Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Case - Shun Electronics Company.pdf I Page A6221, Managerial Accounting for MBAs, Dr. Alireza Daneshfar, University of New Haven Case: Shun Electronics Company CASE OBJECTIVES:




 Case - Shun Electronics Company.pdf
Case - Shun Electronics Company.pdf
I
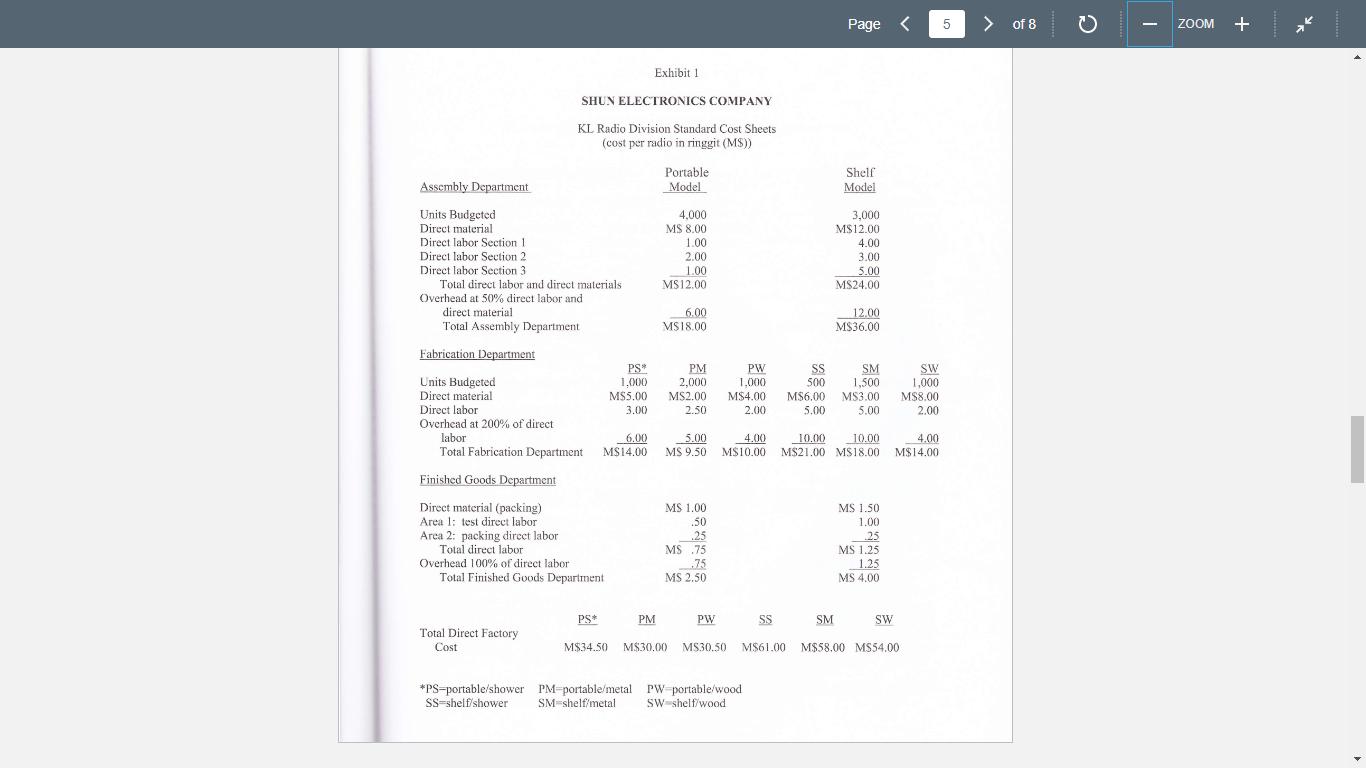
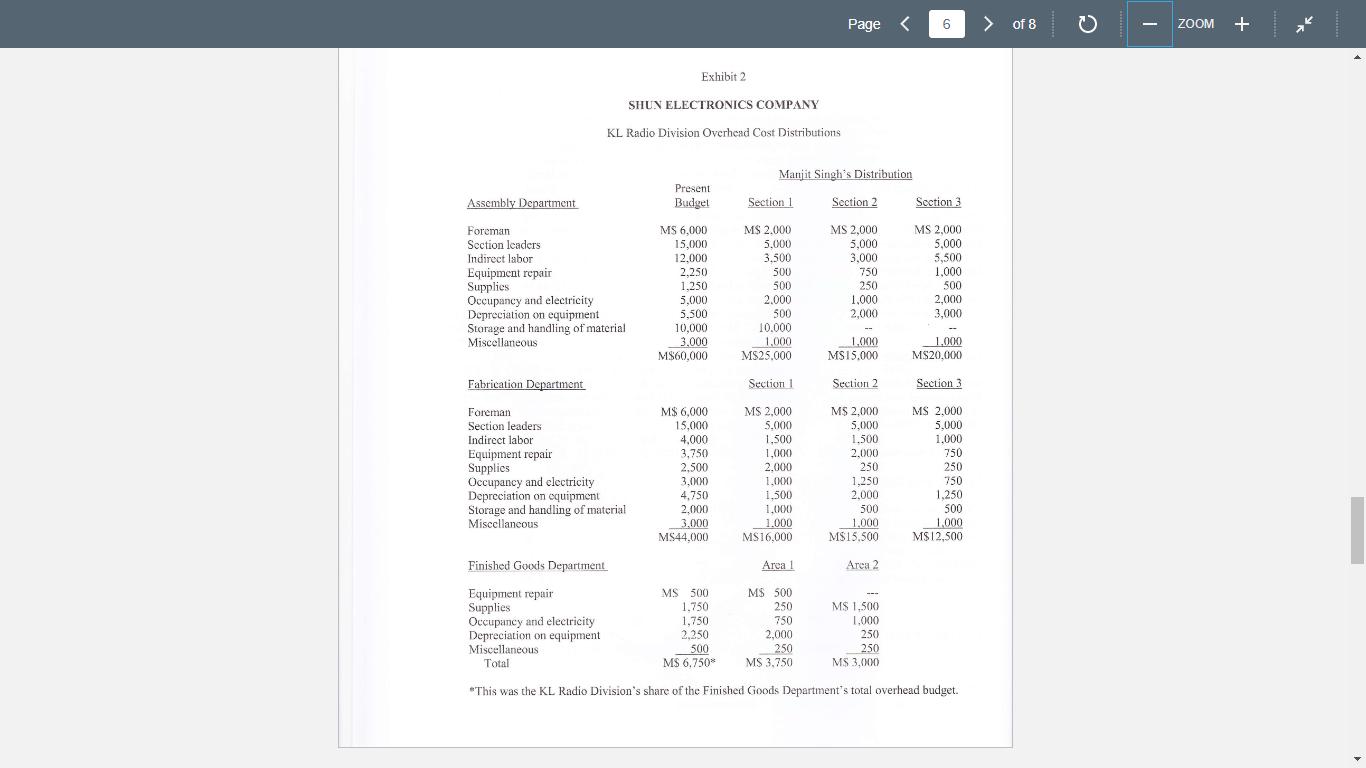
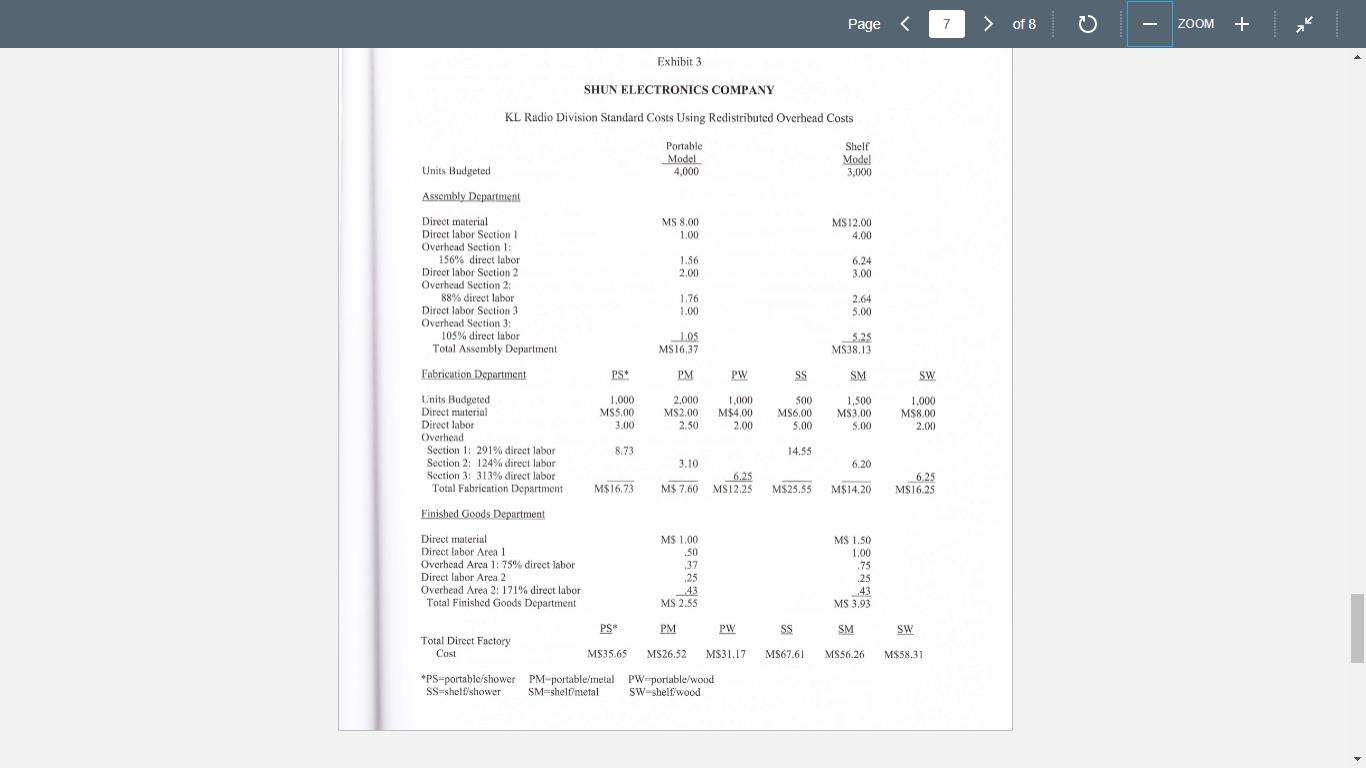
Page A6221, Managerial Accounting for MBAs, Dr. Alireza Daneshfar, University of New Haven Case: Shun Electronics Company CASE OBJECTIVES: This is an introductory-level case on overhead cost allocations and cost systems design. This case helps you understand the design of cost systems, in general, and the creation of cost allocation overhead rates, in particular. Objectives are: 1. To provide a basis for the articulation and specification of an overhead cost system's design. In this regard, overhead cost systems rest on two design choices-(a) the designation of cost pools for aggregating overhead costs and (b) the choice of an allocation base for transporting the overhead costs out of each pool to the end product. 2. To provide opportunities for students to implement a cost system's design. 3. To highlight the fact that the product costs changed without any change in operations or supplier costs. Thus, the product costs changed solely due to the changes in the choice of overhead cost pools allocation base. Requirements: Here are two requirements to start with. However, the case discussion can go beyond these two requirements and you should be prepared for: 1. Where did the figures in case Exhibits 1, 2, and 3 come from and how were they computed? 