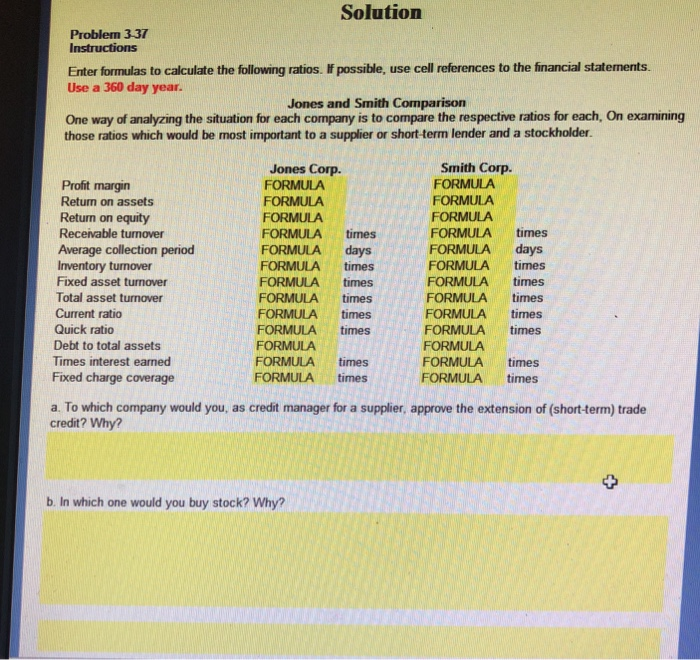
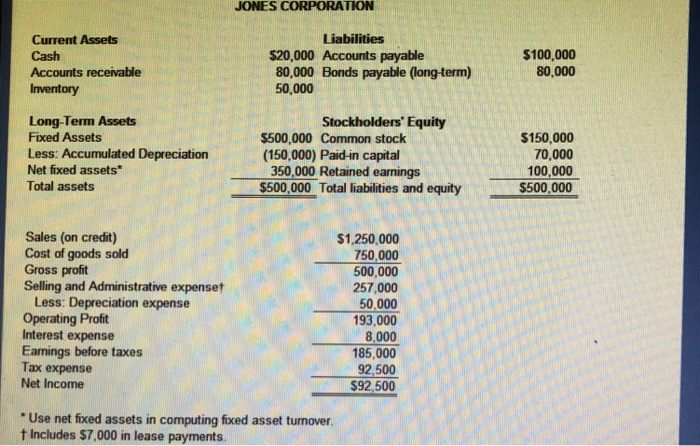
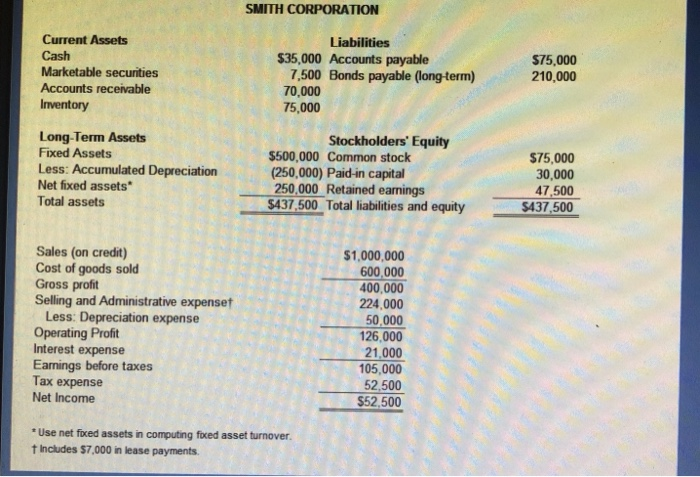
Solution Problem 337 Instructions Enter formulas to calculate the following ratios. If possible, use cell references to the financial statements. Use a 360 day year Jones and Smith Comparison One way of analyzing the situation for each company is to compare the respective ratios for each, On examining those ratios which would be most important to a supplier or short-term lender and a stockholder. Jones Corp. FORMULA FORMULA FORMULA FORMULA times FORMULA days FORMULA times FORMULA times FORMULA times FORMULA times FORMULA times FORMULA FORMULA times FORMULA times Smith Corp. FORMULA FORMULA FORMULA FORMULA times FORMULA days FORMULA times FORMULA times FORMULA times Profit margin Return on assets Return on equity Receivable turnover Average collection period Inventory turnover Fixed asset turnover Total asset turnover Current ratio Quick ratio Debt to total assets Times interest eamed Fixed charge coverage FORMULA times FORMULA times FORMULA FORMULA times FORMULA times a. To which company would you, as credit manager for a supplier, approve the extension of (short-term) trade credit? Why? b. In which one would you buy stock? Why? JONES CORPORATION Current Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Liabilities $20,000 Accounts payable 80,000 Bonds payable (long-term) 50,000 $100,000 80.000 Long-Term Assets Fixed Assets Less: Accumulated Depreciation Net fixed assets Total assets Stockholders' Equity $150,000 70,000 100,000 5500,000 Total liabilities and equity$500,000 $500,000 Common stock (150,000) Paid-in capital 350,000 Retained eanings Sales (on credit) Cost of goods sold Gross proft Selling and Administrative expenset Less: Depreciation expense Operating Profit Interest expense Earnings before taxes Tax expense Net Income $1.250,000 750,000 500,000 257,000 50,000 93,000 8,000 185,000 92,500 S92,500 Use net fixed assets in computing fixed asset turnover t Includes $7,000 in lease payments. SMITH CORPORATION Current Assets Liabilities 35,000 Accounts payable $75,000 210,000 Marketable securities Accounts receivable Inventory 7,500 Bonds payable (longterm) 70,000 75,000 Long-Term Assets Fixed Assets Less: Accumulated Depreciation Net fixed assets Total assets Stockholders' Equity $500,000 Common stock (250,000) Paid-in capital 250,000 Retained eanings S437 500 Total liabilities and equity $437500 $75,000 30,000 47,500 1 Sales (on credit) Cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling and Administrative expenset $1,000,000 600,000 400,000 224,000 50,000 26,000 Less: Depreciation expense Operating Profit Interest expense Eanings before taxes Tax expense Net Income 105,000 52,500 $52,500 Use net fixed assets in computing foxed asset turnover t Includes $7,000 in lease payments