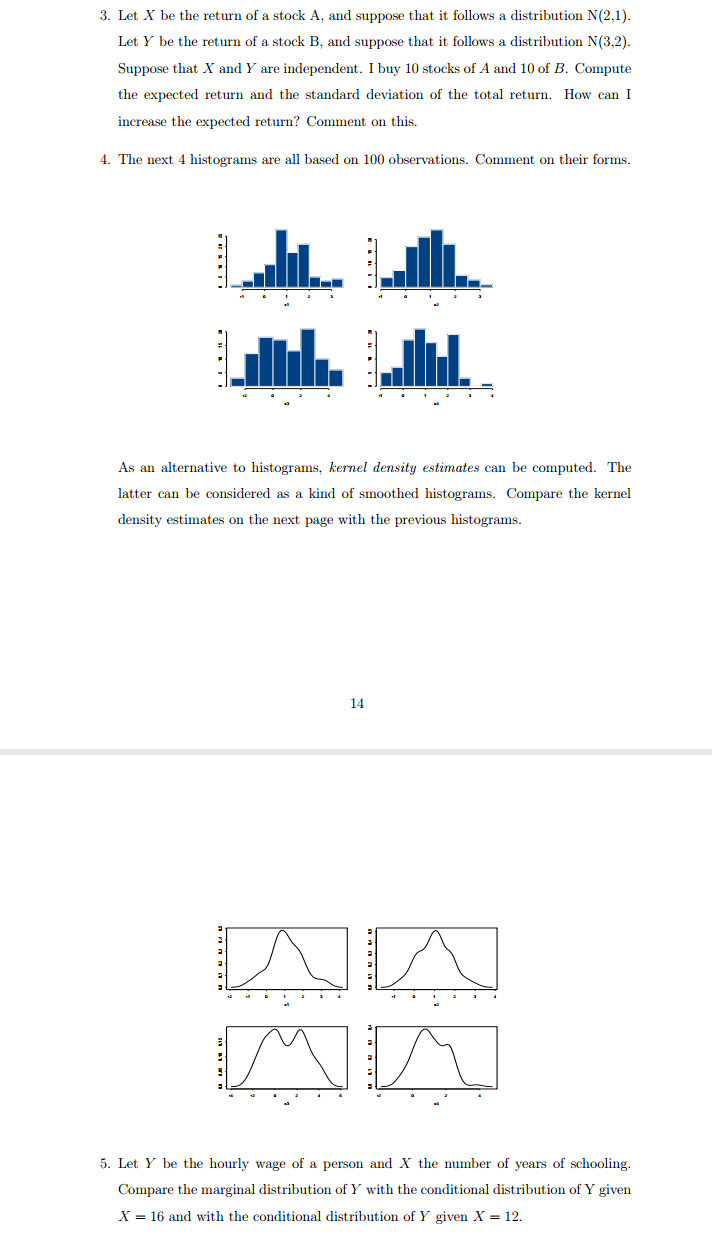
Show your working step by step
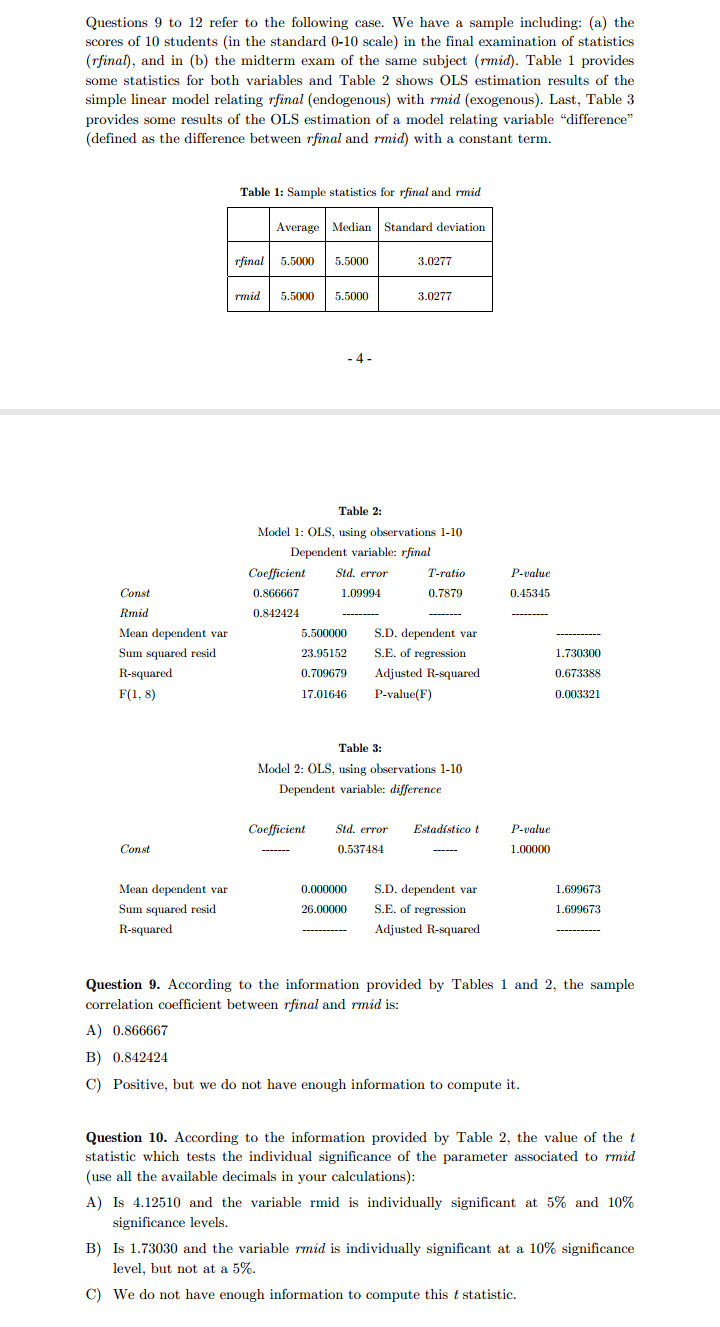
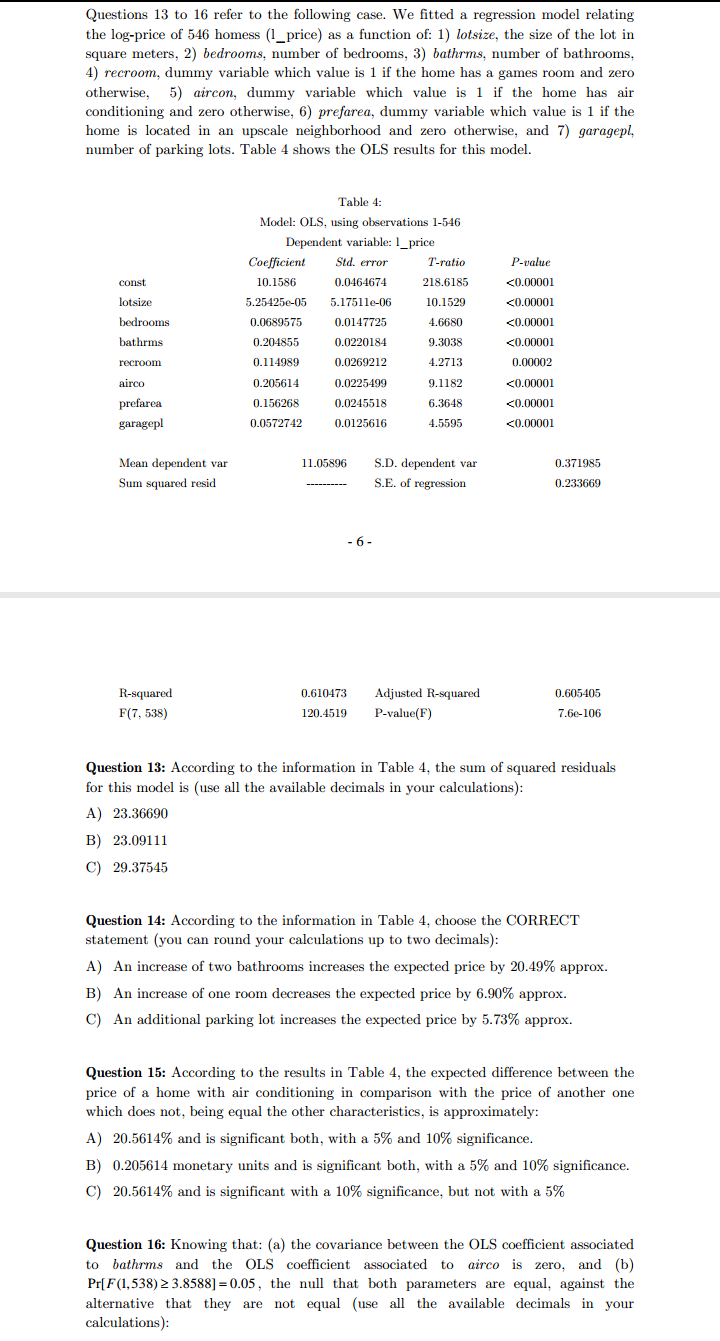
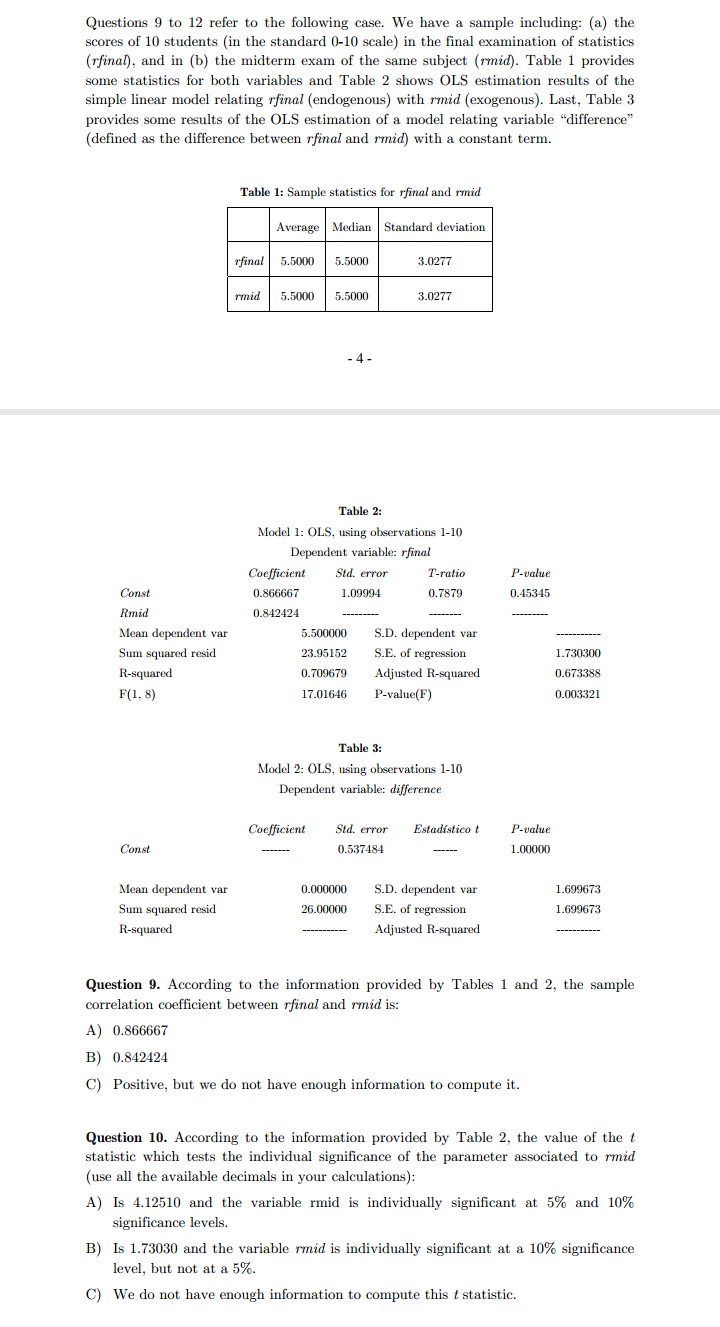
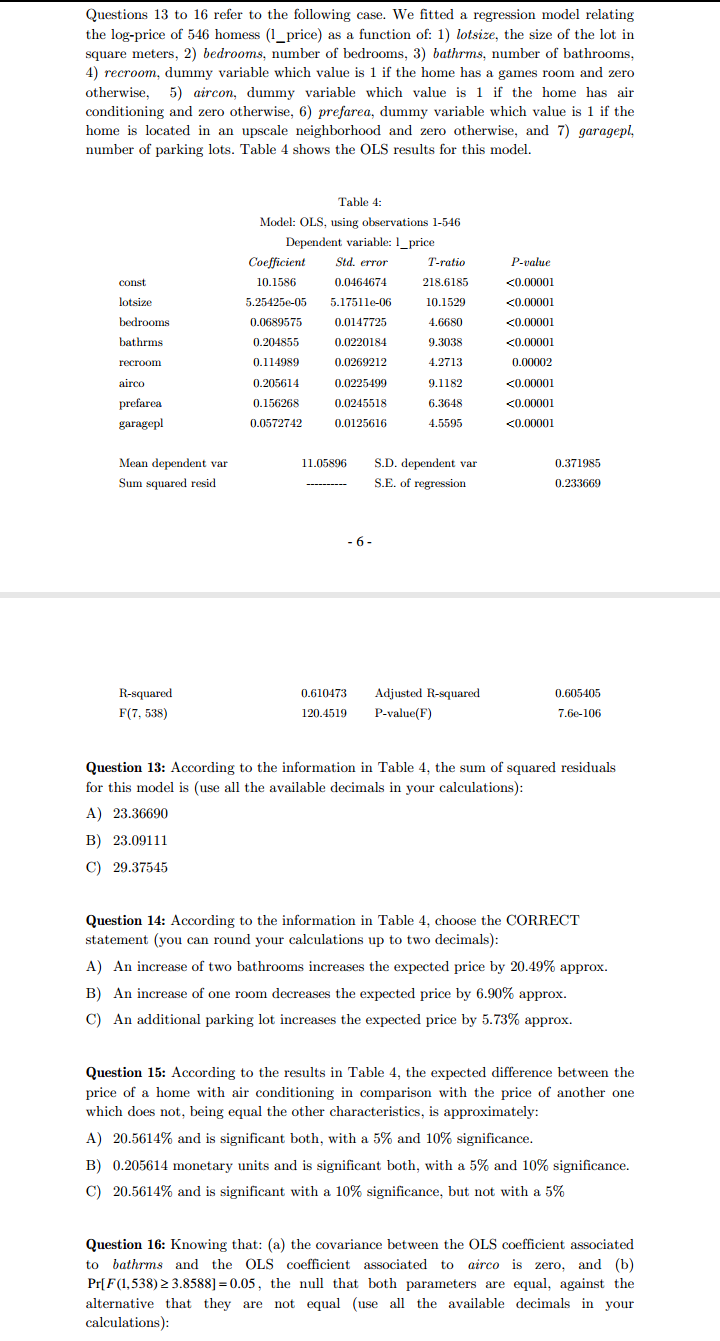
Questions 9 to 12 refer to the following case. We have a sample including: (a) the scores of 10 students (in the standard 0-10 scale) in the final examination of statistics (rfinal), and in (b) the midterm exam of the same subject (rmid). Table 1 provides some statistics for both variables and Table 2 shows OLS estimation results of the simple linear model relating rfinal (endogenous) with rmid (exogenous). Last, Table 3 provides some results of the OLS estimation of a model relating variable "difference" (defined as the difference between rfinal and rmid) with a constant term. Table 1: Sample statistics for rfinal and rmid Average | Median Standard deviation rfinal 5.5000 5.5000 3.0277 rmid 5.5000 5.5000 3.0277 - 4 - Table 2: Model 1: OLS, using observations 1-10 Dependent variable: rfinal Coefficient Std. error T-ratio P-value Const 0.866667 1.09994 0.7879 0.45345 Rmid 0.842424 Mean dependent var 5.500000 S.D. dependent var Sum