




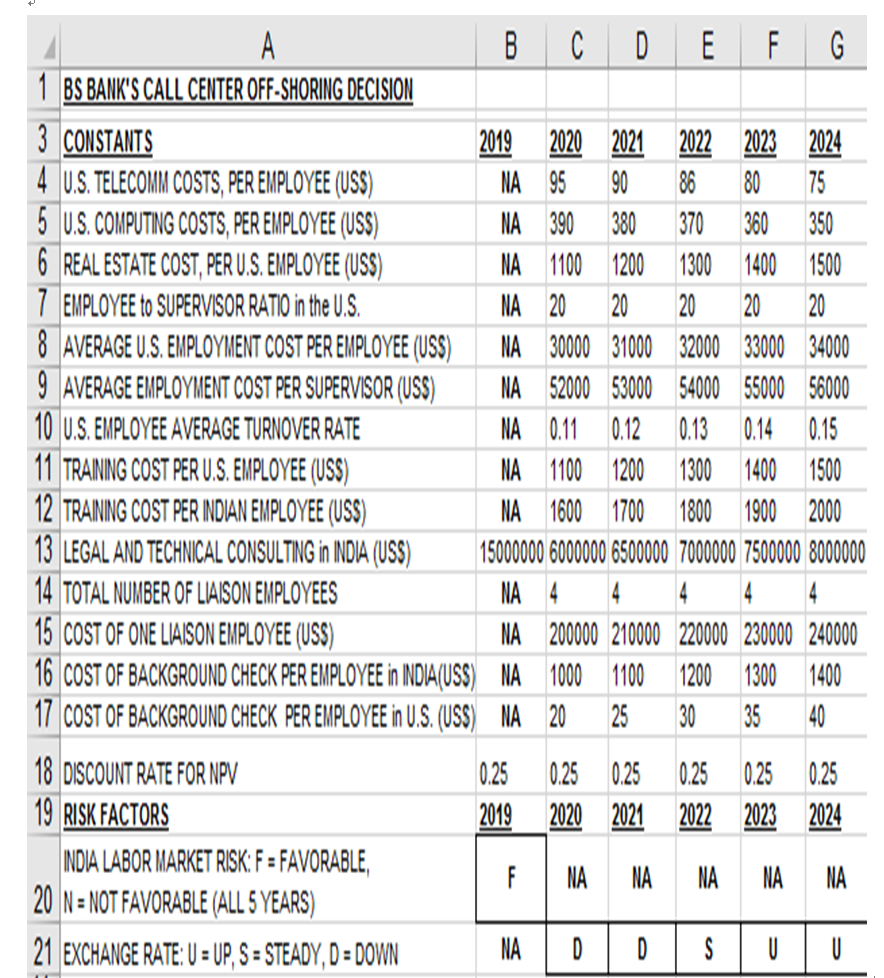
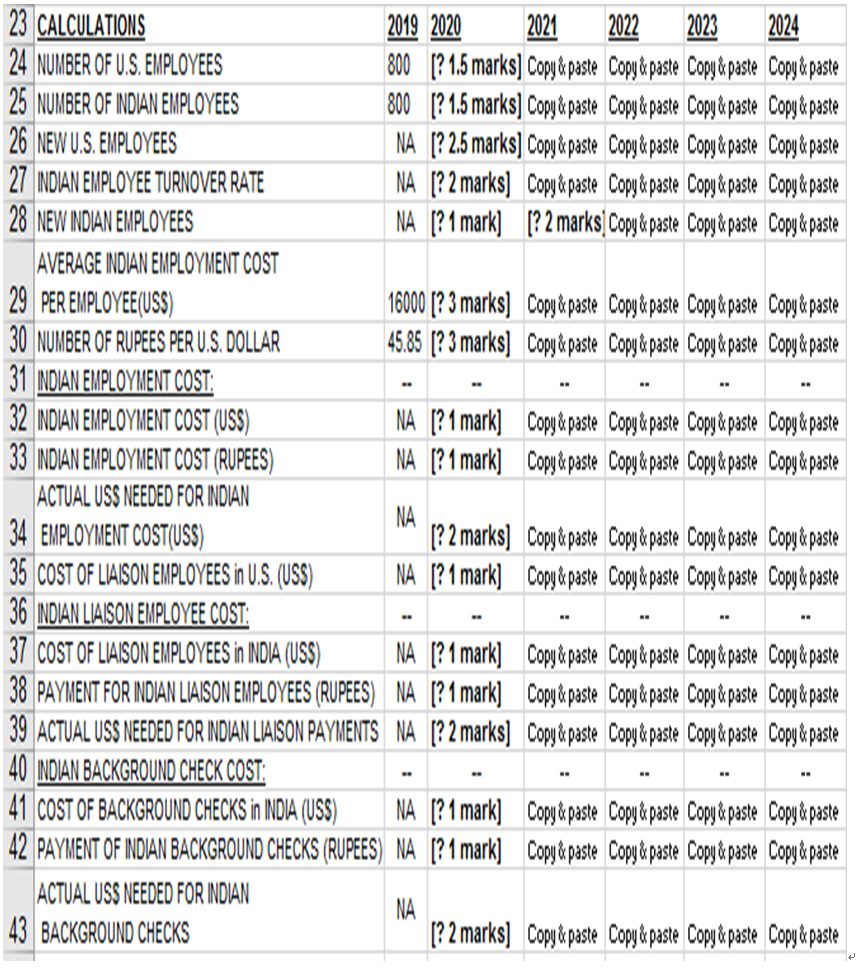
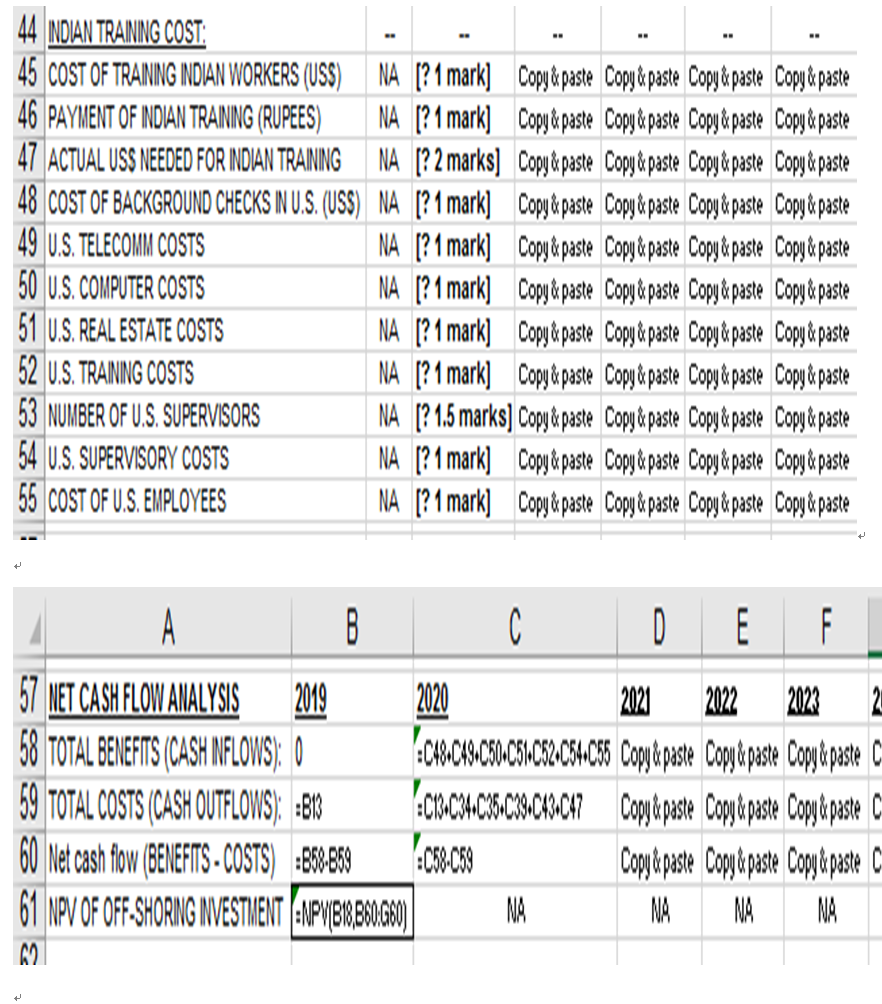
Sofie hidden COSIS (Casli QUITOWS) 01 011-Snoring Operations Inuid would include Training a call centre employee will cost more in India than in the U.S. because Indian employees must be trained to speak like Americans as well as being trained on technical aspects of bani a customer from the U.S. calls about a credit card error, he/she does not want to be distracted by someone with a foreign accent. Training cost per Indian employee (row 12) is expected to be US$1,600 per year in 2020, increasing each year in future. Legal and technical consulting in India (row 13): Costs would involve hiring an Indian law firm for legal advice and hiring an Indian technical firm for technical advice in evaluating the best contractor (BI is chosen). In 2019, BS Bank spent US$15 million for legal & technical consulting fees during the initial setup of "off-shore operation. BS Bank expects to spend US$6 million on maintaining the relationship in 2020, with the amount increasing slightly each year in future. Companies that have outsourced labour in India have noticed that day-to-day communication with their contractor is more successful if some representatives (called liaison employees) are stationed with their contractor. Thus BS Bank would send two of its employees to India to work with BI, and BI would send two of its employees to work with BS Bank in the U.S. (row 14). The cost of a liaison employee is expected to be US$200,000 in 2020, increasing each year (row 15). This expense covers the cost of a liaison employee's salary and housing etc.- Background security checks for new call centre employees: In the U.S., background checks are inexpensive, because so much information about residents is readily available in digital format. In India, however, background information is difficult to obtain and thus, background checks are expensive. A background check would cost US$1,000 per Indian employee in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 16). A background check would cost US$20 per U.S. employee in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 17).- Some financial benefits (or cash inflows) of "off-shoring operations to India would include: At the U.S. call centres, networking and telecommunication costs would be US$95 per employee in 2020, decreasing each year thereafter (row 4). If the centre were off-shored, BS Bank would not have to pay for telecommunications directly. At the U.S. call centres, computing support costs would be US$390 per employee in 2020, decreasing each year thereafter (row 5). If the centre were off-shored, BS Bank would not have to pay for computing support directly. At the U.S. call centres, real estate costs would be US$1,100 per employee in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 6). Real estate costs include upkeep on the call centre building, insurance etc. If the centre is off-shored, BS Bank could use the site for other purposes.' For every 20 U.S. call centre employees, BS Bank employs 1 supervisor (row 7). If the centre is off-shored, supervisors could be used in other areas of the bank; thus a benefit for BS Bank. The average salary cost of a U.S. call centre employee will be US$30,000 in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 8). The average salary cost of a U.S. call centre supervisor will be US$52,000 in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 9). If the centre were off-shored, these salary costs would be forgone. At the U.S. call centres, 11% of call centre employees are expected to leave and be replaced in 2020, and this turnover rate is expected to increase in future years (row 10). It is expected to cost US$1,100 to train a new employee in 2020, increasing in future years (row 11). If the centre were off-shored, these training costs would be forgone. Two important risk factors affecting the costs and benefits of off-shoring operations to India are:- Indian labour market risk (cell B20) has two values: F for "favourable", N for not favourable". As the U.S. demand for offshore operations increases, so does the demand for qualified foreign labour, and thus wages and employee turnover rate are expected to escalate in 2020 2024 (N for this case in cell B20). However, some economic analysts think that as Indian technical schools are expected to turn out more and more qualified people, and thus wages and employee turnover rate will not go up greatly in 2020 2024 (F for this case in cell B20). The currency exchange rate