2. To date, the shelf shower radio was thought to cost M$61.00. Manjit Singh says it's more accurately determined cost is MS67.61. Why the difference? 1 > of 8 C ZOOM + Page A6221, Managerial Accounting for MBAs, Dr. Alireza Daneshfar, University of New Haven Case: Shun Electronics Company CASE OBJECTIVES: This is an introductory-level case on overhead cost allocations and cost systems design. This case helps you understand the design of cost systems, in general, and the creation of cost allocation overhead rates, in particular. Objectives are: 1. To provide a basis for the articulation and specification of an overhead cost system's design. In this regard, overhead cost systems rest on two design choices-(a) the designation of cost pools for aggregating overhead costs and (b) the choice of an allocation base for transporting the overhead costs out of each pool to the end product. 2. To provide opportunities for students to implement a cost system's design. 3. To highlight the fact that the product costs changed without any change in operations or supplier costs. Thus, the product costs changed solely due to the changes in the choice of overhead cost pools allocation base. Requirements: Here are two requirements to start with. However, the case discussion can go beyond these two requirements and you should be prepared for: 1. Where did the figures in case Exhibits 1, 2, and 3 come from and how were they computed? 2. To date, the shelf shower radio was thought to cost M$61.00. Manjit Singh says it's more accurately determined cost is MS67.61. Why the difference? 