So I can see all the correct answers but I need a bit of help with explanations!

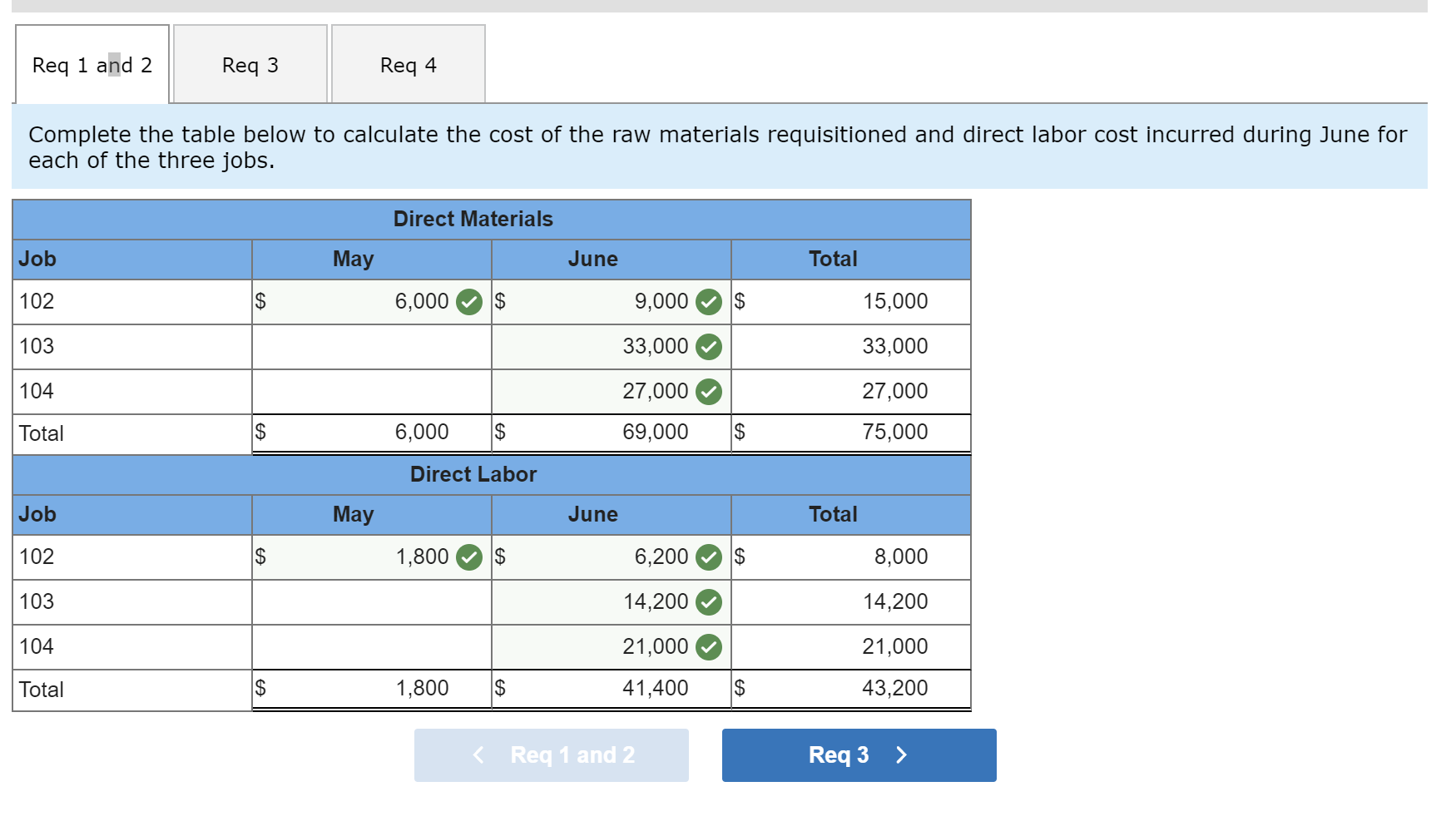
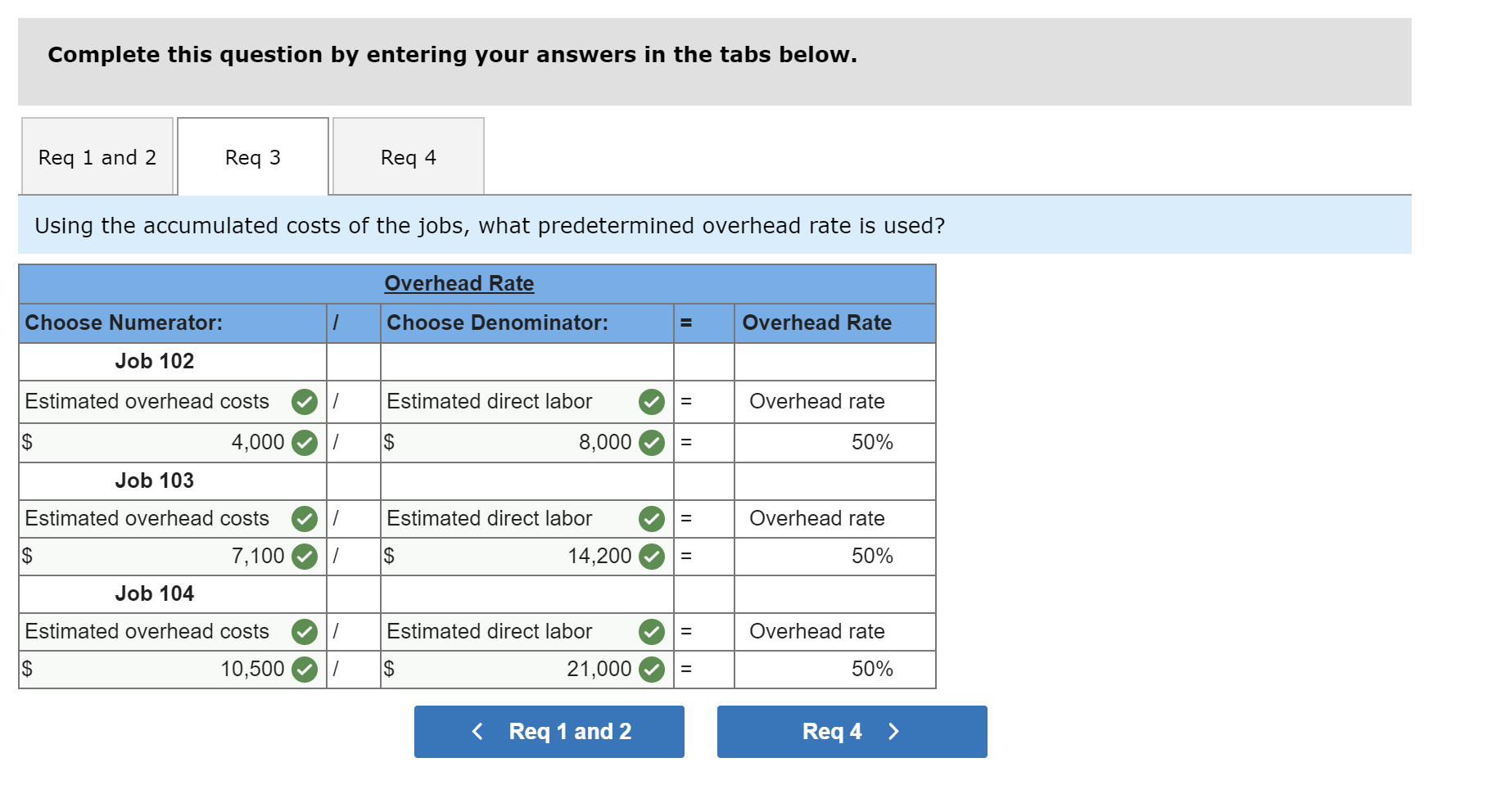
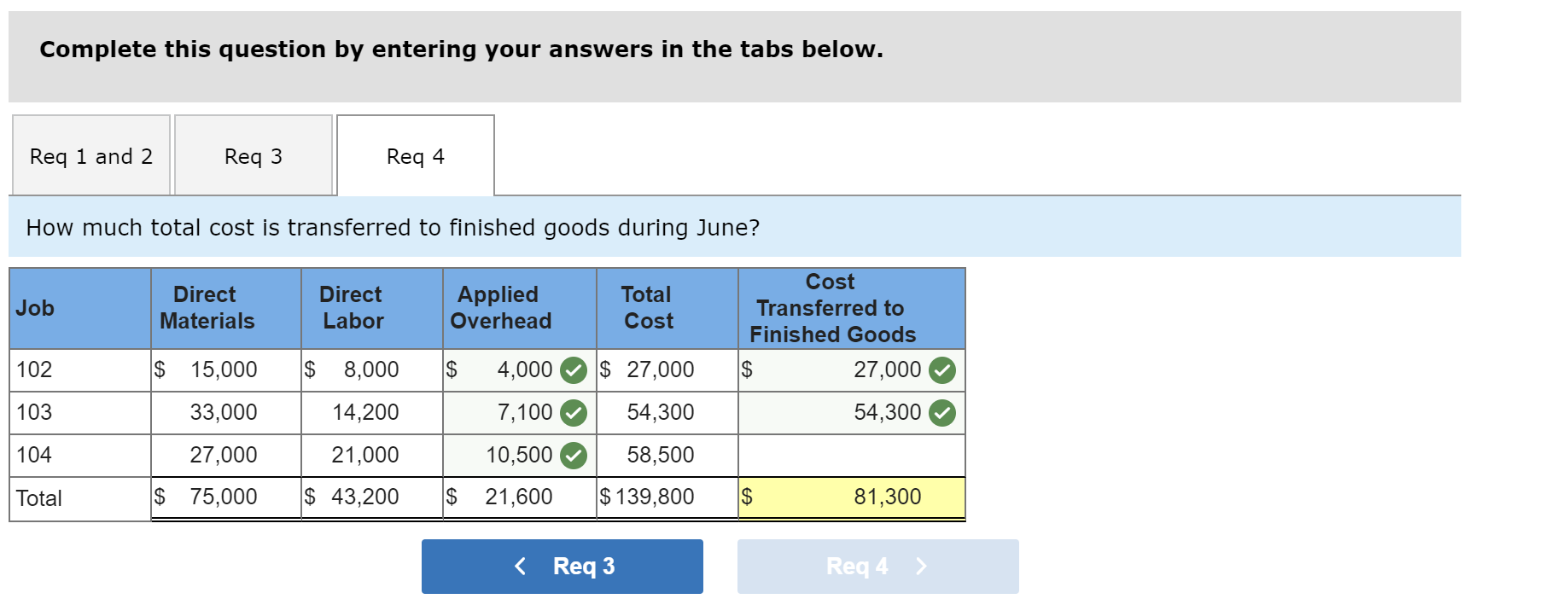
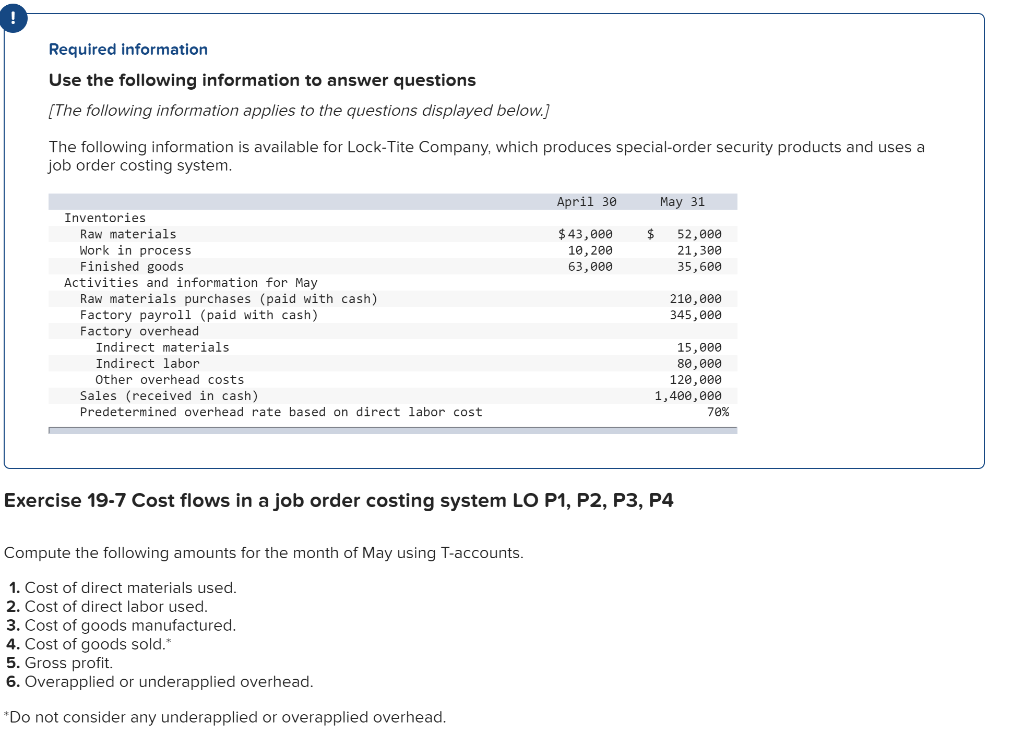
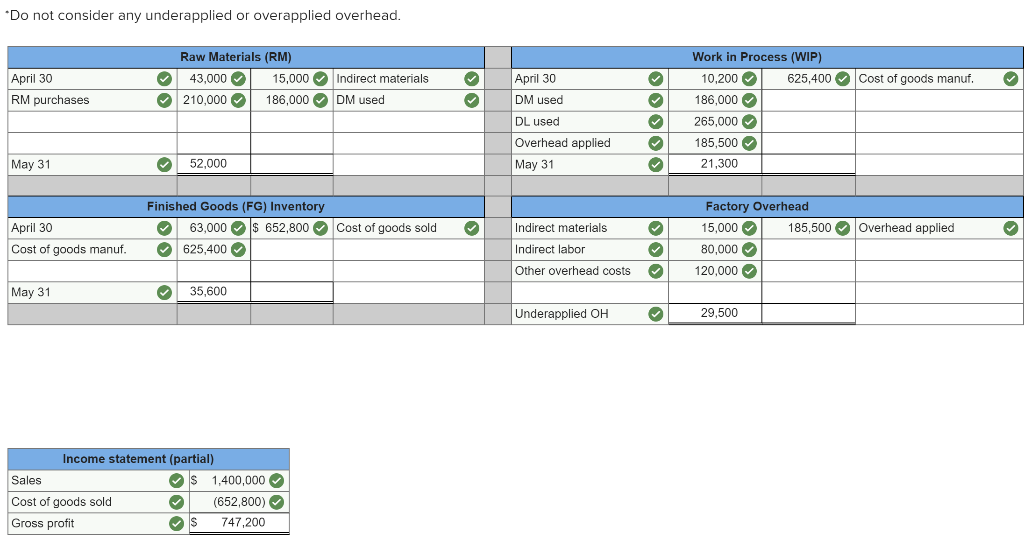
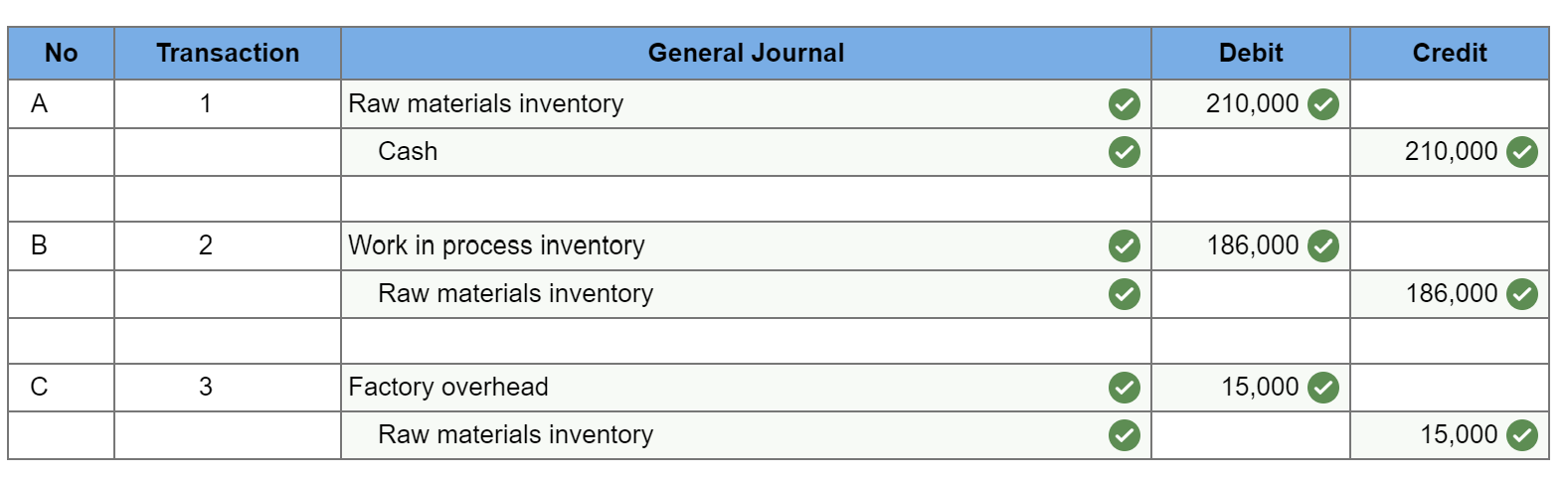
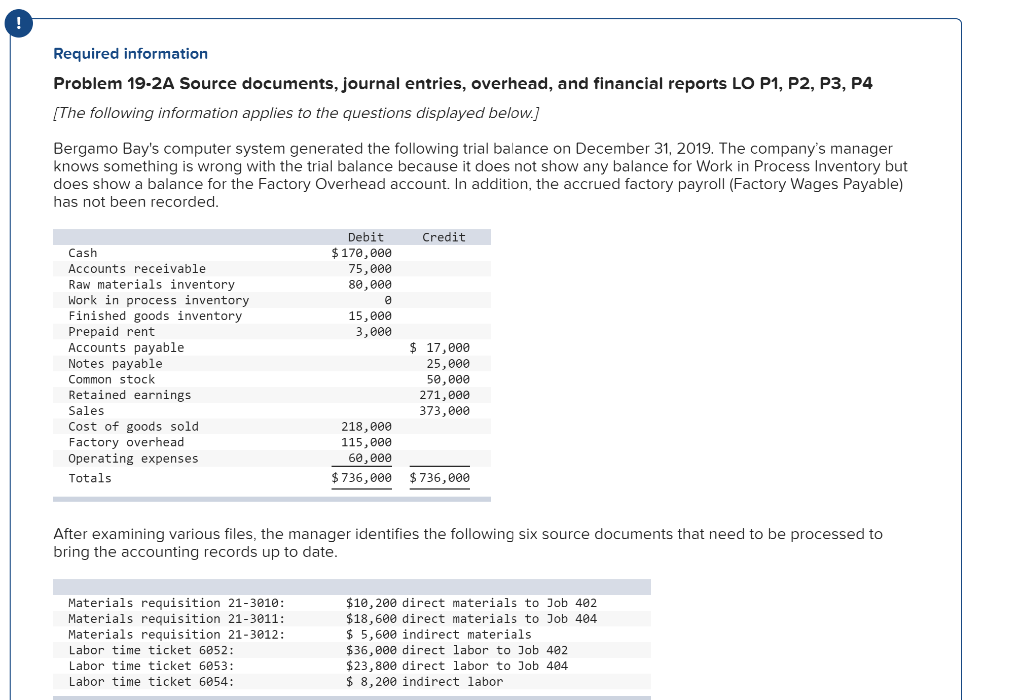
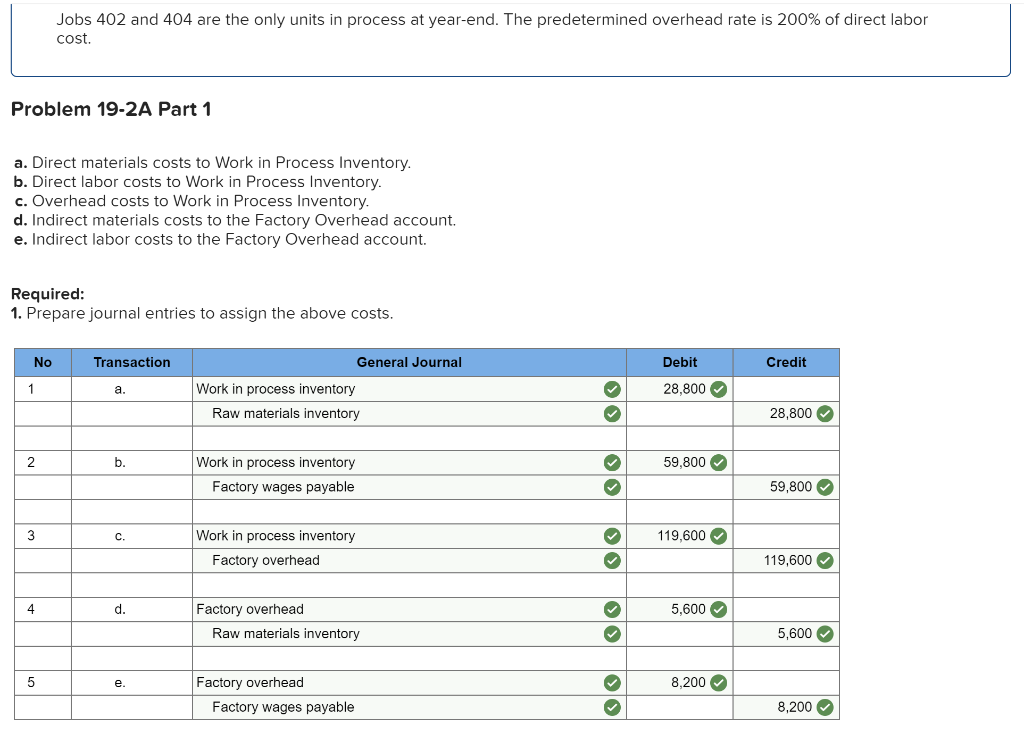
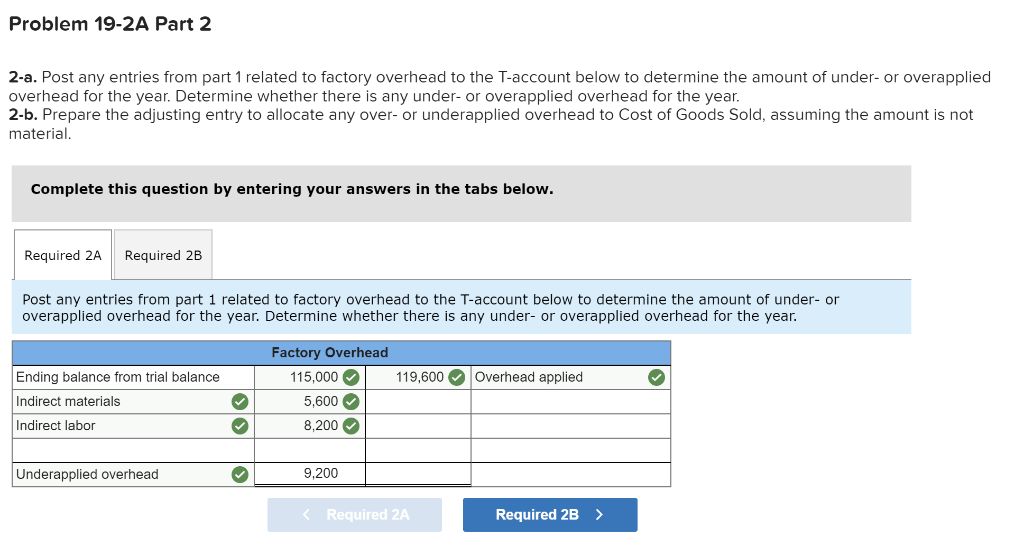
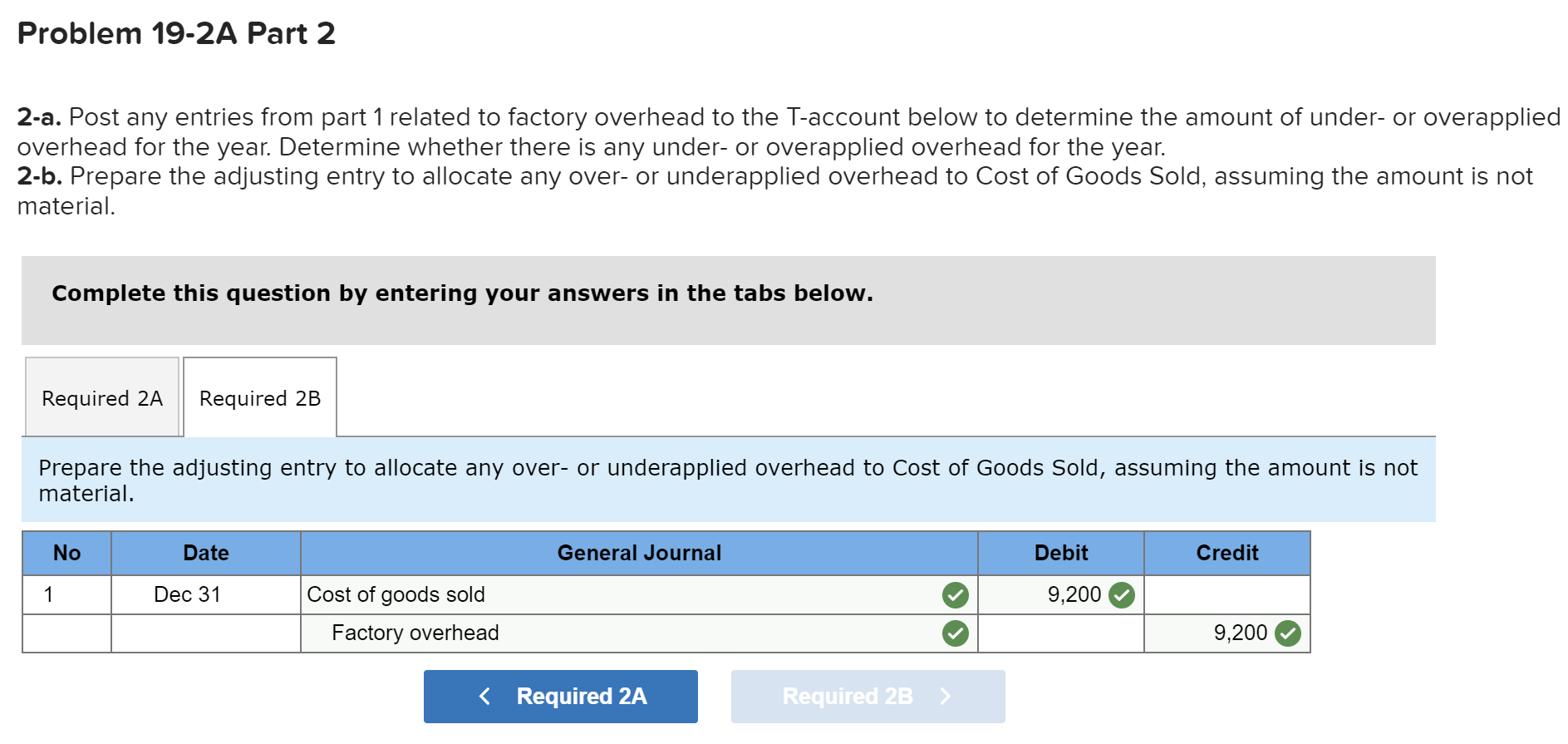
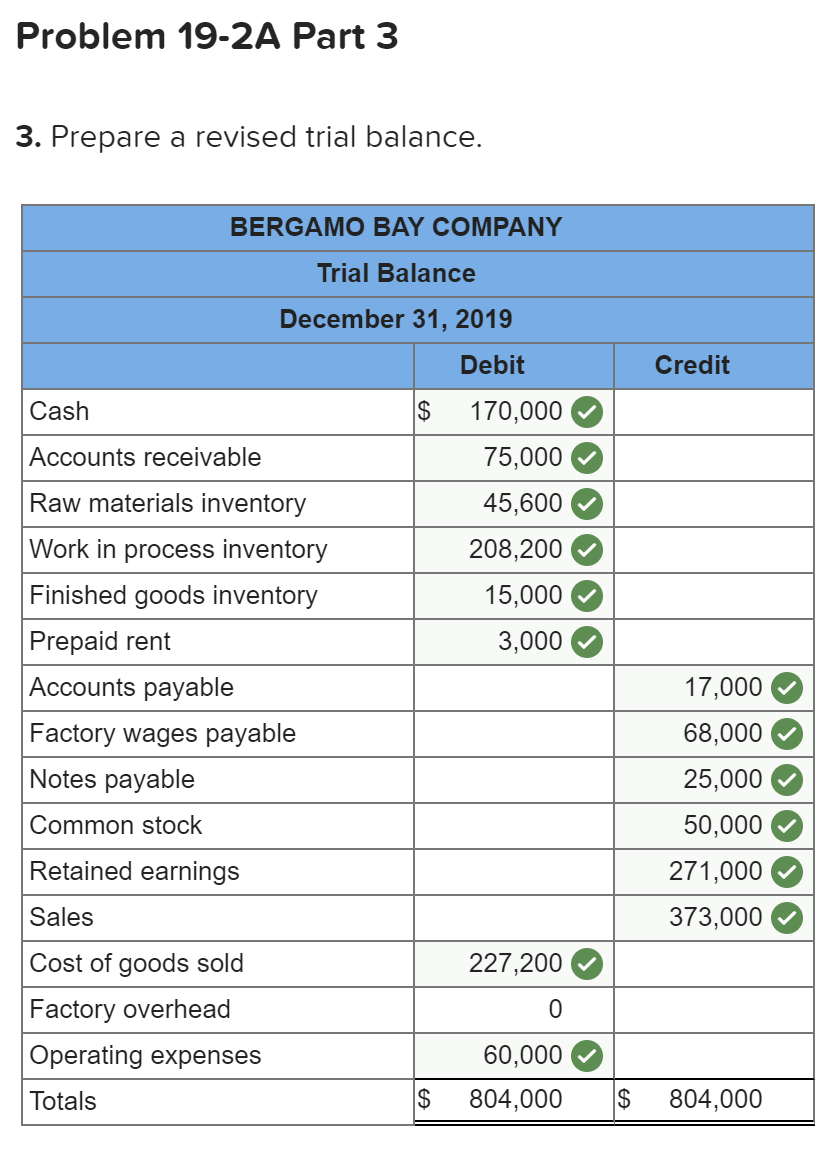
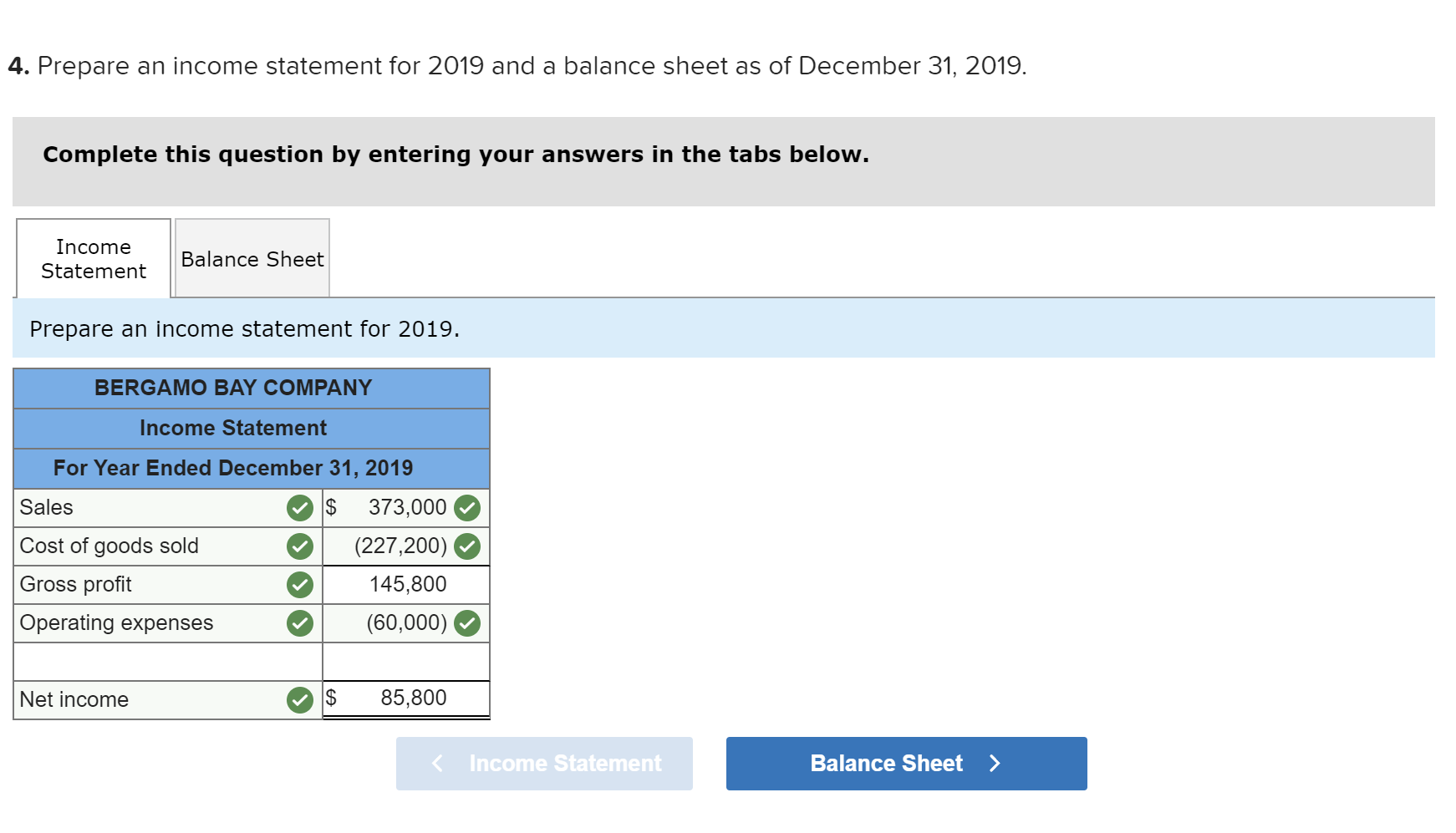
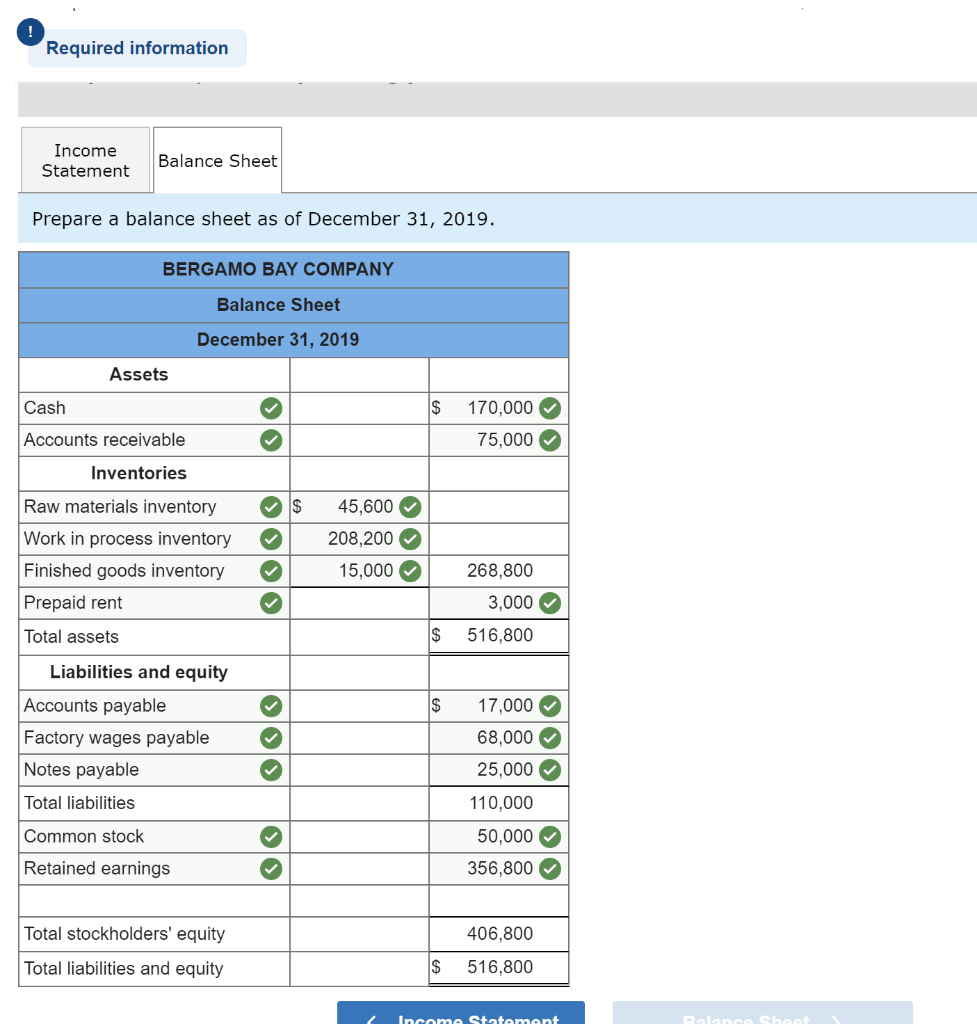
Exercise 19-3 Analyzing of cost flows LO C2 As of the end of June, the job cost sheets at Racing Wheels, Inc., show the following total costs accumulated on three custom jobs. Direct materials Direct labor Overhead applied Job 102 $15,000 8,000 4,000 Job 103 $33,000 14,200 7,100 Job 104 $27,000 21,000 10,500 Job 102 was started in production in May, and the following costs were assigned to it in May: direct materials, $6,000; direct labor, $1,800; and overhead, $900. Jobs 103 and 104 were started in June. Overhead cost is applied with a predetermined rate based on direct labor cost. Jobs 102 and 103 were finished in June, and Job 104 is expected to be finished in July. No raw materials were used indirectly in June. Using this information, answer the following questions. (Assume this company's predetermined overhead rate did not change across these months.) 