between Indian rupees and American dollars (cells C21 to G21) has three values: U for Up, S for Steady", D for "Down. The 5-year contract between BS Bank and BI is made in 2019 and the agreed currency exchange rate is fixed at US$1 dollar to INR$45.85 rupees (cell B30), even though there will be currency fluctuations during the life of the contract. It is agreed that BI contractor will be paid in rupees once per year but BS Bank operates in U.S. dollars. BS Bank may benefit financially by taking advantage of currency fluctuations. BS Bank calculates currency conversion in the following steps: 1st computes the contract fee to BI in U.S. dollars, 2nd converts the contract fee to rupees at the contract's rate of 45.85, + 3rd BS Bank acquires the needed rupees at the current exchange rate. + If more than INR$45.85 rupees are expected to be exchanged for US$1 dollar, U is entered in row 21. If less than INR$45.85 rupees are expected to be exchanged for US$1 dollar, D is entered in row 21. If the currency exchange rate is expected to be steady, S is entered in row 21. An entry is made for each year of the 5-year contract. The pattern of SSSSS in cells c21 to G21 means steady fluctuation is estimated for all 5 years. The pattern of SSDDD in cells C21 to G21 means steady fluctuation is estimated for the first 2 years, and down for the last 3 years. Calculations (rows 24 to 55): Calculate intermediate results of benefits (cash inflows) and costs (cash outflows) for NPV analysis. Number of U.S. employees (row 24): If the off-shoring agreement were not taken, this is the number of non-supervisory U.S. staff needed. There were 800 U.S. call centre employees in 2019, and it is expected to increase 2% per year (that is 2% more than previous year) due to expected banking business growth. Note that the number of employees must be an integer. Number of Indian employees (row 25): If the off-shoring agreement were taken, this is the number of non-supervisory Indian staff needed. Initially, assume there is a 1-to-1 replacement of U.S. employees in 2019, that is 800 Indian employees (B25=800). India's college graduates are expected to be more productive than U.S. employees, thus the number would increase only 1% per year (that is 1% more than previous year) due to expected banking business growth. Note that the number of employees must be an integer. Number of new U.S. employees (row 26): If the off-shoring agreement were not taken, this is the number of new U.S. employees. New U.S. employees are hired for two reasons: expanding business growth (see row 24) and replacing employees who left in prior year (use the U.S. employee turnover rate in row 10). Note that the number of employees must be an integer. Indian employee turnover rate (row 27): If the Indian labour market is expected to be favourable during the life of the 5-year contract, employee turnover rate will be 10% per year. If it is expected to be not favourable, employee turnover rate will be 25% per year. Number of new Indian employees (row 28): If the off-shoring agreement were taken, this is the number of new Indian employees. New Indian employees are hired for the same reasons as new U.S. employees see row 26, thus the logic of calculation is the same as for new U.S. employees, except that in 2020, all Indian employees are new employees. Average Indian employment cost per employee (row 29): In 2019, the average Indian employment cost per employee is US$16,000. If the Indian labour market is expected to be tavourable during the life of the 5-year contract, salary levels will increase 8% per year (that is 8% more than previous year). If it is expected to be not favourable, the increase will be 15% per year (that is 15% more than previous year). Number of rupees per U.S. dollar (row 30): The agreed currency exchange rate is fixed at US$1 dollar to INR$45.85 rupees (cell B30) when the 5-year contract is made in 2019, but currency exchange rate fluctuates each day. If the exchange rate outlook is steady for that year, the number of rupees per U.S. dollar is the same as prior year. If the outlook is up, the number of rupees per U.S. dollar will be 2% more than prior year. If the outlook is down, the number of rupees per U.S. dollar will be 2% less than prior year. + Indian employment cost in U.S. dollar (row 32): This is based on the number of Indian employees and the average Indian employment cost in US$) per employee.