
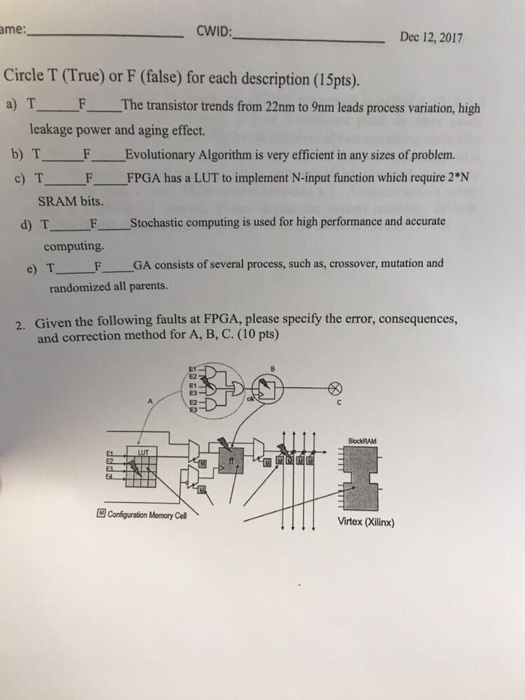
Solve attached
What is the importance of thermodynamics? (2)
Explain the concept of First law of Thermodynamics, with the aid of a diagram and equations involved. (10)
How is thermodynamics used in everyday life? (4)
[16]
Question 2
2.1 Conservation of energy is the ability of a system to store heat, q.
Derive the energy equation from the first law of thermodynamics. (10)
2.2 Explain the 2nd law of Thermodynamics with the aid of a diagram. (4)
2.3 The second law is defined in terms of the entropy of a system. Use the Carnot cycle do describe such occurances. (10)
[24]
Question 1
What is the importance of thermodynamics? (2)
Explain the concept of First law of Thermodynamics, with the aid of a diagram and equations involved. (10)
How is thermodynamics used in everyday life? (4)
[16]
Question 2
2.1 Conservation of energy is the ability of a system to store heat, q.
Derive the energy equation from the first law of thermodynamics. (10)
2.2 Explain the 2nd law of Thermodynamics with the aid of a diagram. (4)
2.3 The second law is defined in terms of the entropy of a system. Use the Carnot cycle do describe such occurances. (10)
[24]
Question 1
What is the importance of thermodynamics? (2)
Explain the concept of First law of Thermodynamics, with the aid of a diagram and equations involved. (10)
How is thermodynamics used in everyday life? (4)
[16]
Question 2
2.1 Conservation of energy is the ability of a system to store heat, q.
Derive the energy equation from the first law of thermodynamics. (10)
2.2 Explain the 2nd law of Thermodynamics with the aid of a diagram. (4)
2.3 The second law is defined in terms of the entropy of a system. Use the Carnot cycle do describe such occurances. (10)
[24]
Question 1
What is the importance of thermodynamics? (2)
Explain the concept of First law of Thermodynamics, with the aid of a diagram and equations involved. (10)
How is thermodynamics used in everyday life? (4)
[16]