1&2. Complete the table below to calculate the cost of the raw materials requisitioned and direct labor cost incurred during June for each of the three jobs. 3. Using the accumulated costs of the jobs, what predetermined overhead rate is used? 4. How much total cost is transferred to finished goods during June? Req 1 and 2 Reg 3 Req 4 Complete the table below to calculate the cost of the raw materials requisitioned and direct labor cost incurred during June for each of the three jobs. Direct Materials May Job 102 Total 15,000 S 6,000 $ $ 103 June 9,000 33,000 27,000 69,000 33,000 104 27,000 75,000 Total $ 6,000 $ $ Direct Labor May June Total Job 102 $ 1,800 $ $ 8,000 103 14,200 6,200 14,200 21,000 41,400 104 21,000 43,200 Total 1,800 $ $ Req 1 and 2 Req3 > Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1 and 2 Req 3 Req 4 Using the accumulated costs of the jobs, what predetermined overhead rate is used? Overhead Rate Choose Denominator: Overhead Rate Estimated direct labor $ 8,000 = = Choose Numerator: Job 102 Estimated overhead costs | 4,000 Job 103 Estimated overhead costs I 7,1001 Job 104 | Overhead rate 50% = Estimated direct labor 14,200 Overhead rate 50% Estimated direct labor Overhead rate Estimated overhead costs $ 10,500 $ 21,000 = 50% Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1 