- Indian employment cost in rupees (row 33): This is the payment of Indian employment cost to BI contractor in rupees, using the agreed exchange rate of 45.85 rupees to US$1. Actual US$ needed for Indian employment cost (row 34): This is the amount of dollars actually required to pay BI contractor as the Indian employment cost for that financial year.' Cost (in US$) of liaison employees living in the U.S. (row 35): This is based on the number of liaison employees living in the U.S. and the cost (in US$) of a liaison employee. Cost (in US$) of liaison employees living in India (row 37): This is based on the number of liaison employees living in India and the cost (in US$) of a liaison employee. Payment of Indian liaison employees in rupees (row 38): The liaison employees living in India will be paid by BS Bank in rupees, calculated at the agreed exchange rate of 45.85 rupees to US$1. Actual US$ needed for Indian liaison payments (row 39): This is the number of dollars actually required to pay for the liaison employees living in India for that financial year.' Cost of background checks in India (row 41): This is the cost (in US$) of background security checks performed by BI for new Indian employees in a year.' Payment of Indian background checks in rupees (row 42): This is the payment of Indian background checks to BI contractor in rupees, using the agreed exchange rate of 45.85 rupees to US$1. Actual US$ needed for Indian background checks (row 43): This is the number of dollars actually.. required to pay for the Indian background checks for that financial year.' Cost of training new Indian employees in U.S. dollar (row 45): This is based on the number of new Indian employees and the training cost (in US$) per Indian employee. Payment of Indian training cost in rupees (row 46): This is the payment of Indian training cost to BI contractor in rupees, at the agreed exchange rate of 45.85 rupees to US$1. Actual US$ needed for Indian training cost (row 47): This is the number of dollars actually required to pay for the Indian training cost for that financial year. - Cost of background checks in the U.S. (row 48): This is the cost in US$) of background security checks performed for new U.S. employees in a year. U.S. telecommunication costs (row 49): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the cost of U.S. telecommunication per call centre employee.. U.S. computer costs (row 50): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the cost of U.S. computer per call centre employee. U.S. real estate costs (row 51): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the cost of U.S. real estate per call centre employee. U.S. training costs (row 52): This is based on the number of new U.S. call centre employees and the cost to train a U.S. call centre employee. Number of U.S. supervisors (row 53): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the ratio of U.S. call centre employees to supervisor. Note that the number of supervisors must be an integer.- Cost of U.S. supervisors (row 54): This is based on the number of U.S. supervisors and the average employment cost for a U.S. call centre supervisor. Cost of U.S. employees (row 55): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the average employment cost for a U.S. employee.- Net Present Value (NPV) calculation (rows 58 61): This is based on the net cash flows in the 5-year investments. The net present value of an investment is calculated by using a discount rate and a time series of payments/costs (negative values) and income/benefits (positive values). The net cash flow in a year is the difference between cash inflows (or investment benefits) and cash outflows (or costs). Formulae for rows 58 to 61 are given, their descriptions are given below; Cash inflows or benefits (row 58): These values are the total amounts that could be saved each year if the call centre is off-shored to India. Cash outflows or costs (row 59): These values are the total amounts that will be paid by BS Bank to BI contractor each year if the call centre is off-shored to India. Net cash flow (row 60): These values are the difference between cash inflows and cash outflows (that is, cash inflows less cash outflows) each year. Net present value (cell B61): Use Microsoft Excel's function - NPVC), to calculate the NPV at 25% discount rate (row 18) for the 5-year contract with BI if the call centre is off-shored to India. B C D E F G 1 BS BANK'S CALL CENTER OFF-SHORING DECISION 3 CONSTANTS 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 4 U.S. TELECOMM COSTS, PER EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 959086 80 75 5 U.S. COMPUTING COSTS, PER EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 390 380 370 360 350 6 REAL ESTATE