 solve Q2 with detailed steps
solve Q2 with detailed steps

 those added materials are good example to apply Question 1,2,3
those added materials are good example to apply Question 1,2,3
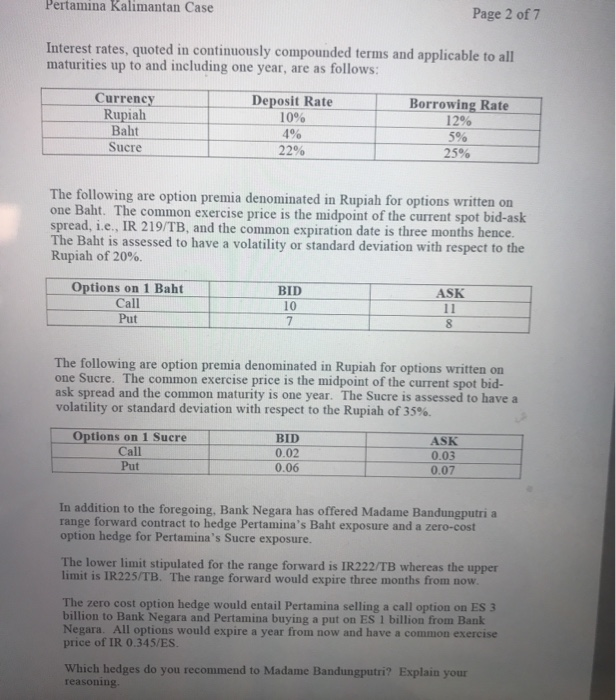


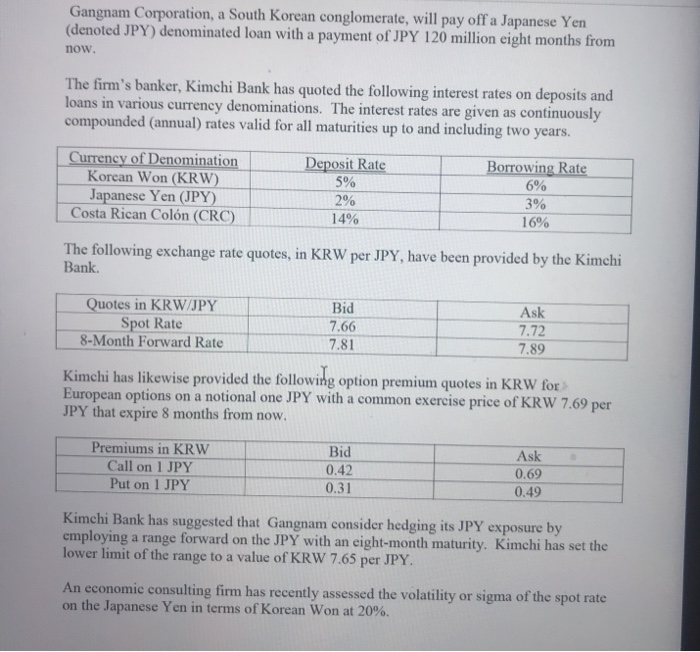
Gangnam Corporation, a South Korean conglomerate, will pay off a Japanese Yen (denoted JPY) denominated loan with a payment of JPY 120 million eight months from now. The firm's banker, Kimchi Bank has quoted the following interest rates on deposits and loans in various currency denominations. The interest rates are given as continuously compounded (annual) rates valid for all maturities up to and including two years. Currency of Denomination Korean Won (KRW) Japanese Yen (JPY) Costa Rican Coln (CRC) Deposit Rate 5% 2% 14% Borrowing Rate 6% 3% 16% The following exchange rate quotes, in KRW per JPY, have been provided by the Kimchi Bank. Quotes in KRW/JPY Spot Rate 8-Month Forward Rate Bid 7.66 7.81 Ask 7.72 7.89 Kimchi has likewise provided the following option premium quotes in KRW for European options on a notional one JPY with a common exercise price of KRW 7.69 per JPY that expire 8 months from now. Premiums in KRW Call on 1 JPY Put on 1 JPY Bid 0.42 0.31 Ask 0.69 0.49 Kimchi Bank has suggested that Gangnam consider hedging its JPY exposure by employing a range forward on the JPY with an eight-month maturity. Kimchi has set the lower limit of the range to a value of KRW 7.65 per JPY. An economic consulting firm has recently assessed the volatility or sigma of the spot rate on the Japanese Yen in terms of Korean Won at 20%. 1. (20%) Detail the transactions required to synthesize the forward contract hedge appropriate for hedging Gangnam's JPY exposure. Consider both ways of forward contract synthetization discussed in class. Cite financial amounts, specifying when the transactions will be undertaken. 2. (15%) Calculate the outright and synthesized forward rates and decide on the best forward hedge for Gangnam's JPY exposure. 3. (15%) Compare the best forward hedge with the option contract, appropriate for hedging the JPY exposure, by calculating the breakeven exchange rate. Interpret the significance of the foregoing number in terms of the decision to hedge via a forward contract versus an option contract. 4. (20%) Employing the spot rate version of the Black-Scholes model for valuing foreign exchange options as benchmark, assess the option premium quotations provided by Kimchi Bank. Are these quotations expensive, cheap, or just right? Specify the numerical values of the model parameters you employ, e.g., the value of the dividend yield," etc. Hint: Recall that, as the Black-Scholes model assumes the absence of bid-ask spreads and gaps between borrowing and deposit rates, to apply the model you must work with the averages of these variables., i.e., the average of the bid and the ask as well as the average of the borrowing and the deposit rates. 5. (15%) Employing the forward rate Version of the Black-Scholes model for valuing foreign exchange options, decide on the correct value of the upper limit of the range forward. Goal Seek is the recommended solution procedure. Confine your answer to only two significant digits. Hint: Recall that a range forward contract is a type of forward contract, which requires no up-front outlay, and that a range forward may be viewed as an option collar. 