squared resid 23.95152 S.E. of regression 1.730300 R-squared 0.709679 Adjusted R-squared 0.673388 F(1, 8) 17.01646 P-value(F) 0.003321 Table 3: Model 2: OLS, using observations 1-10 Dependent variable: difference Coefficient Sid. error Estadistico t P-value Const 0.537484 1.00000 Mean dependent var 0.000000 S.D. dependent var 1.699673 Sum squared resid 26.00000 S.E. of regression 1.699673 R-squared Adjusted R-squared Question 9. According to the information provided by Tables 1 and 2, the sample correlation coefficient between rfinal and rmid is: A) 0.866667 B) 0.842424 C) Positive, but we do not have enough information to compute it. Question 10. According to the information provided by Table 2, the value of the t statistic which tests the individual significance of the parameter associated to rmid (use all the available decimals in your calculations): A) Is 4.12510 and the variable rmid is individually significant at 5% and 10% significance levels. B) Is 1.73030 and the variable rmid is individually significant at a 10% significance level, but not at a 5%. C) We do not have enough information to compute this t statistic.Questions 13 to 16 refer to the following case. We fitted a regression model relating the log-price of 546 homess (1_price) as a function of: 1) lotsize, the size of the lot in square meters, 2) bedrooms, number of bedrooms, 3) bathrms, number of bathrooms, 4) recroom, dummy variable which value is 1 if the home has a games room and zero otherwise, 5) aircon, dummy variable which value is 1 if the home has air conditioning and zero otherwise, 6) prefarea, dummy variable which value is 1 if the home is located in an upscale neighborhood and zero otherwise, and 7) garagepl, number of parking lots. Table 4 shows the OLS results for this model. Table 4: Model: OLS, using observations 1-546 Dependent variable: 1_price Coefficient Std. error T-ratio P-value const 10.1586 0.0464674 218.6185 F* ] C) 1-Pr[F (3,27) 2 F ] Question 7. Consider the model Y, = B+ B2X; +U; (i=1,2,...,20), which OLS residuals are denoted by a; (i=1,2....,20). Assume that the OLS estimation of the regression (with constant term) of Up as a function of X; and X? (i=1,2,...,20 ) yields a R- value of 0.35. If Pr[x (2) $ 4.61]=0.90 and Prix (2) $5.99]=0.95, the null that the model errors (U; ) are homoscedastic: A) Must be rejected