Question
Sora Industries has 61million outstanding shares, $ 125 million in debt, $ 41million in cash, and the following projected free cash flow for the next
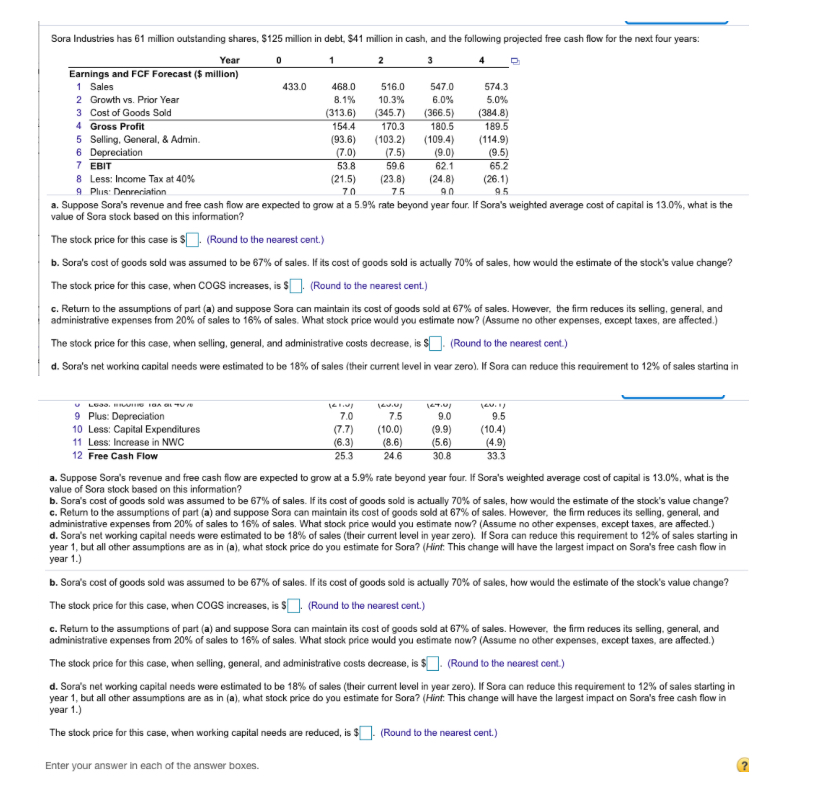
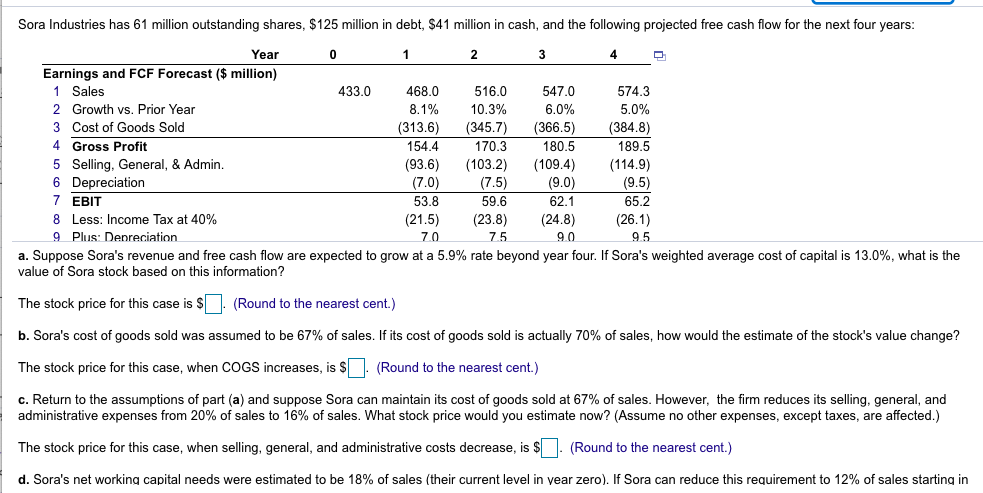
Sora Industries has 61million outstanding shares, $ 125 million in debt, $ 41million in cash, and the following projected free cash flow for the next four years:
a.Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9 %rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0 % what is the value of Sora stock based on this information?
b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change?
c.Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.)
d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in
(a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora?
(Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.)
a.Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a
5.9 %rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0 %,
what is the value of Sora stock based on this information?
The stock price for this case is _____.
(Round to the nearest cent.)
b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change?
The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is
$________.
(Round to the nearest cent.)
c.Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.)
The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is
$___________.
(Round to the nearest cent.)
d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora?
(Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.)
The stock price for this case, when working capital needs are reduced, is
$_________.
(Round to the nearest cent.)
