Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
solve Q9 in 30 mins i will give thumb up Here is another realistic scenario. Consider the above graph that shows demand for excess reserves
solve Q9 in 30 mins i will give thumb up
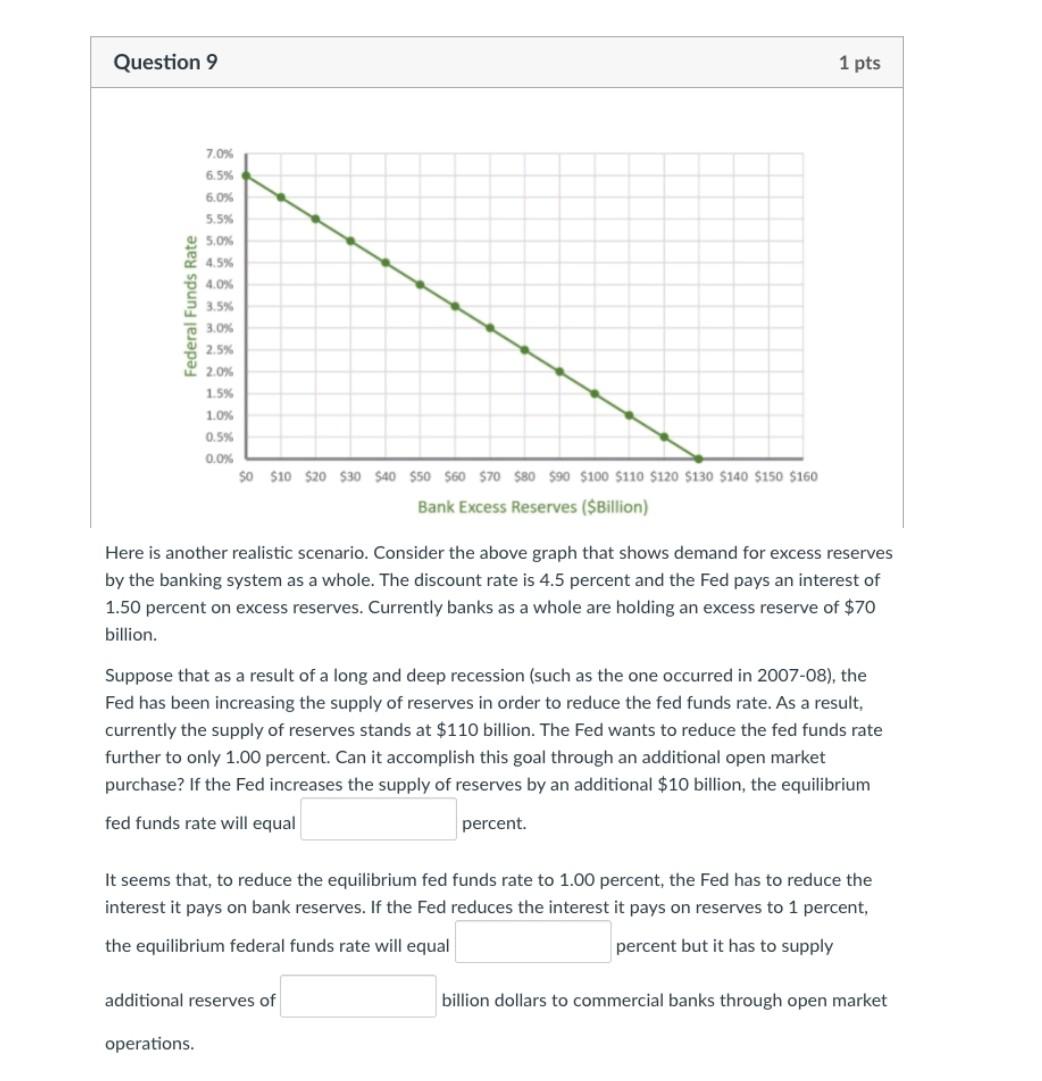
Here is another realistic scenario. Consider the above graph that shows demand for excess reserves by the banking system as a whole. The discount rate is 4.5 percent and the Fed pays an interest of 1.50 percent on excess reserves. Currently banks as a whole are holding an excess reserve of $70 billion. Suppose that as a result of a long and deep recession (such as the one occurred in 2007-08), the Fed has been increasing the supply of reserves in order to reduce the fed funds rate. As a result, currently the supply of reserves stands at $110 billion. The Fed wants to reduce the fed funds rate further to only 1.00 percent. Can it accomplish this goal through an additional open market purchase? If the Fed increases the supply of reserves by an additional $10 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will equal percent. It seems that, to reduce the equilibrium fed funds rate to 1.00 percent, the Fed has to reduce the interest it pays on bank reserves. If the Fed reduces the interest it pays on reserves to 1 percent, the equilibrium federal funds rate will equal percent but it has to supply additional reserves of billion dollars to commercial banks through open market operations. Here is another realistic scenario. Consider the above graph that shows demand for excess reserves by the banking system as a whole. The discount rate is 4.5 percent and the Fed pays an interest of 1.50 percent on excess reserves. Currently banks as a whole are holding an excess reserve of $70 billion. Suppose that as a result of a long and deep recession (such as the one occurred in 2007-08), the Fed has been increasing the supply of reserves in order to reduce the fed funds rate. As a result, currently the supply of reserves stands at $110 billion. The Fed wants to reduce the fed funds rate further to only 1.00 percent. Can it accomplish this goal through an additional open market purchase? If the Fed increases the supply of reserves by an additional $10 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will equal percent. It seems that, to reduce the equilibrium fed funds rate to 1.00 percent, the Fed has to reduce the interest it pays on bank reserves. If the Fed reduces the interest it pays on reserves to 1 percent, the equilibrium federal funds rate will equal percent but it has to supply additional reserves of billion dollars to commercial banks through open market operationsStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


