Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Solve the exercise Review Problem 1: Cost Terms Many new cost terms have been introduced in this chapter. It will take you some time to
Solve the exercise
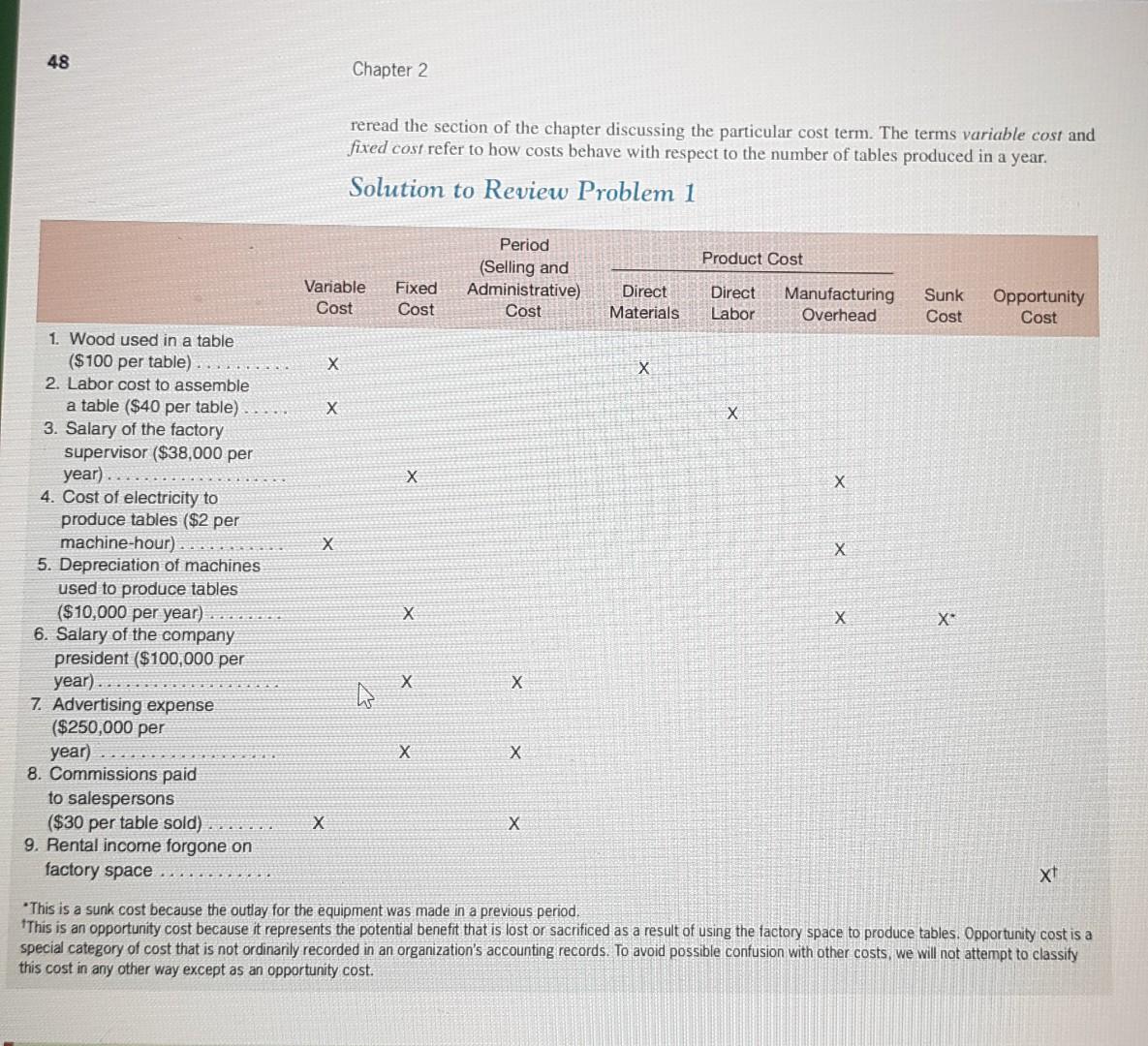
Review Problem 1: Cost Terms Many new cost terms have been introduced in this chapter. It will take you some time to learn what each term means and how to properly classify costs in an organization. Consider the following example: Porter Company manufactures furniture, including tables. Selected costs are given below: 1. The tables are made of wood that costs $100 per table. 2. The tables are assembled by workers, at a wage cost of $40 per table. 3. Workers assembling the tables are supervised by a factory supervisor who is paid $38,000 per year. 4. Electrical costs are $2 per machine-hour. Four machine-hours are required to produce a table. 5. The depreciation on the machines used to make the tables totals $10,000 per year. The machines have no resale value and do not wear out through use. 6. The salary of the president of the company is $100,000 per year. 7. The company spends $250,000 per year to advertise its products. 8. Salespersons are paid a commission of $30 for each table sold. 9. Instead of producing the tables, the company could rent its factory space for $50,000 per year. Required: Classify these costs according to the various cost terms used in the chapter. Carefully study the classification of each cost. If you don't understand why a particular cost is classified the way it is, Chapter 2 reread the section of the chapter discussing the particular cost term. The terms variable cost and fixed cost refer to how costs behave with respect to the number of tables produced in a year, Solution to Review Problem 1 48 Chapter 2 reread the section of the chapter discussing the particular cost term. The terms variable cost and fixed cost refer to how costs behave with respect to the number of tables produced in a year. Solution to Review Problem 1 Product Cost Variable Cost Period (Selling and Administrative) Cost Fixed Cost Direct Materials Direct Labor Manufacturing Overhead Sunk Cost Opportunity Cost X X 1 Wood used in a table ($100 per table) 2. Labor cost to assemble a table ($40 per table) 3. Salary of the factory supervisor ($38,000 per year) 4. Cost of electricity to produce tables ($2 per machine-hour) 5. Depreciation of machines used to produce tables ($10,000 per year) 6. Salary of the company president ($100,000 per year) 7. Advertising expense ($250,000 per year) 8. Commissions paid to salespersons ($30 per table sold) 9. Rental income forgone on factory space x X xt *This is a sunk cost because the outlay for the equipment was made in a previous period. *This is an opportunity cost because it represents the potential benefit that is lost or sacrificed as a result of using the factory space to produce tables. Opportunity cost is a special category of cost that is not ordinarily recorded in an organization's accounting records. To avoid possible confusion with other costs, we will not attempt to classify this cost in any other way except as an opportunity costStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


