solve it with detailed steps of how you solve it
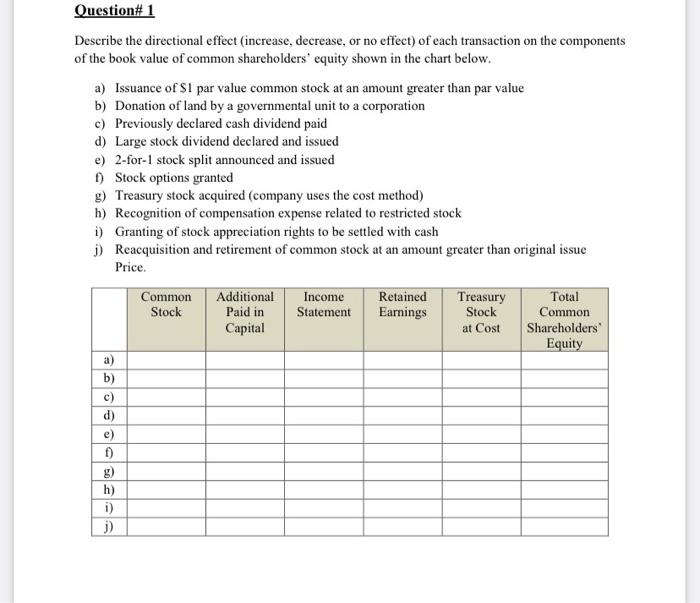
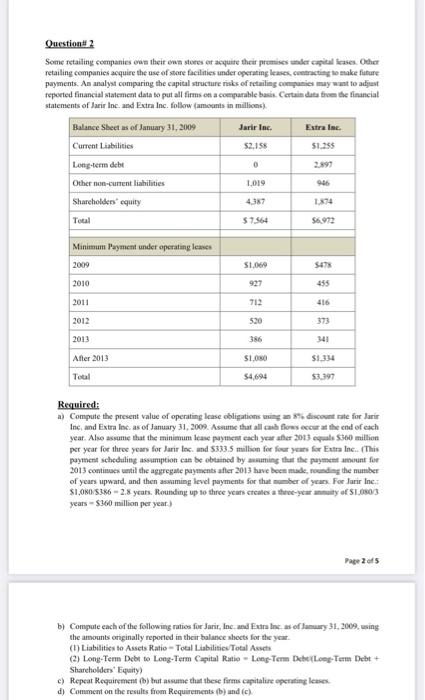
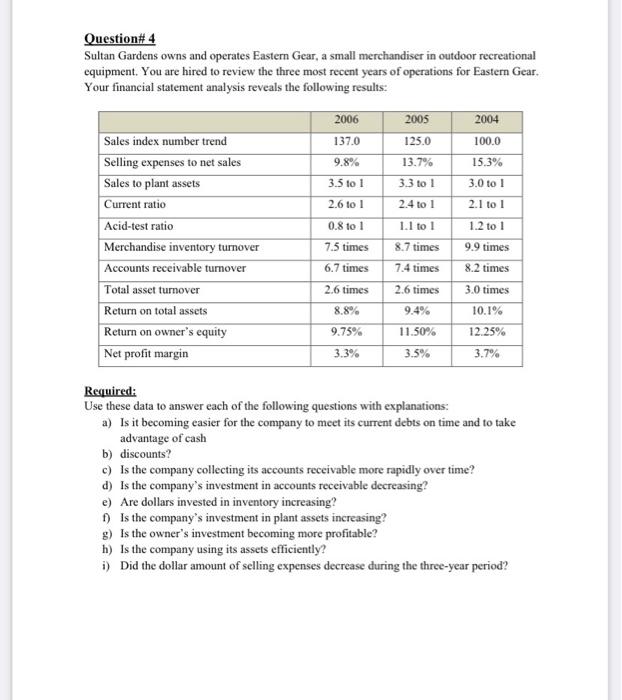
Question# 1 Describe the directional effect (increase, decrease, or no effect) of each transaction on the components of the book value of common shareholders' equity shown in the chart below. a) Issuance of S1 par value common stock at an amount greater than par value b) Donation of land by a governmental unit to a corporation c) Previously declared cash dividend paid d) Large stock dividend declared and issued e) 2-for-1 stock split announced and issued f) Stock options granted g) Treasury stock acquired (company uses the cost method) h) Recognition of compensation expense related to restricted stock i) Granting of stock appreciation rights to be settled with cash 1) Reacquisition and retirement of common stock at an amount greater than original issue Price. Common Stock Additional Paid in Capital Income Statement Retained Earnings Treasury Stock at Cost Total Common Shareholders Equity a) b) c) d) e) 1) g) h) i) j) Question 2 Some retailing companies own their own stores or acquire their premises under capital leases. Other retailing companies acquire the use of store facilities under operating lases, contracting to make future payments. An analyst comparing the capital structure risks of retailing companies may want to adjust reported financial statement data to put all firms on a comparable basis. Certain data from the financial statements of Jarir Inc. and Extra Inc. follow amounts in millions Jarir Inc Extra Inc. 52,158 51.255 0 Balance Sheets of January 31, 2009 Current Liabilities Long-term det Other non-current liabilities Shareholders equity Total 1,019 946 431 1874 $ 7.564 $6.972 Minimum Payment under operating less 2009 2010 S1.060 S473 927 455 2011 712 2012 520 2013 386 341 $1.00 $1.334 After 2013 Total $4,694 53.397 Required: a) Compute the present value of operating lease obligations using a discount rate for Jarir Inc and Extra Inc, as of January 31, 2009. Assume that all cash flows occur at the end of each year. Also assume that the minimum case payment each year after 2013 equals 5360 million per year for three years for Janir Inc. and $333.5 million for four years for Extra Inc. (This payment scheduling assumption can be obtained by assuming tut the payment amount for 2013 continues until the aggregate payments after 2013 have been made runding the number of years upward, and then assuming level payments for that ber of years. For Jarir Ine. $1,050/5386 -2.8 years. Rounding up to three years creates a three-year muity of $1,0803 years - $360 million per year.) Page 2 of 5 b) Compute each of the following rates for Jurir, Inc. and Fries of January 31, 2009, using the amounts orginally reported in their balance sheets for the year (1) Liabilities to Assets Ratio - Total Liabilities. Total Assets 2) Long-Term Debt to Long-Term Capital Ratio - Long-Term Dabei Long-Term Debt + Shareholders' Equity) c) Repeat Requirement (b) but assume that these firms capitalire operating lases d) Comment on the results from Requirements b) and (c) Question# 3 Xiomi Co. is a retailer dealing in a single product. Beginning inventory at January 1 of this year is zero, operating expenses for this same year are $5,000, and there are 2,000 common shares Outstanding. The following purchases are made this year: Units 100 300 January March June October December Total Per Unit S 10 11 12 14 15 600 300 500 1800 Cost $1,000 3,300 7,200 4,200 7.500 23,200 