Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
solve Q12 in 40 mins i will give thumb up The model of the federal funds market that we have learned is sometimes called the
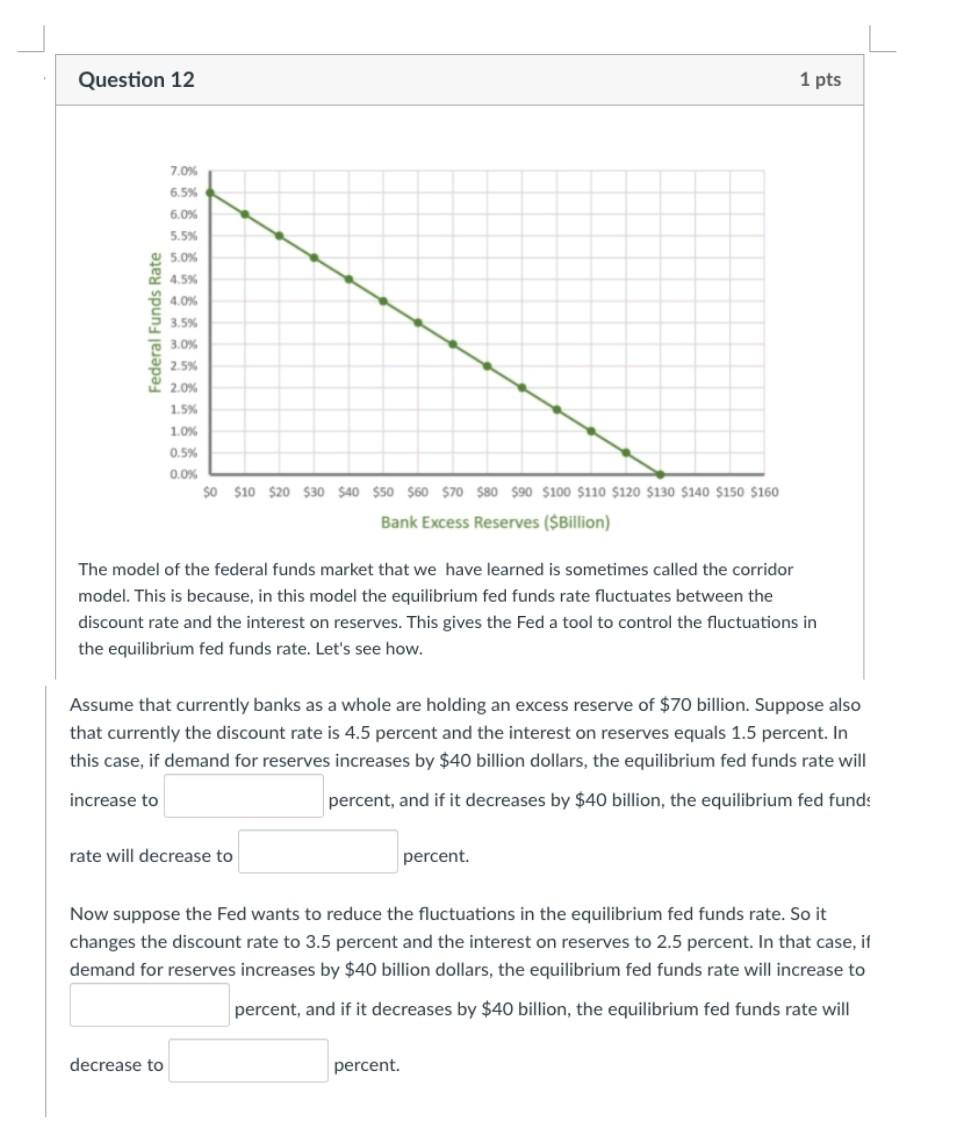
solve Q12 in 40 mins i will give thumb up
The model of the federal funds market that we have learned is sometimes called the corridor model. This is because, in this model the equilibrium fed funds rate fluctuates between the discount rate and the interest on reserves. This gives the Fed a tool to control the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. Let's see how. Assume that currently banks as a whole are holding an excess reserve of $70 billion. Suppose also that currently the discount rate is 4.5 percent and the interest on reserves equals 1.5 percent. In this case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to percent, and if it decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to percent. Now suppose the Fed wants to reduce the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. So it changes the discount rate to 3.5 percent and the interest on reserves to 2.5 percent. In that case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to percent, and if it decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to percent. The model of the federal funds market that we have learned is sometimes called the corridor model. This is because, in this model the equilibrium fed funds rate fluctuates between the discount rate and the interest on reserves. This gives the Fed a tool to control the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. Let's see how. Assume that currently banks as a whole are holding an excess reserve of $70 billion. Suppose also that currently the discount rate is 4.5 percent and the interest on reserves equals 1.5 percent. In this case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to percent, and if it decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to percent. Now suppose the Fed wants to reduce the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. So it changes the discount rate to 3.5 percent and the interest on reserves to 2.5 percent. In that case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to percent, and if it decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to percentStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


