Solve the following attachments
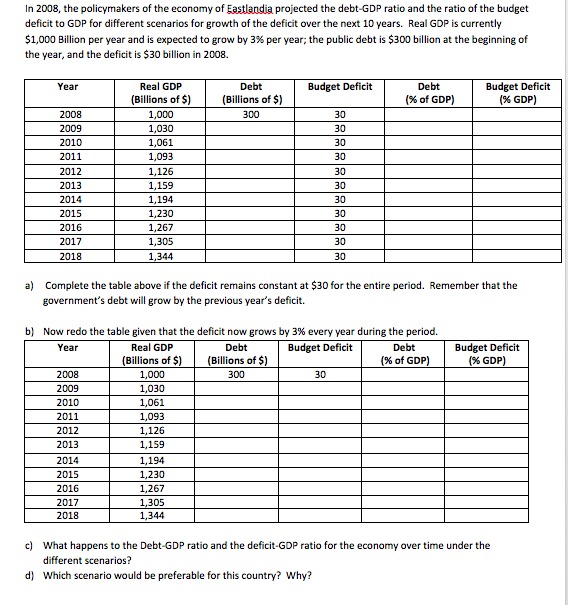
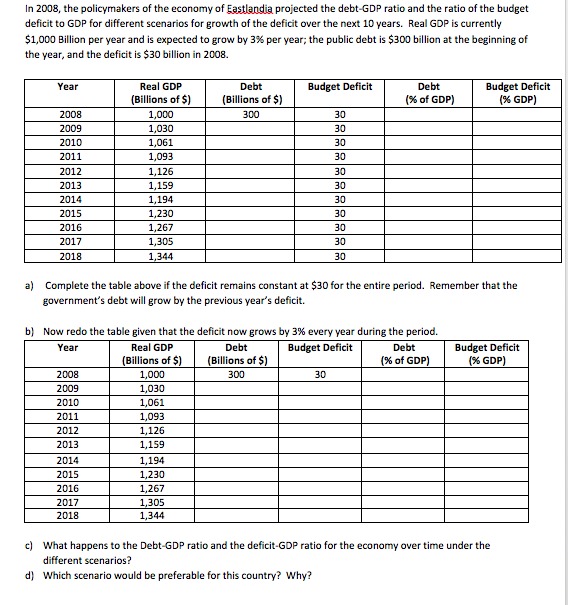
The Pristine River Case The Pristine River has two polluting firms on its banks. Acme Industrial and Creative Chemicals each dump 100 tons of glop into the river each year. The cost of reducing glop emissions per ton equals $10 for Acme and $100 for Creative. The local government wants to reduce overall pollution from 200 tons to 50 tons. a. If the government knew the cost of reduction for each firm, what reductions would it impose to reach its overall goal? What would be the cost to each firm and the total cost to the firms together? b. In a more typical situation, the government would not know the cost of pollution reduction at each firm. If the government decided to reach its overall goal by imposing uniform reductions on the firms, calculate the reduction made by each firm, the cost to each firm, and the total cost to the firms together. c. Compare the total cost of pollution reduction in parts (a) and (b). If the government does not know the cost of reduction for each firm, is there still some way for it to reduce pollution to 50 tons at the total cost you calculated in part (a)? Explain.Q1 Perfect Bayesian Equilibrium You are considering a leveraged buyout of Corporation X. The stock of X is worth either a low (1.) value, 51 = $3/share, or a high (H) value, Sy = $5/share. The owner of the company (the seller) knows what the company is worth, and decides whether to put up the company for sale at a high (H) price per share Py = $4/share or at a low (L.) price per share P, = $2.5/share for 20 thousand shares outstanding. All you know is that the probability that the company is worth 5, = $5/share is p(H) = 60% It costs management $40,000 to cook the books if it has to make the company look better that it really is. If the company does not trade hands, the seller and the buyer get nothing from the exchange. Let t denote whether the company is of high or low value. Nature chooses the company's type, that H when S, = $5 share 53 L when S, = share The seller has to choose whether to sell the company at a high or low price, P given by $4 PH = share P . $2.5 share The buyer's strategy of whether to buy or not the company is given by b = [1 if buyer buys company 10 if buyer does NOT buy company The seller's payoff depends on whether the company is of high or low value, on the seller's sale price strategy and on the buyer's buying strategy, and on whether or not the seller cooks the books. The seller's payoff is then given by ITS (t, P. b) The buyer's payoff also depends on these strategies HA (t, PA.b) (a) Under what circumstances does the seller cook the books? (b) Calculate the seller's payoff under all possible circumstances the seller might face. For each one of the seller's payoffs specify and explain all the conditions leading to that payoff. For example, when Nature makes the company high value (t = H), the seller charges a high price (Py = 4) and the buyer bays the company (b = 1), the seller's payoff is given by my(t = H, Py = 4, b = 1). (Hint you must find eight different payoffs for the seller). (c) What is the value of the company to the buyer under the high (Vg ) and the low (Vy ) state of nature?4. (30 points) Consider the following game. There are ten dollars to divide. Two players are each required to simultaneously name an integer between 0 and 10. The player who names the higher number gets to keep the money. If they name the same number, the money is equally shared between them. (a) Describe the set of players N, the set of strategies { Silien, and the payoff function QuitiEN. (b) Are there strategies that are strictly dominated? Demonstrate your reasoning. What are the resulting strategies after iterated elimination of strictly dominated strategies? (c) Find the best responses (correspondence) for each player. That is, find the strategies that maximize a player's payoff given what the other player does. (d) Find the Nash equilibria of the game. (e) Suppose now the game is changed. Whenever there is a tie, each player receives nothing. Answer the same questions in parts (b) and (c). Find the pure-strategy Nash equilibria of the game.In 2008, the policymakers of the economy of Eastlandia projected the debt-GDP ratio and the ratio of the budget deficit to GDP for different scenarios for growth of the deficit over the next 10 years. Real GDP is currently $1,000 Billion per year and is expected to grow by 3% per year; the public debt is $300 billion at the beginning of the year, and the deficit is $30 billion in 2008 Year Real GDP Debt Budget Deficit Debt Budget Deficit Billions of $) Billions of $) % of GDP) (X GDP) 2008 1,000 300 30 200 1,030 30 2010 1,061 30 2011 1,093 DE 2012 1,126 30 2013 1,159 30 2014 1,194 30 2015 1,230 30 2016 1,267 30 2017 1,305 30 2018 1,344 30 ) Complete the table above if the deficit remains constant at $30 for the entire period. Remember that the government's debt will grow by the previous year's deficit. b) Now redo the table given that the deficit now grows by 3% every year during the period. Year Real GDP Deb Budget Deficit Debt Budget Deficit Billions of $) (Billions of $) (% of GDP) %% GDP) 2008 1,000 300 30 1009 1,030 2010 1,061 2011 1,093 2012 1,120 201 1,159 2014 1,194 2015 1,230 2016 1,267 2017 1,30 2018 1,344 c) What happens to the Debt-GDP ratio and the deficit-GDP ratio for the economy over time under the different scenarios? d) Which scenario would be preferable for this country? Why