Ending inventory at December 31 is 800 units. End-of-year assets, excluding inventories, amount to $75,000, of which $50,000 of the $75,000 are current. Current liabilities amount to $25,000, and long-term liabilities equal $10,000, Required: a) Determine net income for this year under each of the following inventory methods. Assume a sales price of $25 per unit and ignore income taxes. i) FIFO ii) LIFO iii) Average cost b) Compute the following ratios under each of the inventory methods of FIFO, LIFO, and average cost. i) Current ratio ii) Debt-to-equity ratio iii) Inventory turnover iv) Return on total assets v) Gross margin as a percent of sales vi) Net profit as a percent of sales c) Discuss the effects of inventory accounting methods for financial statement analysis given the results from parts (a) and (b). Question#4 Sultan Gardens owns and operates Eastern Gear, a small merchandiser in outdoor recreational equipment. You are hired to review the three most recent years of operations for Eastern Gear. Your financial statement analysis reveals the following results: 2006 137.0 2005 125.0 13.7% 3.3 to 1 9.8% 3.5 to 1 2.4 to 1 1.1 to 1 Sales index number trend Selling expenses to net sales Sales to plant assets Current ratio Acid-test ratio Merchandise inventory turnover Accounts receivable turnover Total asset turnover Return on total assets Return on owner's equity Net profit margin 2.6 to 1 0.8 to 1 7.5 times 6.7 times 2004 100.0 15.3% 3.0 to 1 2.1 to 1 1.2 to 1 9.9 times 8.2 times 3.0 times 10.1% 12.25% 3.7% 2.6 times 8.7 times 7.4 times 2.6 times 9.4% 11.50% 3.5% 8.8% 9.75% 3.3% Required: Use these data to answer each of the following questions with explanations: a) Is it becoming easier for the company to meet its current debts on time and to take advantage of cash b) discounts? c) Is the company collecting its accounts receivable more rapidly over time? d) Is the company's investment in accounts receivable decreasing? e) Are dollars invested in inventory increasing? ) Is the company's investment in plant assets increasing? 9) Is the owner's investment becoming more profitable? h) Is the company using its assets efficiently? i) Did the dollar amount of selling expenses decrease during the three-year period? Question# 5 You are planning to analyse Zamil Company's December 31, Year 6, balance sheet. The following information is available: 1) Beginning and ending balances are identical for both accounts receivable and inventory. 2) Net income is $1,300. 3) Times interest earned is 5 (income taxes are zero). Company has 5% bonds outstanding and issued at par. 4) Net profit margin is 10%. Gross profit margin is 30%. Inventory turnover is 5. 5) Days' sales in receivables is 72 days. 6) Sales to end-of-year working capital is 4. Current ratio is 1.5. 7) Acid-test ratio is 1.0 (excludes prepaid expenses). 8) Plant and equipment (net) is $6,000. It is one-third depreciated. 9) Dividends paid on 8% nonparticipating preferred stock are $40. There is no change in common shares outstanding during Year 6. Preferred shares were issued two years ago at par. 10) Earnings per common share are $3.75. 