and 2 Reg 3 Reg 4 How much total cost is transferred to finished goods during June? Job Direct Materials Direct Direct Labor Direct Total Cost Cost Transferred to Finished Goods $ 27,000 54,300 102 Applied Overhead $ 4,000 7,100 10,500 $ 21,600 $ 15,000 33,000 27,000 $ 75,000 103 $ 8,000 14,200 21,000 $ 43,200 $ 27,000 54,300 58,500 $ 139,800 104 Total $ 81,300 Required information Use the following information to answer questions [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system. April 30 May 31 $ $43,000 10,200 63,000 52,000 21,300 35,600 Inventories Raw materials Work in process Finished goods Activities and information for May Raw materials purchases (paid with cash) Factory payroll (paid with cash) Factory overhead Indirect materials Indirect labor Other overhead costs Sales (received in cash) Predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor cost 210,000 345,000 15,000 80,000 120,000 1,400,000 70% Exercise 19-7 Cost flows in a job order costing system LO P1, P2, P3, P4 Compute the following amounts for the month of May using T-accounts. 1. Cost of direct materials used. 2. Cost of direct labor used. 3. Cost of goods manufactured. 4. Cost of goods sold.* 5. Gross profit. 6. Overapplied or underapplied overhead. "Do not consider any underapplied or overapplied overhead. "Do not consider any underapplied or overapplied overhead. Raw Materials (RM) 43,000 15,000 210,000 186,000 April 30 RM purchases Cost of goods manuf. Indirect materials DM used April 30 DM used DL used Overhead applied May 31 Work in Process (WIP) 10,200 625,400 186,000 265,000 185,500 21,300 May 31 52,000 Finished Goods (FG) Inventory 63,000 $ 652,800 625,400 Cost of goods sold April 30 Cost of goods manuf. Overhead applied Indirect materials Indirect labor Other overhead costs Factory Overhead 15,000 185,500 80,000 120,000 May 31 35,600 Underapplied OH 29,500 Income statement (partial) Sales $ 1,400,000 Cost of goods sold (652,800) Gross profit $ 747,200 Required information Use the following information to answer questions (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system. April 30 May 31 $ $43,000 10,200 63,000 52,000 21,300 35,600 Inventories Raw materials Work in process Finished goods Activities and information for May Raw materials purchases (paid with cash) Factory payroll (paid with cash) Factory overhead Indirect materials Indirect labor Other overhead costs Sales (received in cash) Predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor cost 210,000 345,000 15,000 80,000 120,000 1,400,000 70% Exercise 19-8 Journal entries for materials LO P1 1. Raw materials purchases for cash. 2. Direct materials usage. 