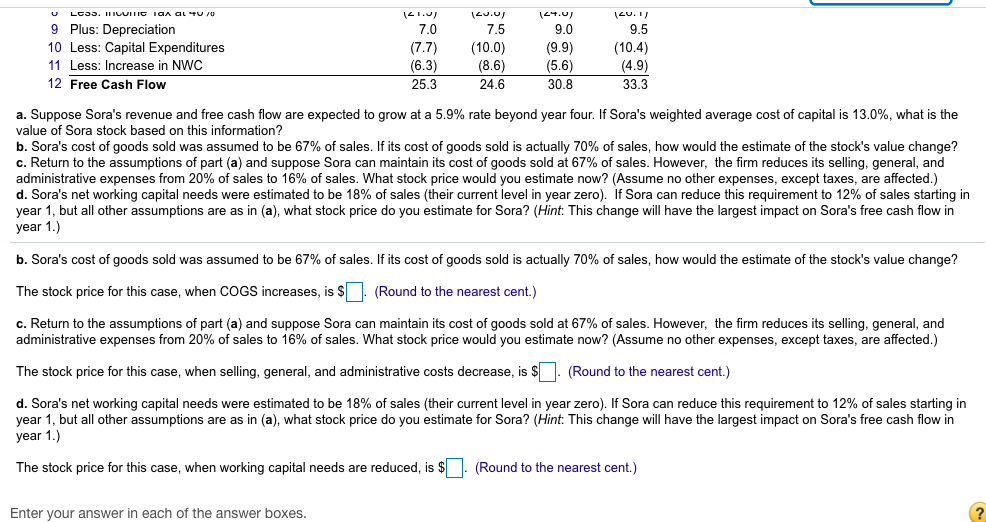
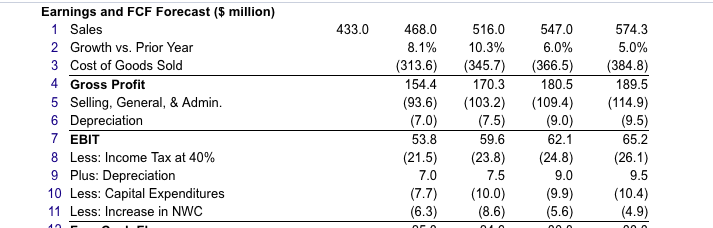
Sora Industries has 61 million outstanding shares, $125 million in debt, S41 million in cash, and the following projected free cash flow for the next four years: Year 0 1 2 3 4 Earnings and FCF Forecast ($ million) 1 Sales 433.0 468.0 516.0 547.0 574.3 2 Growth vs. Prior Year 8.1% 10.3% 6.0% 5.0% 3 Cost of Goods Sold (313.6) (345.7) (366.5) (384.8) 4 Gross Profit 154.4 170.3 180.5 189.5 5 Selling, General, & Admin (93.6) (103.2) (109.4) (114.9) 6 Depreciation (7.0) (7.5) (9.0) (9.5) 7 EBIT 53.8 59.6 62.1 65.2 8 Less: Income Tax at 40% (21.5) (23.8) (24.8) (26.1) 9 Plus: Depreciation 70 75 9.0 a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9% rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora stock based on this information? The stock price for this case is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected) The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is $ ! (Round to the nearest cent.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in vear zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in LOSS. HITO O GLV 9 Plus: Depreciation 10 Less: Capital Expenditures 11 Less: Increase in NWC 12 Free Cash Flow 7.0 (7.7) (6.3) 25. 3 75 (10.0) (8.6) 24.6 90 (9.9) (5.6) 30.8 9.5 (10.4) (4.9) 33.3 a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9% rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora stock based on this information? b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) d. Sora's networking capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is (Round to the nearest cent.) c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) d. Sora's networking capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) The stock price for this case, when working capital needs are reduced, is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) Enter your answer in each of the answer boxes. Sora Industries has 61 million outstanding shares, $125 million in debt, $41 million in cash, and the following projected free cash flow for the next four years: Year 0 1 2 3 4 Earnings and FCF Forecast ($ million) 1 Sales 433.0 468. 0 5 16.0 547.0 574.3 2 Growth vs. Prior Year 8.1% 10.3% 6.0% 5.0% 3 Cost of Goods Sold (313.6) (345.7) (366.5) (384.8) 4 Gross Profit 154.4 170.3 180.5 189.5 5 Selling, General, & Admin. (93.6) (103.2) (109.4) (114.9) 6 Depreciation (7.0) (7.5) (9.0) (9.5) 7 EBIT 53.8 59.6 62.1 65.2 8 Less: Income Tax at 40% (21.5) (23.8) (24.8) (26.1) 9 Plus: Depreciation 70 75 90 9.5 a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9% rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora stock based on this information? The stock price for this case is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in ULCSS. MIVUIHIC IAA AL TU70 9 Plus: Depreciation 10 Less: Capital Expenditures 11 Less: Increase in NWC 12 Free Cash Flow 121.1 7.0 (7.7) (6.3) 25.3 120.01 7.5 (10.0) (8.6) 24.6 149.0) 9.0 (9.9) (5.6) 30.8 120.1) 9.5 (10.4) (4.9) 33.3 a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9% rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora stock based on this information? b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) The stock price for this case, when working capital needs are reduced, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) Enter your answer in each of the answer boxes. 433.0 Earnings and FCF Forecast ($ million) 1 Sales 2 Growth vs. Prior Year 3 Cost of Goods Sold 4 Gross Profit 5 Selling, General, & Admin. 6 Depreciation 7 EBIT 8 Less: Income Tax at 40% 9 Plus: Depreciation 10 Less: Capital Expenditures 11 Less: Increase in NWC 468.0 8.1% (313.6) 154.4 (93.6) (7.0) 53.8 (21.5) 7.0 (7.7) (6.3) 516.0 10.3% (345.7) 170.3 (103.2) (7.5) 59.6 547.0 6.0% (366.5) 180.5 (109.4) (9.0) 62.1 (24.8) 574.3 5.0% (384.8) 189.5 (114.9) (9.5) 65.2 (26.1) 9.5 (10.4) (4.9) 7.5 (10.0) (8.6) 9.0 (9.9) (5.6) Sora Industries has 61 million outstanding shares, $125 million in debt, S41 million in cash, and the following projected free cash flow for the next four years: Year 0 1 2 3 4 Earnings and FCF Forecast ($ million) 1 Sales 433.0 468.0 516.0 