COST, PER U.S. EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 7 EMPLOYEE to SUPERVISOR RATIO in the U.S. NA 20 20 20 20 20 8 AVERAGE U.S. EMPLOYMENT COST PER EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 30000 31000 32000 33000 34000 9 AVERAGE EMPLOYMENT COST PER SUPERVISOR (USS) NA 52000 53000 54000 55000 56000 10 U.S. EMPLOYEE AVERAGE TURNOVER RATE NA 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 11 TRAINING COST PER U.S. EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 12 TRAINING COST PER INDIAN EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 13 LEGAL AND TECHNICAL CONSULTING in INDIA (USS) 15000000 6000000 6500000 7000000 7500000 8000000 14 TOTAL NUMBER OF LIAISON EMPLOYEES NA 4 4 4 4 4 15 COST OF ONE LIAISON EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 200000 210000 220000 230000 240000 16 COST OF BACKGROUND CHECK PER EMPLOYEE in INDIA(USS) NA 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 17 COST OF BACKGROUND CHECK PER EMPLOYEE in U.S. (USS) NA 20 25 30 35 40 18 DISCOUNT RATE FOR NPV 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 19 RISK FACTORS 2019_2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 INDIA LABOR MARKET RISK: F = FAVORABLE. 20 N = NOT FAVORABLE (ALL 5 YEARS) 21 EXCHANGE RATE:U = UP, S = STEADY, D = DOWN NA 0 o s u u 23 CALCULATIONS 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 24 NUMBER OF U.S. EMPLOYEES 800 [?1.5 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 25 NUMBER OF INDIAN EMPLOYEES 800 [? 1.5 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 26 NEW U.S. EMPLOYEES NA [? 2.5 marks] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 27 INDIAN EMPLOYEE TURNOVER RATE NA [? 2 marks] Copy & paste Copy&paste Copy&paste Copy & paste 28 NEW INDIAN EMPLOYEES NA [? 1 mark] [? 2 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste AVERAGE INDIAN EMPLOYMENT COST 29 PER EMPLOYEE(USS) 16000 [? 3 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 30 NUMBER OF RUPEES PER U.S. DOLLAR 45.85 [? 3 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 31 INDIAN EMPLOYMENT COST: 32 INDIAN EMPLOYMENT COST (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 33 INDIAN EMPLOYMENT COST (RUPEES) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste ACTUAL USS NEEDED FOR INDIAN 34 EMPLOYMENT COST(USS) 1?2 marks] Copy & paste Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 35 COST OF LIAISON EMPLOYEES in U.S. (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 36 INDIAN LIAISON EMPLOYEE COST: 37 COST OF LIAISON EMPLOYEES IN INDIA (USS) NA [?1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 38 PAYMENT FOR NDIAN LIAISON EMPLOYEES (RUPEES) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 39 ACTUAL USS NEEDED FOR INDIAN LIAISON PAYMENTS NA [? 2 marks] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 40 INDIAN BACKGROUND CHECK COST: 41 COST OF BACKGROUND CHECKS in INDIA (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 42 PAYMENT OF INDIAN BACKGROUND CHECKS (RUPEES) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste ACTUAL USS NEEDED FOR INDIAN 43 BACKGROUND CHECKS ste Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 44 INDIAN TRAINING COST: 45 COST OF TRAINING INDIAN WORKERS (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy&paste 46 PAYMENT OF INDIAN TRAINING (RUPEES) NA 1? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 47 ACTUAL USS NEEDED FOR INDIAN TRAINING NA [? 2 marks] Copy&paste Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 48 COST OF BACKGROUND CHECKS IN U.S. (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 49 U.S. TELECOMM COSTS NA [?1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 50 U.S. COMPUTER COSTS NA [?1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 51 U.S. REAL ESTATE COSTS NA [?1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 52 U.S. TRAINING COSTS NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 53 NUMBER OF U.S. SUPERVISORS NA [? 1.5 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 54 U.S. SUPERVISORY COSTS NA [? 