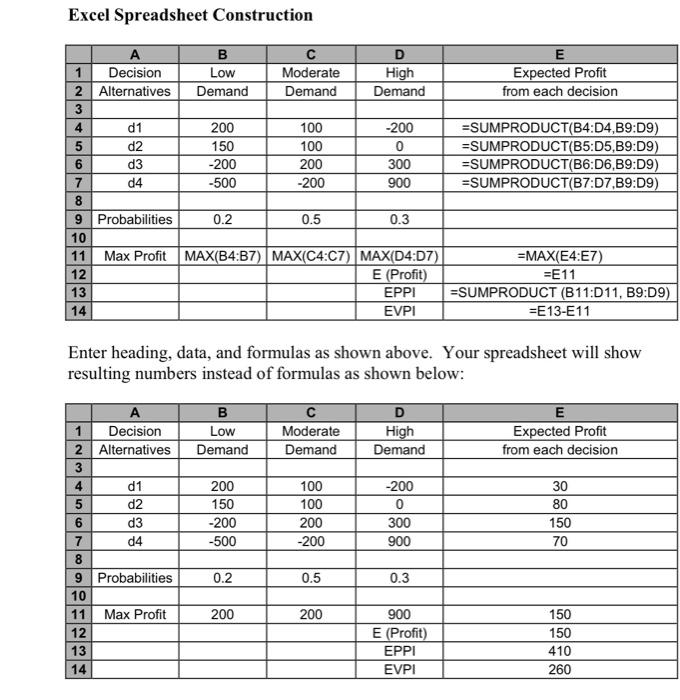
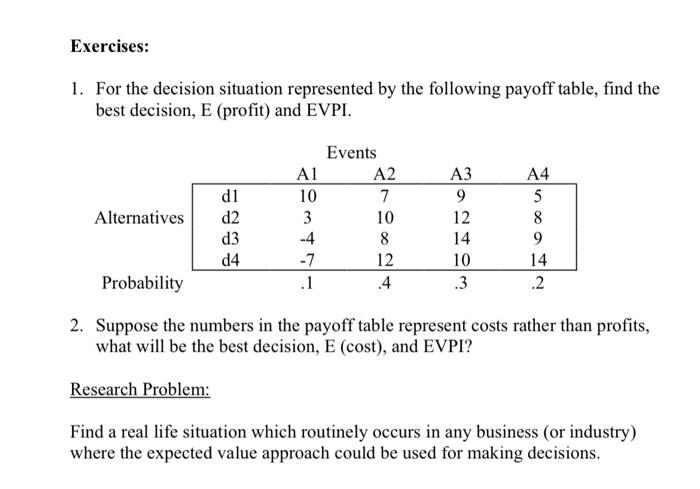
Software Development Corporation (SDC) has developed a new encryption software to facilitate secure commercial transactions over the internet. The feasibility of the product has been proven, but each sale will require significant customer support. SDC must make a decision regarding the level of sales and development resources that must be allocated to this product next year. The least expensive decision alternative (d1) is to start selling the new product through existing sales channels and provide customer support as needed. The next alternative (d2) is to assign one full-time sales-person and one software specialist to focus on this product. The third alternative (d3) is to have a team of six people dedicated to this product. Finally, a complete division (d4) consisting of about twelve people may be created to fully automate the product and engage in an extensive marketing campaign. The potential profit from each decision alternative depends on the market acceptance or demand for this product which may be high, moderate or low. If market acceptance is high, each of the four decision alternatives, d1 through d4 will yield a profit of 200,0,300, and 900 thousand dollars respectively. If there is a moderate demand, the profits are likely to be 100,100,200, and -200 thousand dollars respectively. If the demand turns out to be low, then the profits will be 200,150,200, and -500 thousand dollars respectively. The industry experience with such products provides a probability estimate of demand to be high, moderate and low as .3,.5, and .2 respectively. Which of the four decision alternatives should be selected by SDC? What will be the expected profit from this decision? If a market research firm can provide perfect information about demand to SDC (i.e. whether it will be high, moderate, or low) before a product launching decision is made, how much is that information worth to SDC? To structure this decision-making problem, we begin by constructing a pavoff table. The rows of a payoff table represent the decision alternatives, which in our example consist of four different levels of resources (d1,d2,d3,d4,)assignedtothe new product by SDC. The columns of a payoff table represent events or states of nature, which in our example indicate market acceptance (low, moderate, high) or demand. Our payoff table will, therefore, have 4 rows and 3 columns. The numbers inside the payoff table will represent the profit we will make for each combination of demand and decision alternative. The payoff table (in thousands of dollars) for the SDC decision making problem is shown below along with probabilities of each event or demand level. The decision maker can choose the appropriate decision (row) of the table to use, but the demand (or column) is beyond his or her control. The most common approach to solve such decision-making problems with known probabilities is to use the expected value approach. The decision alternative with the highest expected profit is selected. Using the expected value formula we obtain: E(profitfromd1)=.2200+.5100+.3(200)=30E(profitfromd2)=.2150+.5100+.3(0)=80E(profitfromd3)=.2(200)+.5200+.3(300)=150E(profitfromd4)=.2(500)+.5(200)+.3(900)=70 Solution: The best decision is d3 and E (profit) =$150,000. The highest expected profit results from decision alternative d3. This implies that the average profit from d3 is $150,000. Even though the actual profit from d3 will be either $200,000$200,000, or $300,000 depending on the demand, the average profit will be $150,000 if this decision situation or experiment is repeated a large number of times. SDC is going to make this decision only once, so it is, therefore, possible that the company may lose $200,000 by selecting d3. For risk aversion approach to decision making see the "decision making without probability" section of this workbook. Finding Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI) Now suppose that the market research gave us perfect information about the demand before we made the decision. We will then be able to pick the highest profit decision alternative for each demand level (i.e. the highest number in each column of the payoff table). The expected profit from perfect information (EPPI) is as follows: EPPI=.2200+.5200+.3900=410 We can, therefore, make an average of $410,000 if we have perfect information about the demand. EVPI=EPPIE(profit)=$410,000$150,000=$260,000 The perfect information increases our average profit from $150,000 to $410,000. Therefore, the value of this information, or EVPI, is $260,000. SDC should consider getting market research information if the cost of getting such information is reasonable (i.e. significantly less than $260,000 ). Excel Spreadsheet Construction Enter heading, data, and formulas as shown above. Your spreadsheet will show resulting numbers instead of formulas as shown below: 1. For the decision situation represented by the following payoff table, find the best decision, E (profit) and EVPI. 2. Suppose the numbers in the payoff table represent costs rather than profits, what will be the best decision, E (cost), and EVPI? ResearchProblem: Find a real life situation which routinely occurs in any business (or industry) where the expected value approach could be used for making decisions