Question 2
2.1 Conservation of energy is the ability of a system to store heat, q.
Derive the energy equation from the first law of thermodynamics. (10)
2.2 Explain the 2nd law of Thermodynamics with the aid of a diagram. (4)
2.3 The second law is defined in terms of the entropy of a system. Use the Carnot cycle do describe such occurances. (10)
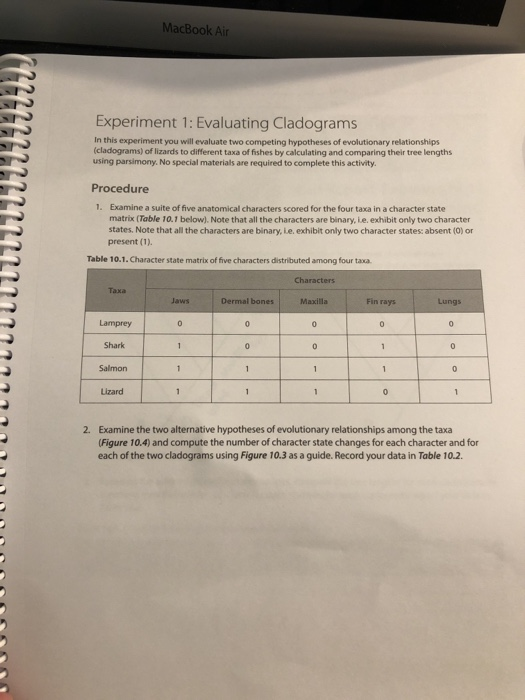
If every nucleotide in two homologous DNA sequences evolves at the same rate of substitution (7L), under the J -C model, the evolutionary distance between the two sequences is given by, 3 4- d = 111'l (1 D), where D is the difference between the two sequences. However, if different nucleotides in the two DNA sequences evolve at different rates, and the rates 7L follow a y-distribution, then the evolutionaiy distance between the two sequences is given by, 1 3a 4 'E '1 =T[(1_D) '11' where a is a parameter of the v-distribution. Compute the cl values for D=0.5 when, 1) the sequences evolve at the same rate, and 2) the sequences evolve at varying rates with a ydistribution and a:l, Explain the reason for the difference III. One evolutionary theory of jealousy argues that men become more upset by a partner's sexual infidelity than are women, whereas women are more upset by a partner's emotional infidelity than are men. Men and women are asked to imagine that their partner becomes romantically interested in another person. They are then asked to indicate whether imagining their partner having sex with the person is more upsetting or whether imagining their partner falling in love with the person is more upsetting. The data are as follows (1 = imagining partner having sex with other is more upsetting, 2 = imagining partner falling in love with other is more upsetting): Women N NN NN NNN NN - NNN 2 NN Men - N 2 2 NN - - N - NN N - - - Determine if there if is a relationship between gender and the type of infidelity chosen as most upsetting (use a = .05): A. What are the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis? B. What is the critical value (make sure to indicate what degrees of freedom were used to determine this)? C. Use SPSS to calculate your test statistic. D. Use SPSS to compute Cramer's v. E. What do you conclude based on your hypothesis test? Are the data consistent with this evolutionary theory of jealousy? Why or why not?ame: CWID: Dec 12, 2017 Circle T (True) or F (false) for each description (15pts). a) T F_The transistor trends from 22nm to 9nm leads process variation, high leakage power and aging effect. b) T Evolutionary Algorithm is very efficient in any sizes of problem. C) T F FPGA has a LUT to implement N-input function which require 2*N SRAM bits. d) T F Stochastic computing is used for high performance and accurate computing. e) T_ F GA consists of several process, such as, crossover, mutation and randomized all parents. 2. Given the following faults at FPGA, please specify the error, consequences, and correction method for A, B, C. (10 pts) LUT Li] Configuration Memory Cell Virtex (Xilinx)MacBook Air Experiment 1: Evaluating Cladograms In this experiment you will evaluate two competing hypotheses of evolutionary relationships (cladograms) of lizards to different taxa of fishes by calculating and comparing their tree lengths using parsimony. No special materials are required to complete this activity. Procedure 1. Examine a suite of five anatomical characters scored for the four taxa in a character state matrix (Table 10.1 below). Note that all the characters are binary, Le. exhibit only two character states, Note that all the characters are binary, Le, exhibit only two character states: absent (0) or present (1). Table 10.1. Character state matrix of five characters distributed among four taxa Characters Dermal bones Maxilla Fin ray's Lungs Lamprey Shark 1 Salmon 1 Lizard 2. Examine the two alternative hypotheses of evolutionary relationships among the taxa (Figure 10.4) and compute the number of character state changes for each character and for each of the two cladograms using Figure 10.3 as a guide. Record your data in Table 10.2