3. Indirect materials usage. Prepare journal entries for the above transactions for the month of May. No Transaction General Journal Credit Debit 210,000 A Raw materials inventory Cash 210,000 | B 1 2 186,000 Work in process inventory Raw materials inventory 186,000 15,000 Factory overhead Raw materials inventory 15,000 Required information Problem 19-2A Source documents, journal entries, overhead, and financial reports LO P1, P2, P3, P4 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Bergamo Bay's computer system generated the following trial balance on December 31, 2019. The company's manager knows something is wrong with the trial balance because it does not show any balance for Work in Process Inventory but does show a balance for the Factory Overhead account. In addition, the accrued factory payroll (Factory Wages Payable) has not been recorded. Credit Debit $ 170,000 75,000 80,000 15,000 3,000 Cash Accounts receivable Raw materials inventory Work in process inventory Finished goods inventory Prepaid rent Accounts payable Notes payable Common stock Retained earnings Sales Cost of goods sold Factory overhead Operating expenses Totals $ 17,000 25,000 50,000 271,000 373,000 218,000 115,000 60,000 $ 736,000 $ 736,000 After examining various files, the manager identifies the following six source documents that need to be processed to bring the accounting records up to date. Materials requisition 21-3010: Materials requisition 21-3011: Materials requisition 21-3012: Labor time ticket 6052: Labor