Question
Sorry, it was too long for chegg to post as text and it is python, thanks for your help. Only manipulate the first huge chunk
Sorry, it was too long for chegg to post as text and it is python, thanks for your help.

 Only manipulate the first huge chunk of code and use python code. Thanks for your help
Only manipulate the first huge chunk of code and use python code. Thanks for your help
Lab 04: Array-Backed Lists
ArrayList
And now for the task at hand. We've partitioned the ArrayList methods you need to implement (and the test cases that follow) into seven categories:
- Subscript-based access (completed in class)
- Stringification
- Single-element manipulation
- Predicates (True/False queries)
- Queries
- Bulk operations
- Iteration
All told, there are 23 methods --- a handful of which have already been implemented for you --- whose behavior are specified in their docstrings below. Note that we left out API support for slices (e.g., lst[start:stop:step]); you can read about how to support slices in the Python docs, but we just don't think it's worth the extra busywork.
Hints / Advice
We strongly advise that you start with the first category of functions and move down the list sequentially, pausing after each to run the corresponding test cases. The only category that might be worth skipping to early on is Iteration --- which can help simplify several other methods. Keep in mind that while you're not permitted to make use of high level APIs in the underlying list, you can certainly make use of ArrayList methods you've already implemented.
For instance, your implementations of pop and remove can (and should) use the del operator on your own list to remove elements from the middle, and it probably makes sense to use extend in your __add__ and copy methods.
In [ ]:
class ArrayList:
def __init__(self):
self.data = ConstrainedList() # don't change this line!
### subscript-based access ###
def _normalize_idx(self, idx):
nidx = idx
if nidxnidx += len(self.data)if nidxnidx = 0return nidxdef __getitem__(self, idx):"""Implements `x = self[idx]`"""assert(isinstance(idx, int))nidx = self._normalize_idx(idx)if nidx >= len(self.data):raise IndexErrorreturn self.data[nidx]def __setitem__(self, idx, value):"""Implements `self[idx] = x`"""assert(isinstance(idx, int))nidx = self._normalize_idx(idx)if nidx >= len(self.data):raise IndexErrorself.data[nidx] = valuedef __delitem__(self, idx):"""Implements `del self[idx]`"""assert(isinstance(idx, int))nidx = self._normalize_idx(idx)if nidx >= len(self.data):raise IndexErrorfor i in range(nidx+1, len(self.data)):self.data[i-1] = self.data[i]del self.data[len(self.data)-1]### stringification ###def __str__(self):"""Implements `str(self)`. Returns '[]' if the list is empty, elsereturns `str(x)` for all values `x` in this list, separated by commasand enclosed by square brackets. E.g., for a list containing values1, 2 and 3, returns '[1, 2, 3]'."""def __repr__(self):"""Supports REPL inspection. (Same behavior as `str`.)"""### single-element manipulation ###def append(self, value):"""Appends value to the end of this list."""def insert(self, idx, value):"""Inserts value at position idx, shifting the original elements down thelist, as needed. Note that inserting a value at len(self) --- equivalentto appending the value --- is permitted. Raises IndexError if idx is invalid."""def pop(self, idx=-1):"""Deletes and returns the element at idx (which is the last element,by default)."""def remove(self, value):"""Removes the first (closest to the front) instance of value from thelist. Raises a ValueError if value is not found in the list."""### predicates (T/F queries) ###def __eq__(self, other):"""Returns True if this ArrayList contains the same elements (in order) asother. If other is not an ArrayList, returns False."""def __contains__(self, value):"""Implements `val in self`. Returns true if value is found in this list."""### queries ###def __len__(self):"""Implements `len(self)`"""def min(self):"""Returns the minimum value in this list."""def max(self):"""Returns the maximum value in this list."""def index(self, value, i=0, j=None):"""Returns the index of the first instance of value encountered inthis list between index i (inclusive) and j (exclusive). If j is notspecified, search through the end of the list for value. If valueis not in the list, raise a ValueError."""def count(self, value):"""Returns the number of times value appears in this list."""### bulk operations ###def __add__(self, other):"""Implements `self + other_array_list`. Returns a new ArrayListinstance that contains the values in this list followed by thoseof other."""def clear(self):self.data = ConstrainedList() # don't change this!def copy(self):"""Returns a new ArrayList instance (with a separate data store), thatcontains the same values as this list."""def extend(self, other):"""Adds all elements, in order, from other --- an Iterable --- to this list."""### iteration ###def __iter__(self):"""Supports iteration (via `iter(self)`)"""GradedStarter Code(DON'T CHANGE ANY OF THE CODE BELOW AND FOLLOW THE TESTS, THANKS.)