11) Common stock has a S5 par value and was issued at par. 12) Retained carnings at January 1, Year 6, are $350. Required: a) Given the information available, prepare this company's income statement and balance sheet as of December 31, Year 6 (include the following account classifications: cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid expenses, plant and equipment (net), current liabilities, bonds payable, and stockholders' equity). b) Determine the amount of dividends paid on common stock in Year 6. Question# 1 Describe the directional effect (increase, decrease, or no effect) of each transaction on the components of the book value of common shareholders' equity shown in the chart below. a) Issuance of S1 par value common stock at an amount greater than par value b) Donation of land by a governmental unit to a corporation c) Previously declared cash dividend paid d) Large stock dividend declared and issued e) 2-for-1 stock split announced and issued f) Stock options granted g) Treasury stock acquired (company uses the cost method) h) Recognition of compensation expense related to restricted stock i) Granting of stock appreciation rights to be settled with cash 1) Reacquisition and retirement of common stock at an amount greater than original issue Price. Common Stock Additional Paid in Capital Income Statement Retained Earnings Treasury Stock at Cost Total Common Shareholders Equity a) b) c) d) e) 1) g) h) i) j) Question 2 Some retailing companies own their own stores or acquire their premises under capital leases. Other retailing companies acquire the use of store facilities under operating lases, contracting to make future payments. An analyst comparing the capital structure risks of retailing companies may want to adjust reported financial statement data to put all firms on a comparable basis. Certain data from the financial statements of Jarir Inc. and Extra Inc. follow amounts in millions Jarir Inc Extra Inc. 52,158 51.255 0 Balance Sheets of January 31, 2009 Current Liabilities Long-term det Other non-current liabilities Shareholders equity Total 1,019 946 431 1874 $ 7.564 $6.972 Minimum Payment under operating less 2009 2010 S1.060 S473 927 455 2011 712 2012 520 2013 386 341 $1.00 $1.334 After 2013 Total $4,694 53.397 Required: a) Compute the present value of operating lease obligations using a discount rate for Jarir Inc and Extra Inc, as of January 31, 2009. Assume that all cash flows occur at the end of each year. Also assume that the minimum case payment each year after 2013 equals 5360 million per year for three years for Janir Inc. and $333.5 million for four years for Extra Inc. (This payment scheduling assumption can be obtained by assuming tut the payment amount for 2013 continues until the aggregate payments after 2013 have been made runding the number of years upward, and then assuming level payments for that ber of years. For Jarir Ine. $1,050/5386 -2.8 years. Rounding up to three years creates a three-year muity of $1,0803 years - $360 million per year.) Page 2 of 5 b) Compute each of the following rates for Jurir, Inc. and Fries of January 31, 2009, using the amounts orginally reported in their balance sheets for the year (1) Liabilities to Assets Ratio - Total Liabilities. Total Assets 2) Long-Term Debt to Long-Term Capital Ratio - Long-Term Dabei Long-Term Debt + Shareholders' Equity) c) Repeat Requirement (b) but assume that these firms capitalire operating lases d) Comment on the results from Requirements b) and (c) Question# 3 Xiomi Co. is a retailer dealing in a single product. Beginning inventory at January 1 of this year is zero, operating expenses for this same year are $5,000, and there are 2,000 common shares Outstanding. The following purchases are made this year: Units 100 300 January March June October December Total Per Unit S 10 11 12 14 15 600 300 500 1800 Cost $1,000 3,300 7,200 4,200 7.500 23,200 Ending inventory at December 31 is 800 units. End-of-year assets, excluding