6. (15%) Gangnam's joint venture partner in Costa Rica, Electrodomsticos Costarisenses SA, is scheduled to pay back a loan to Gangnam in the amount of CRC 0.5 billion two years from now. CRC denotes the Costa Rican Coln. Kimchi has quoted the following exchange rates, given in terms of CRC per KRW Quotes in CRC/KRW Spot Rate 2-Year Forward Rate Bid 0.59 0.74 Ask 0.61 0.77 Detail the required transactions to construct a money market hedge, citing financial amounts. Based on your comparison of the outright forward rate with the synthesized forward rate, which of these forward hedges would you recommend? First Case: Pertamina Kalimantan PT Madame Bandungputri, CFO of the eponymous Indonesian petroleum firm, Pertamina Kalimantan PT, faces the problem of dealing with two foreign exchange exposures The first exposure relates to the payment, due three months from now, of half a million Thai Baht, henceforth denoted as "TB." This liability arises from the importation from a Bangkok-based firm of rice, which Pertamina has recently received and dispensed to its employees in the form of a year-end remuneration bonus. Parenthetical note: This is standard practice in many Southeast Asian countries. The second exposure derives from Pertamina's joint venture with Hidrocarburos Ecuatorianos, SA, to conduct oil and gas exploration and development activities in the altiplano region of Ecuador. Pertamina's 50% interest in the joint venture entitles Pertamina to receive 50% of annual joint venture profits. This annual payment is remitted to Pertamina at the end of the corresponding (i.e., same) year, the remittance being denominated in Ecuadorian Sucres. The latter currency is henceforth denoted as "ES." During the financial year that has just started, the joint venture is projected to generate net profits of ES 2 billion. Bank Negara Indonesia has quoted Pertamina the following data. The following are spot and forward rates denominated in Indonesian Rupiah (henceforth symbolized as "IR") per Baht: In IR per TB Spot 3-month Forward BID 218 221 ASK 220 223 The following are spot and forward rates denominated in Rupiah per Sucre: In IR per ES Spot 1-year Forward BID 0.34 0.30 ASK 0.35 0.31 Solution of Pertamina Kalimantan PT First exposure: TB0.5 million payable. Forward hedges: 1. Buy outright forward: IR223/TB 2. Money market hedge, synthesized forward rate: IR224.44/TB 224.44 = 220 (12%-4%)(-25) Borrow IR, buy TB in spot market, deposit proceeds in TB denominated money market securities. MMH Transactions Now: Borrow IR 108.9M - TB0.5M(220)/e^(4%x.25) Buy TB spot; obtain TB0.495M - IR 108.9/220 Deposit TBS After 3 months: Close out TB account. Obtain TB0.5M = TB0.495Me (4%x.25); use this to meet liability Payback IR loan; pay IR112.22M-IR108.9Me (12%x.25) - TB0.5Mx224.44 3. Option collar that synthesizes a buy forward: IR223.12/TB. 223.12 = 219 + e(1296)(25) (4) Buy call, sell put, financing the IR4/TB initial outlay at 12%. OC Transactions Now: I Buy call, pay 11(TB0.5M) Sell put, receive 7(TB0.5M) Borrow difference, i.e., IR2M = 4(TB0.5M) After 3 months: Receive TB0.5M, use this to satisfy TB payable: pay IR 109.5M - 219(TBO.5M) Pay off IR loan, pay IR2.06M = IR2Me (12%x.25) Total Payment = IR111.56M - TB0.5Mx223.12 The best forward, observing the Buy Low rule, is the outright forward Compare buy call with buy outright forward. Pertamina Kalimantan Case Page 4 of 7 S (IR/TB) Breakeven point, B = IR211.665/TB B = 223-1le (129)(25) = 211.665 S 211.665, buy outright forward is superior Analysis of Range Forward, with a lower limit of IR222/TB and an upper limit of IR 225/TB. This is an option collar that involves purchasing a call with X = 225 and selling a put with X = 222 As 222 approximates the forward rate, Call(X-222) = Put (X-222). Note that Call(X=222) refers to the value of a call option with exercise set at 222. But Call(X=225)
211.665, buy outright forward is superior Analysis of Range Forward, with a lower limit of IR222/TB and an upper limit of IR 225/TB. This is an option collar that involves purchasing a call with X = 225 and selling a put with X = 222 As 222 approximates the forward rate, Call(X-222) = Put (X-222). Note that Call(X=222) refers to the value of a call option with exercise set at 222. But Call(X=225)
 solve Q2 with detailed steps
solve Q2 with detailed steps
 those added materials are good example to apply Question 1,2,3
those added materials are good example to apply Question 1,2,3