with a 5% significance, but not with a 10% B) Must be rejected both, with a 5% and a 10% significance. C) Must be rejected with a 10% significance, but not with a 5%1.1.5 Exercises 1. Below we see a graphical representation of the total number of bankruptcies in Belgium over the last 4 months. We clearly see a significant increase, indicating the start of a recession. Comment on this. 1560 1560 1540 runbair 1580 1520 1510 2. Let X be the total amount of money (cash) that a family keeps at home. From a sample of size n = 100 we obtain a sample mean of 800 euro with standard error 50 euro. The sample standard deviation is given by 500 euro. (a) Construct a 95% confidence interval for E[X]. (b) Construct a 99% confidence interval for E[X]. (c) Construct an interval that will contain approximately 95% of the outcomes of X. 13 (d) Do you think that the distribution of X is normal? (e) Would it be a good idea to construct my sample by interviewing 100 persons waiting at the railway station? Would you suggest another way of selecting a sample? Which one? 3. Let X be the return of a stock A, and suppose that it follows a distribution N(2,1). Let Y be the return of a stock B, and suppose that it follows a distribution N(3,2). Suppose that X and Y are independent. I buy 10 stocks of A and 10 of B. Compute the expected return and the standard deviation of the total return. How can I increase the expected return? Comment on this.3. Let X be the return of a stock A, and suppose that it follows a distribution N(2,1). Let Y be the return of a stock B, and suppose that it follows a distribution N(3,2). Suppose that X and Y are independent. I buy 10 stocks of A and 10 of B. Compute the expected return and the standard deviation of the total return. How can I increase the expected return? Comment on this. 4. The next 4 histograms are all based on 100 observations. Comment on their forms. * 15 As an alternative to histograms, kernel density estimates can be computed. The latter can be considered as a kind of smoothed histograms. Compare the kernel density estimates on the next page with the previous histograms. 14 5. Let Y be the hourly wage of a person and X the number of years of schooling. Compare the marginal distribution of Y with the conditional distribution of Y given X = 16 and with the conditional distribution of Y given X = 12