inventories, amount to $75,000, of which $50,000 of the $75,000 are current. Current liabilities amount to $25,000, and long-term liabilities equal $10,000, Required: a) Determine net income for this year under each of the following inventory methods. Assume a sales price of $25 per unit and ignore income taxes. i) FIFO ii) LIFO iii) Average cost b) Compute the following ratios under each of the inventory methods of FIFO, LIFO, and average cost. i) Current ratio ii) Debt-to-equity ratio iii) Inventory turnover iv) Return on total assets v) Gross margin as a percent of sales vi) Net profit as a percent of sales c) Discuss the effects of inventory accounting methods for financial statement analysis given the results from parts (a) and (b). Question#4 Sultan Gardens owns and operates Eastern Gear, a small merchandiser in outdoor recreational equipment. You are hired to review the three most recent years of operations for Eastern Gear. Your financial statement analysis reveals the following results: 2006 137.0 2005 125.0 13.7% 3.3 to 1 9.8% 3.5 to 1 2.4 to 1 1.1 to 1 Sales index number trend Selling expenses to net sales Sales to plant assets Current ratio Acid-test ratio Merchandise inventory turnover Accounts receivable turnover Total asset turnover Return on total assets Return on owner's equity Net profit margin 2.6 to 1 0.8 to 1 7.5 times 6.7 times 2004 100.0 15.3% 3.0 to 1 2.1 to 1 1.2 to 1 9.9 times 8.2 times 3.0 times 10.1% 12.25% 3.7% 2.6 times 8.7 times 7.4 times 2.6 times 9.4% 11.50% 3.5% 8.8% 9.75% 3.3% Required: Use these data to answer each of the following questions with explanations: a) Is it becoming easier for the company to meet its current debts on time and to take advantage of cash b) discounts? c) Is the company collecting its accounts receivable more rapidly over time? d) Is the company's investment in accounts receivable decreasing? e) Are dollars invested in inventory increasing? ) Is the company's investment in plant assets increasing? 9) Is the owner's investment becoming more profitable? h) Is the company using its assets efficiently? i) Did the dollar amount of selling expenses decrease during the three-year period? Question# 5 You are planning to analyse Zamil Company's December 31, Year 6, balance sheet. The following information is available: 1) Beginning and ending balances are identical for both accounts receivable and inventory. 2) Net income is $1,300. 3) Times interest earned is 5 (income taxes are zero). Company has 5% bonds outstanding and issued at par. 4) Net profit margin is 10%. Gross profit margin is 30%. Inventory turnover is 5. 5) Days' sales in receivables is 72 days. 6) Sales to end-of-year working capital is 4. Current ratio is 1.5. 7) Acid-test ratio is 1.0 (excludes prepaid expenses). 8) Plant and equipment (net) is $6,000. It is one-third depreciated. 9) Dividends paid on 8% nonparticipating preferred stock are $40. There is no change in common shares outstanding during Year 6. Preferred shares were issued two years ago at par. 10) Earnings per common share are $3.75. 11) Common stock has a S5 par value and was issued at par. 12) Retained carnings at January 1, Year 6, are $350. Required: a) Given the information available, prepare this company's income statement and balance sheet as of December 31, Year 6 (include the following account classifications: cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid expenses, plant and equipment (net), current liabilities, bonds payable, and stockholders' equity). b) Determine the amount of dividends paid on common stock in Year 6