1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 55 COST OF U.S. EMPLOYEES NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste B C D E F 57 NET CASH FLOW ANALYSIS 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2 58 TOTAL BENEFITS (CASH NFLOWS): 0 :C48C49-C50-C66C52051C5Copy&paste Copy&paste Copy&paste o 59 TOTAL COSTS (CASH OUTFLOWS) :813 :C1B_C346C5C99.C4%C47 Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 60 Net cash flow (BENEFITS - COSTS) 55.889 1:08.089 Copy&paste Copy&paste Copy&paste C 61 NPV OF OFF.SHORING INVESTIMENT NPWEXBOGO) NA NA NA NA BB Sofie hidden COSIS (Casli QUITOWS) 01 011-Snoring Operations Inuid would include Training a call centre employee will cost more in India than in the U.S. because Indian employees must be trained to speak like Americans as well as being trained on technical aspects of bani a customer from the U.S. calls about a credit card error, he/she does not want to be distracted by someone with a foreign accent. Training cost per Indian employee (row 12) is expected to be US$1,600 per year in 2020, increasing each year in future. Legal and technical consulting in India (row 13): Costs would involve hiring an Indian law firm for legal advice and hiring an Indian technical firm for technical advice in evaluating the best contractor (BI is chosen). In 2019, BS Bank spent US$15 million for legal & technical consulting fees during the initial setup of "off-shore operation. BS Bank expects to spend US$6 million on maintaining the relationship in 2020, with the amount increasing slightly each year in future. Companies that have outsourced labour in India have noticed that day-to-day communication with their contractor is more successful if some representatives (called liaison employees) are stationed with their contractor. Thus BS Bank would send two of its employees to India to work with BI, and BI would send two of its employees to work with BS Bank in the U.S. (row 14). The cost of a liaison employee is expected to be US$200,000 in 2020, increasing each year (row 15). This expense covers the cost of a liaison employee's salary and housing etc.- Background security checks for new call centre employees: In the U.S., background checks are inexpensive, because so much information about residents is readily available in digital format. In India, however, background information is difficult to obtain and thus, background checks are expensive. A background check would cost US$1,000 per Indian employee in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 16). A background check would cost US$20 per U.S. employee in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 17).- Some financial benefits (or cash inflows) of "off-shoring operations to India would include: At the U.S. call centres, networking and telecommunication costs would be US$95 per employee in 2020, decreasing each year thereafter (row 4). If the centre were off-shored, BS Bank would not have to pay for telecommunications directly. At the U.S. call centres, computing support costs would be US$390 per employee in 2020, decreasing each year thereafter (row 5). If the centre were off-shored, BS Bank would not have to pay for computing support directly. At the U.S. call centres, real estate costs would be US$1,100 per employee in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 6). Real estate costs include upkeep on the call centre building, insurance etc. If the centre is off-shored, BS Bank could use the site for other purposes.' For every 20 U.S. call centre employees, BS Bank employs 1 supervisor (row 7). If the centre is off-shored, supervisors could be used in other areas of the bank; thus a benefit for BS Bank. The average salary cost of a U.S. call centre employee will be US$30,000 in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 8). The average salary cost of a U.S. call centre supervisor will be US$52,000 in 2020, increasing each year thereafter (row 9). If the centre were off-shored, these salary costs would be forgone. At the U.S. call centres, 11% of call centre employees are expected to leave and be replaced in 2020, and this turnover rate is expected to increase in future years (row 10). It is expected to cost US$1,100 to train a new employee in 2020, increasing in future years (row 11). If the centre were off-shored, these training costs would be forgone. Two important risk factors affecting the costs and benefits of off-shoring operations to India are:- Indian labour market risk (cell B20) has two values: F for "favourable", N for not favourable". As the U.S. demand for offshore operations increases, so does the demand for qualified foreign labour, and thus wages and employee turnover rate are expected to escalate in 2020 2024 (N for this case in cell B20). However, some economic analysts think that as Indian technical schools are expected to turn out more and more qualified people, and thus wages and employee turnover rate will not go up greatly in 2020 2024 (F for this case in cell B20). The currency exchange rate between Indian rupees and American dollars (cells C21 to G21) has three values: U for Up, S for Steady", D for "Down. The 5-year contract between BS Bank and BI is made in 2019 and the agreed currency exchange rate is fixed at US$1 dollar to INR$45.85 rupees (cell B30), even though there will be currency fluctuations during the life of the contract. It is agreed that BI contractor will be paid in rupees once per year but BS Bank operates in U.S. dollars. BS Bank may benefit financially by taking advantage of currency fluctuations. BS Bank calculates currency conversion in the following steps: 1st computes the contract fee to BI in U.S. dollars, 2nd converts the contract fee to rupees at the contract's rate of 45.85, + 3rd BS Bank acquires the needed rupees at the current exchange rate. + If more than INR$45.85 rupees are expected to be exchanged for US$1 dollar, U is entered in row 21. If less than INR$45.85 rupees are expected to be exchanged for US$1 dollar, D is entered in row 21. If the currency exchange rate is expected to be steady, S is entered in row 21. An entry is made for each year of the 5-year contract. The pattern of SSSSS in cells c21 to G21 means steady fluctuation is estimated for all 5 years. The pattern of SSDDD in cells C21 to G21 means steady fluctuation is estimated for the first 2 years, and down for the last 3 years. Calculations (rows 24 to 55): Calculate intermediate results of benefits (cash inflows) and costs (cash outflows) for NPV analysis. Number of U.S. employees (row 24): If the off-shoring agreement were not taken, this is the number of non-supervisory U.S. staff needed. There were 800 U.S. call centre employees in 2019, and it is expected to increase 2% per year (that is 2% more than previous year) due to expected banking business growth. Note that the number of employees must be an integer. Number of Indian employees (row 25): If the off-shoring agreement were taken, this is the number of non-supervisory Indian staff needed. Initially, assume there is a 1-to-1 replacement of U.S. employees in 2019, that is 800 Indian employees (B25=800). India's college graduates are expected to be more productive than U.S. employees, thus the number would increase only 1% per year (that is 1% more than previous year) due to expected banking business growth. Note that the number of employees must be an integer. Number of new U.S. employees (row 26): If the off-shoring agreement were not taken, this is the number of new U.S. employees. New U.S. employees are hired for two reasons: expanding business growth (see row 24) and replacing employees who left in prior year (use the U.S. employee turnover rate in row 10). Note that the number of employees must be an integer. Indian employee turnover rate (row 27): If the Indian labour market is expected to be favourable during the life of the 5-year contract, employee turnover rate will be 10% per year. If it is expected to be not favourable, employee turnover rate will be 25% per year. Number of new Indian employees (row 28): If the off-shoring agreement were taken, this is the number of new Indian employees. New Indian employees are hired for the same reasons as new U.S. employees see row 26, thus the logic of calculation is the same as for new U.S. employees, except that in 2020, all Indian employees are new employees. Average Indian employment cost per employee (row 29): In 2019, the average Indian employment cost per employee is US$16,000. If the Indian labour market is expected to be tavourable during the life of the 5-year contract, salary levels will increase 8% per year (that is 8% more than previous year). If it is expected to be not favourable, the increase will be 15% per year (that is 15% more than previous year). Number of rupees per U.S. dollar (row 30): The agreed currency exchange rate is fixed at US$1 dollar to INR$45.85 rupees (cell B30) when the 5-year contract is made in 2019, but currency exchange rate fluctuates each day. If the exchange rate outlook is steady for that year, the number of rupees per U.S. dollar is the same as prior year. If the outlook is up, the number of rupees per U.S. dollar will be 2% more than prior year. If the outlook is down, the number of rupees per U.S. dollar will be 2% less than prior year. + Indian employment cost in U.S. dollar (row 32): This is based on the number of Indian employees and the average Indian employment cost in US$) per employee.