1 > of 8 C ZOOM + Page A6221, Managerial Accounting for MBAs, Dr. Alireza Daneshfar, University of New Haven Case: Shun Electronics Company CASE OBJECTIVES: This is an introductory-level case on overhead cost allocations and cost systems design. This case helps you understand the design of cost systems, in general, and the creation of cost allocation overhead rates, in particular. Objectives are: 1. To provide a basis for the articulation and specification of an overhead cost system's design. In this regard, overhead cost systems rest on two design choices-(a) the designation of cost pools for aggregating overhead costs and (b) the choice of an allocation base for transporting the overhead costs out of each pool to the end product. 2. To provide opportunities for students to implement a cost system's design. 3. To highlight the fact that the product costs changed without any change in operations or supplier costs. Thus, the product costs changed solely due to the changes in the choice of overhead cost pools allocation base. Requirements: Here are two requirements to start with. However, the case discussion can go beyond these two requirements and you should be prepared for: 1. Where did the figures in case Exhibits 1, 2, and 3 come from and how were they computed? 2. To date, the shelf shower radio was thought to cost M$61.00. Manjit Singh says it's more accurately determined cost is MS67.61. Why the difference? 1 > of 8 C ZOOM +
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.42 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 The total direct factory cost of product PS in exhibit 1 is calculated as follows Direct material ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