time ticket 6053: Labor time ticket 6054: $10,200 direct materials to Job 402 $18,600 direct materials to Job 404 $ 5,600 indirect materials $36,000 direct labor to Job 402 $23,800 direct labor to Job 494 $ 8,200 indirect labor Jobs 402 and 404 are the only units in process at year-end. The predetermined overhead rate is 200% of direct labor cost. Problem 19-2A Part 1 a. Direct materials costs to Work in Process Inventory. b. Direct labor costs to Work in Process Inventory. c. Overhead costs to Work in Process Inventory. d. Indirect materials costs to the Factory Overhead account. e. Indirect labor costs to the Factory Overhead account. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to assign the above costs. No Transaction General Journal Credit Debit 28,800 a. Work in process inventory Raw materials inventory 28,800 59,800 Work in process inventory Factory wages payable 59,800 119,600 Work in process inventory Factory overhead 119,600 5,600 Factory overhead Raw materials inventory 5,600 Factory overhead 8,200 Factory wages payable 8,200 Problem 19-2A Part 2 2-a. Post any entries from part 1 related to factory overhead to the T-account below to determine the amount of under-or overapplied overhead for the year. Determine whether there is any under-or overapplied overhead for the year. 2-b. Prepare the adjusting entry to allocate any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold, assuming the amount is not material. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 2A Required 2B Post any entries from part 1 related to factory overhead to the T-account below to determine the amount of under- or overapplied overhead for the year. Determine whether there is any under- or overapplied overhead for the year. 119,600 Overhead applied Ending balance from trial balance Indirect materials Indirect labor Factory Overhead 115,000 5,600 8,200 Underapplied overhead 1 9 ,200 Required 2A Required 2B > Problem 19-2A Part 2 2-a. Post any entries from part 1 related to factory overhead to the T-account below to determine the amount of under- or overapplied overhead for the year. Determine whether there is any under- or overapplied overhead for the year. 2-b. Prepare the adjusting entry to allocate any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold, assuming the amount is not material. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 2A Required 2B Prepare the adjusting entry to allocate any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold, assuming the amount is not material. No Date General Journal Credit Debit 9,200 Dec 31 Cost of goods sold Factory overhead 9,200 Problem 19-2A Part 3 3. Prepare a revised trial balance. BERGAMO BAY COMPANY Credit Trial Balance December 31, 2019 Debit Cash $ 170,000 Accounts receivable 75,000 Raw materials inventory 45,600 Work in process inventory 208,200 Finished goods inventory 15,000 Prepaid rent 3,000 Accounts payable Factory wages payable Notes payable Common stock Retained earnings Sales 17,000 68,000 25,000 50,000 271,000 373,000 Cost of goods sold 227,200 Factory overhead Operating expenses 0 60,000 804,000 Totals $ $ 804,000 4. Prepare an income statement for 2019 and a balance sheet as of December 31, 2019. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Income Statement Balance Sheet Prepare an income statement for 2019. BERGAMO BAY COMPANY Income Statement For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales $ 373,000 Cost of goods sold (227,200) Gross profit 145,800 Operating expenses (60,000) Net income $ 85,800 Required information Income Statement Balance Sheet Prepare a balance sheet as of December 31, 2019. BERGAMO BAY COMPANY Balance Sheet December 31, 2019 Assets $ Cash Accounts receivable 170,000 75,000 $ Inventories Raw materials inventory Work in process inventory Finished goods inventory Prepaid rent Total assets Liabilities and equity 45,600 208,200 15,000 268,800 3,000 516,800 $ Accounts payable Factory wages payable Notes payable 17,000 68,000 25,000 110,000 50,000 356,800 Total liabilities Common stock Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and equity 406,800 516,800 $ Income Statement Polanco Shoot





