- Indian employment cost in rupees (row 33): This is the payment of Indian employment cost to BI contractor in rupees, using the agreed exchange rate of 45.85 rupees to US$1. Actual US$ needed for Indian employment cost (row 34): This is the amount of dollars actually required to pay BI contractor as the Indian employment cost for that financial year.' Cost (in US$) of liaison employees living in the U.S. (row 35): This is based on the number of liaison employees living in the U.S. and the cost (in US$) of a liaison employee. Cost (in US$) of liaison employees living in India (row 37): This is based on the number of liaison employees living in India and the cost (in US$) of a liaison employee. Payment of Indian liaison employees in rupees (row 38): The liaison employees living in India will be paid by BS Bank in rupees, calculated at the agreed exchange rate of 45.85 rupees to US$1. Actual US$ needed for Indian liaison payments (row 39): This is the number of dollars actually required to pay for the liaison employees living in India for that financial year.' Cost of background checks in India (row 41): This is the cost (in US$) of background security checks performed by BI for new Indian employees in a year.' Payment of Indian background checks in rupees (row 42): This is the payment of Indian background checks to BI contractor in rupees, using the agreed exchange rate of 45.85 rupees to US$1. Actual US$ needed for Indian background checks (row 43): This is the number of dollars actually.. required to pay for the Indian background checks for that financial year.' Cost of training new Indian employees in U.S. dollar (row 45): This is based on the number of new Indian employees and the training cost (in US$) per Indian employee. Payment of Indian training cost in rupees (row 46): This is the payment of Indian training cost to BI contractor in rupees, at the agreed exchange rate of 45.85 rupees to US$1. Actual US$ needed for Indian training cost (row 47): This is the number of dollars actually required to pay for the Indian training cost for that financial year. - Cost of background checks in the U.S. (row 48): This is the cost in US$) of background security checks performed for new U.S. employees in a year. U.S. telecommunication costs (row 49): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the cost of U.S. telecommunication per call centre employee.. U.S. computer costs (row 50): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the cost of U.S. computer per call centre employee. U.S. real estate costs (row 51): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the cost of U.S. real estate per call centre employee. U.S. training costs (row 52): This is based on the number of new U.S. call centre employees and the cost to train a U.S. call centre employee. Number of U.S. supervisors (row 53): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the ratio of U.S. call centre employees to supervisor. Note that the number of supervisors must be an integer.- Cost of U.S. supervisors (row 54): This is based on the number of U.S. supervisors and the average employment cost for a U.S. call centre supervisor. Cost of U.S. employees (row 55): This is based on the number of U.S. call centre employees and the average employment cost for a U.S. employee.- Net Present Value (NPV) calculation (rows 58 61): This is based on the net cash flows in the 5-year investments. The net present value of an investment is calculated by using a discount rate and a time series of payments/costs (negative values) and income/benefits (positive values). The net cash flow in a year is the difference between cash inflows (or investment benefits) and cash outflows (or costs). Formulae for rows 58 to 61 are given, their descriptions are given below; Cash inflows or benefits (row 58): These values are the total amounts that could be saved each year if the call centre is off-shored to India. Cash outflows or costs (row 59): These values are the total amounts that will be paid by BS Bank to BI contractor each year if the call centre is off-shored to India. Net cash flow (row 60): These values are the difference between cash inflows and cash outflows (that is, cash inflows less cash outflows) each year. Net present value (cell B61): Use Microsoft Excel's function - NPVC), to calculate the NPV at 25% discount rate (row 18) for the 5-year contract with BI if the call centre is off-shored to India. B C D E F G 1 BS BANK'S CALL CENTER OFF-SHORING DECISION 3 CONSTANTS 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 4 U.S. TELECOMM COSTS, PER EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 959086 80 75 5 U.S. COMPUTING COSTS, PER EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 390 380 370 360 350 6 REAL ESTATE COST, PER U.S. EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 