547.0 574.3 2 Growth vs. Prior Year 8.1% 10.3% 6.0% 5.0% 3 Cost of Goods Sold (313.6) (345.7) (366.5) (384.8) 4 Gross Profit 154.4 170.3 180.5 189.5 5 Selling, General, & Admin (93.6) (103.2) (109.4) (114.9) 6 Depreciation (7.0) (7.5) (9.0) (9.5) 7 EBIT 53.8 59.6 62.1 65.2 8 Less: Income Tax at 40% (21.5) (23.8) (24.8) (26.1) 9 Plus: Depreciation 70 75 9.0 a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9% rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora stock based on this information? The stock price for this case is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected) The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is $ ! (Round to the nearest cent.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in vear zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in LOSS. HITO O GLV 9 Plus: Depreciation 10 Less: Capital Expenditures 11 Less: Increase in NWC 12 Free Cash Flow 7.0 (7.7) (6.3) 25. 3 75 (10.0) (8.6) 24.6 90 (9.9) (5.6) 30.8 9.5 (10.4) (4.9) 33.3 a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9% rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora stock based on this information? b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) d. Sora's networking capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is (Round to the nearest cent.) c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) d. Sora's networking capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) The stock price for this case, when working capital needs are reduced, is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) Enter your answer in each of the answer boxes. Sora Industries has 61 million outstanding shares, $125 million in debt, $41 million in cash, and the following projected free cash flow for the next four years: Year 0 1 2 3 4 Earnings and FCF Forecast ($ million) 1 Sales 433.0 468. 0 5 16.0 547.0 574.3 2 Growth vs. Prior Year 8.1% 10.3% 6.0% 5.0% 3 Cost of Goods Sold (313.6) (345.7) (366.5) (384.8) 4 Gross Profit 154.4 170.3 180.5 189.5 5 Selling, General, & Admin. (93.6) (103.2) (109.4) (114.9) 6 Depreciation (7.0) (7.5) (9.0) (9.5) 7 EBIT 53.8 59.6 62.1 65.2 8 Less: Income Tax at 40% (21.5) (23.8) (24.8) (26.1) 9 Plus: Depreciation 70 75 90 9.5 a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9% rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora stock based on this information? The stock price for this case is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in ULCSS. MIVUIHIC IAA AL TU70 9 Plus: Depreciation 10 Less: Capital Expenditures 11 Less: Increase in NWC 12 Free Cash Flow 121.1 7.0 (7.7) (6.3) 25.3 120.01 7.5 (10.0) (8.6) 24.6 149.0) 9.0 (9.9) (5.6) 30.8 120.1) 9.5 (10.4) (4.9) 33.3 a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash flow are expected to grow at a 5.9% rate beyond year four. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora stock based on this information? b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) c. Return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, the firm reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) The stock price for this case, when selling, general, and administrative costs decrease, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (their current level in year zero). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions are as in (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash flow in year 1.) The stock price for this case, when working capital needs are reduced, is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) Enter your answer in each of the answer boxes. 433.0 Earnings and FCF Forecast ($ million) 1 Sales 2 Growth vs. Prior Year 3 Cost of Goods Sold 4 Gross Profit 5 Selling, General, & Admin. 6 Depreciation 7 EBIT 8 Less: Income Tax at 40% 9 Plus: Depreciation 10 Less: Capital Expenditures 11 Less: Increase in NWC 468.0 8.1% (313.6) 154.4 (93.6) (7.0) 53.8 (21.5) 7.0 (7.7) (6.3) 516.0 10.3% (345.7) 170.3 (103.2) (7.5) 59.6 547.0 6.0% (366.5) 180.5 (109.4) (9.0) 62.1 (24.8) 574.3 5.0% (384.8) 189.5 (114.9) (9.5) 65.2 (26.1) 9.5 (10.4) (4.9) 7.5 (10.0) (8.6) 9.0 (9.9) (5.6)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


