Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
solve problem 6-2A . Used the periodic inventory table in problem 6-1A to solve problem 6-2A. file://home/chronos/u-85e4d 13e1f5f79c1 7331 679e7acti 44938753b65/Downloads/Fundamentar%2o.. 01,0 DO+m. Units Acquired
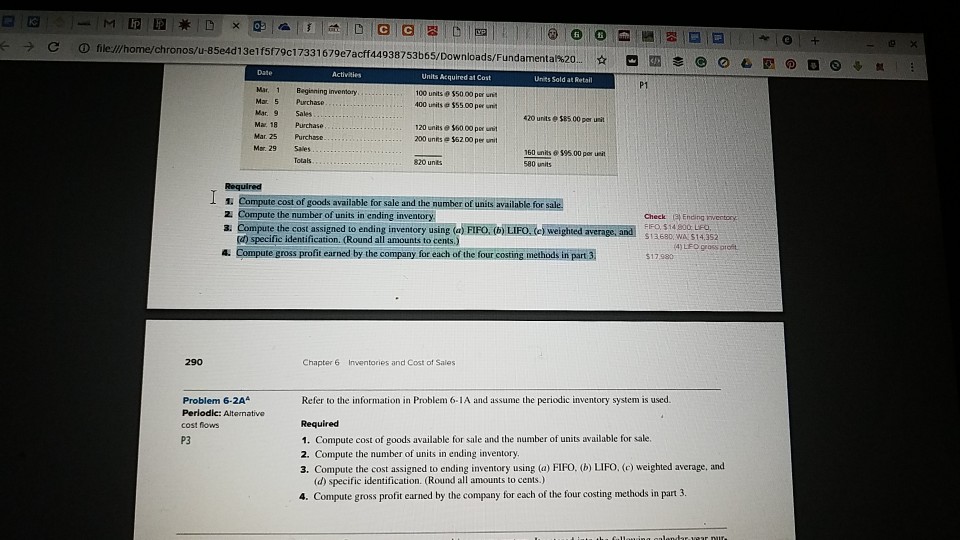
solve problem 6-2A . Used the periodic inventory table in problem 6-1A to solve problem 6-2A.
file://home/chronos/u-85e4d 13e1f5f79c1 7331 679e7acti 44938753b65/Downloads/Fundamentar%2o.. 01,0 DO+m. Units Acquired at Cost 100 units $50.00 per 400 units & $55.00 pee Units Sold at Retail P1 Mar. 1 Beginning invemary Mar. 5 Purchase Mar 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase. Mar 29 Sales 420 units $85 00 per unit 120 units $60.00 pse uni 200 unts e S6200per unit 160 units 6595.00 por ueit 580 units 820 units Required 1 Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. 2 Compute the number of units in ending inventory Check 181 Ending rventory a: Co specific identification (Round all mventory using POLweg te nerag an ssa suecosus iE b a) specific identification. (Round all amounts to cents.) a. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3, 4) LEO gross ptoft $17980 290 Chapter 6 Inventories and Cost of Sales Refer to the information in Problem 6-1A and assume the periodic inventory system is used. Problem 6-2AA Perlodic: Alternative cost fows P3 Required 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO. (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification. (Round all amounts to cents.) 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3 file://home/chronos/u-85e4d 13e1f5f79c1 7331 679e7acti 44938753b65/Downloads/Fundamentar%2o.. 01,0 DO+m. Units Acquired at Cost 100 units $50.00 per 400 units & $55.00 pee Units Sold at Retail P1 Mar. 1 Beginning invemary Mar. 5 Purchase Mar 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase. Mar 29 Sales 420 units $85 00 per unit 120 units $60.00 pse uni 200 unts e S6200per unit 160 units 6595.00 por ueit 580 units 820 units Required 1 Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. 2 Compute the number of units in ending inventory Check 181 Ending rventory a: Co specific identification (Round all mventory using POLweg te nerag an ssa suecosus iE b a) specific identification. (Round all amounts to cents.) a. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3, 4) LEO gross ptoft $17980 290 Chapter 6 Inventories and Cost of Sales Refer to the information in Problem 6-1A and assume the periodic inventory system is used. Problem 6-2AA Perlodic: Alternative cost fows P3 Required 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO. (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification. (Round all amounts to cents.) 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