7 EMPLOYEE to SUPERVISOR RATIO in the U.S. NA 20 20 20 20 20 8 AVERAGE U.S. EMPLOYMENT COST PER EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 30000 31000 32000 33000 34000 9 AVERAGE EMPLOYMENT COST PER SUPERVISOR (USS) NA 52000 53000 54000 55000 56000 10 U.S. EMPLOYEE AVERAGE TURNOVER RATE NA 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 11 TRAINING COST PER U.S. EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 12 TRAINING COST PER INDIAN EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 13 LEGAL AND TECHNICAL CONSULTING in INDIA (USS) 15000000 6000000 6500000 7000000 7500000 8000000 14 TOTAL NUMBER OF LIAISON EMPLOYEES NA 4 4 4 4 4 15 COST OF ONE LIAISON EMPLOYEE (USS) NA 200000 210000 220000 230000 240000 16 COST OF BACKGROUND CHECK PER EMPLOYEE in INDIA(USS) NA 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 17 COST OF BACKGROUND CHECK PER EMPLOYEE in U.S. (USS) NA 20 25 30 35 40 18 DISCOUNT RATE FOR NPV 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 19 RISK FACTORS 2019_2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 INDIA LABOR MARKET RISK: F = FAVORABLE. 20 N = NOT FAVORABLE (ALL 5 YEARS) 21 EXCHANGE RATE:U = UP, S = STEADY, D = DOWN NA 0 o s u u 23 CALCULATIONS 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 24 NUMBER OF U.S. EMPLOYEES 800 [?1.5 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 25 NUMBER OF INDIAN EMPLOYEES 800 [? 1.5 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 26 NEW U.S. EMPLOYEES NA [? 2.5 marks] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 27 INDIAN EMPLOYEE TURNOVER RATE NA [? 2 marks] Copy & paste Copy&paste Copy&paste Copy & paste 28 NEW INDIAN EMPLOYEES NA [? 1 mark] [? 2 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste AVERAGE INDIAN EMPLOYMENT COST 29 PER EMPLOYEE(USS) 16000 [? 3 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 30 NUMBER OF RUPEES PER U.S. DOLLAR 45.85 [? 3 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 31 INDIAN EMPLOYMENT COST: 32 INDIAN EMPLOYMENT COST (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 33 INDIAN EMPLOYMENT COST (RUPEES) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste ACTUAL USS NEEDED FOR INDIAN 34 EMPLOYMENT COST(USS) 1?2 marks] Copy & paste Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 35 COST OF LIAISON EMPLOYEES in U.S. (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 36 INDIAN LIAISON EMPLOYEE COST: 37 COST OF LIAISON EMPLOYEES IN INDIA (USS) NA [?1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 38 PAYMENT FOR NDIAN LIAISON EMPLOYEES (RUPEES) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 39 ACTUAL USS NEEDED FOR INDIAN LIAISON PAYMENTS NA [? 2 marks] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 40 INDIAN BACKGROUND CHECK COST: 41 COST OF BACKGROUND CHECKS in INDIA (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 42 PAYMENT OF INDIAN BACKGROUND CHECKS (RUPEES) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste ACTUAL USS NEEDED FOR INDIAN 43 BACKGROUND CHECKS ste Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 44 INDIAN TRAINING COST: 45 COST OF TRAINING INDIAN WORKERS (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy&paste 46 PAYMENT OF INDIAN TRAINING (RUPEES) NA 1? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 47 ACTUAL USS NEEDED FOR INDIAN TRAINING NA [? 2 marks] Copy&paste Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 48 COST OF BACKGROUND CHECKS IN U.S. (USS) NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 49 U.S. TELECOMM COSTS NA [?1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 50 U.S. COMPUTER COSTS NA [?1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 51 U.S. REAL ESTATE COSTS NA [?1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 52 U.S. TRAINING COSTS NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 53 NUMBER OF U.S. SUPERVISORS NA [? 1.5 marks] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 54 U.S. SUPERVISORY COSTS NA [? 1 mark] Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 55 COST OF U.S. EMPLOYEES NA [? 1 mark] Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste Copy & paste B C D E F 57 NET CASH FLOW ANALYSIS 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2 58 TOTAL BENEFITS (CASH NFLOWS): 0 :C48C49-C50-C66C52051C5Copy&paste Copy&paste Copy&paste o 59 TOTAL COSTS (CASH OUTFLOWS) :813 :C1B_C346C5C99.C4%C47 Copy&paste Copy & paste Copy & paste 60 Net cash flow (BENEFITS - COSTS) 55.889 1:08.089 Copy&paste Copy&paste Copy&paste C 61 NPV OF OFF.SHORING INVESTIMENT NPWEXBOGO) NA NA NA NA BB