In [ ]:
# (6 points) test subscript-based accessfrom unittest import TestCaseimport randomtc = TestCase()lst = ArrayList()data = [1, 2, 3, 4]lst.data = ConstrainedList(data)for i in range(len(data)):tc.assertEqual(lst[i], data[i])with tc.assertRaises(IndexError):x = lst[100]with tc.assertRaises(IndexError):lst[100] = 0with tc.assertRaises(IndexError):del lst[100]lst[1] = data[1] = 20del data[0]del lst[0]for i in range(len(data)):tc.assertEqual(lst[i], data[i])data = [random.randint(1, 100) for _ in range(100)]lst.data = ConstrainedList(data)for i in range(len(data)):lst[i] = data[i] = random.randint(101, 200)for i in range(50):to_del = random.randrange(len(data))del lst[to_del]del data[to_del]for i in range(len(data)):tc.assertEqual(lst[i], data[i])for i in range(0, -len(data), -1):tc.assertEqual(lst[i], data[i])Read Only
In [ ]:
# (4 points) test stringificationfrom unittest import TestCasetc = TestCase()lst = ArrayList()tc.assertIsInstance(lst.data, ConstrainedList)tc.assertEqual('[]', str(lst))tc.assertEqual('[]', repr(lst))lst.data = ConstrainedList([1])tc.assertEqual('[1]', str(lst))tc.assertEqual('[1]', repr(lst))lst.data = ConstrainedList([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])tc.assertEqual('[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]', str(lst))tc.assertEqual('[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]', repr(lst))Read Only
In [ ]:
# (8 points) test single-element manipulationfrom unittest import TestCaseimport randomtc = TestCase()lst = ArrayList()data = []for _ in range(100):to_add = random.randrange(1000)data.append(to_add)lst.append(to_add)tc.assertIsInstance(lst.data, ConstrainedList)tc.assertEqual(data, lst.data._as_list())for _ in range(100):to_ins = random.randrange(1000)ins_idx = random.randrange(len(data)+1)data.insert(ins_idx, to_ins)lst.insert(ins_idx, to_ins)tc.assertEqual(data, lst.data._as_list())for _ in range(100):pop_idx = random.randrange(len(data))tc.assertEqual(data.pop(pop_idx), lst.pop(pop_idx))tc.assertEqual(data, lst.data._as_list())for _ in range(25):to_rem = data[random.randrange(len(data))]data.remove(to_rem)lst.remove(to_rem)tc.assertEqual(data, lst.data._as_list())with tc.assertRaises(ValueError):lst.remove(9999)Read Only
In [ ]:
# (4 points) test predicatesfrom unittest import TestCasetc = TestCase()lst = ArrayList()lst2 = ArrayList()lst.data = ConstrainedList([])lst2.data = ConstrainedList([1, 2, 3])tc.assertNotEqual(lst, lst2)lst.data = ConstrainedList([1, 2, 3])tc.assertEqual(lst, lst2)lst.data = ConstrainedList([])tc.assertFalse(1 in lst)tc.assertFalse(None in lst)lst.data = ConstrainedList(range(100))tc.assertFalse(100 in lst)tc.assertTrue(50 in lst)Read Only
In [ ]:
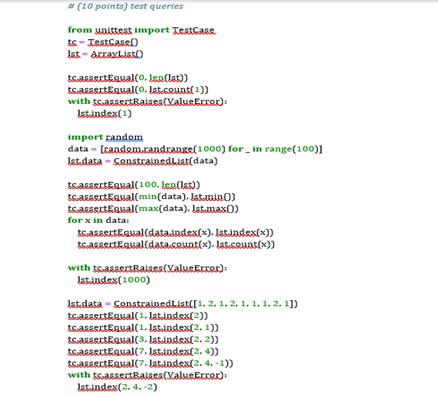
# (10 points) test queriesfrom unittest import TestCasetc = TestCase()lst = ArrayList()tc.assertEqual(0, len(lst))tc.assertEqual(0, lst.count(1))with tc.assertRaises(ValueError):lst.index(1)import randomdata = [random.randrange(1000) for _ in range(100)]lst.data = ConstrainedList(data)tc.assertEqual(100, len(lst))tc.assertEqual(min(data), lst.min())tc.assertEqual(max(data), lst.max())for x in data:tc.assertEqual(data.index(x), lst.index(x))tc.assertEqual(data.count(x), lst.count(x))with tc.assertRaises(ValueError):lst.index(1000)lst.data = ConstrainedList([1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1])tc.assertEqual(1, lst.index(2))tc.assertEqual(1, lst.index(2, 1))tc.assertEqual(3, lst.index(2, 2))tc.assertEqual(7, lst.index(2, 4))tc.assertEqual(7, lst.index(2, 4, -1))with tc.assertRaises(ValueError):lst.index(2, 4, -2)Read Only
In [ ]:
# (6 points) test bulk operationsfrom unittest import TestCasetc = TestCase()lst = ArrayList()lst2 = ArrayList()lst3 = lst+lst2tc.assertIsInstance(lst3, ArrayList)tc.assertEqual([], lst3.data._as_list())import randomdata = [random.randrange(1000) for _ in range(50)]data2 = [random.randrange(1000) for _ in range(50)]lst.data = ConstrainedList(data)lst2.data = ConstrainedList(data2)lst3 = lst + lst2tc.assertEqual(100, len(lst3))tc.assertEqual(data + data2, lst3.data._as_list())lst.clear()tc.assertEqual([], lst.data._as_list())lst.data = ConstrainedList([random.randrange(1000) for _ in range(50)])lst2 = lst.copy()tc.assertIsNot(lst, lst2)tc.assertIsNot(lst.data, lst2.data)tc.assertEqual(lst.data._as_list(), lst2.data._as_list())lst.clear()lst.extend(range(10))lst.extend(range(10,0,-1))lst.extend(data.copy())tc.assertEqual(70, len(lst))tc.assertEqual(list(range(10))+list(range(10,0,-1))+data, lst.data._as_list())Read Only
In [ ]:
# (2 points) test iterationfrom unittest import TestCasetc = TestCase()lst = ArrayList()import randomdata = [random.randrange(1000) for _ in range(100)]lst.data = ConstrainedList(data)tc.assertEqual(data, [x for x in lst])it1 = iter(lst)it2 = iter(lst)for x in data:tc.assertEqual(next(it1), x)tc.assertEqual(next(it2), x)Only manipulate the first huge chunk of code.
class Constrained list (list) ***Constrains the list class so it offers only the following primitive array API: - "latfor getting and setting a value at an existing positive index" -"Isllat) to obtain the number of slots - "Istarred (None) to grow the list by one slot at a time del latlleallat)-11 to delete the last slot in a list All other operations will result in an exception being raised. definit_(self. args) super_it_(*args) def append(self.value): if value is not Noner raise ValueError('Can only append None to constrained list!') super().append(value) def _setitem_(self, idx): if idx -len(self): raise ValueExcexf'Can only use positive, valid indexes on constrained lists!) return superstitem_(dx) def_setitem_(self. Idx.value) if idx len(self) raise ValueExcerf 'Can only use positive, valid indexes on constrained lists!) super()._setitem_Cid value) def_delitem_(self. Idx): if idx-les(self)-1: raise ValueError('Can only delete last item in constrained list!') super_delitem_idx) def_setattribute(self, name) if name in ('insert', 'pop', 'remove','min', "max'. "index', 'count', 'clear'.'copy','extend'). raise AttributeError'Method" + name + " not supported on constrained list!) else: return super().setattribute_(name) class Constrained list (list) ***Constrains the list class so it offers only the following primitive array API: - "latfor getting and setting a value at an existing positive index" -"Isllat) to obtain the number of slots - "Istarred (None) to grow the list by one slot at a time del latlleallat)-11 to delete the last slot in a list All other operations will result in an exception being raised. definit_(self. args) super_it_(*args) def append(self.value): if value is not Noner raise ValueError('Can only append None to constrained list!') super().append(value) def _setitem_(self, idx): if idx -len(self): raise ValueExcexf'Can only use positive, valid indexes on constrained lists!) return superstitem_(dx) def_setitem_(self. Idx.value) if idx len(self) raise ValueExcerf 'Can only use positive, valid indexes on constrained lists!) super()._setitem_Cid value) def_delitem_(self. Idx): if idx-les(self)-1: raise ValueError('Can only delete last item in constrained list!') super_delitem_idx) def_setattribute(self, name) if name in ('insert', 'pop', 'remove','min', "max'. "index', 'count', 'clear'.'copy','extend'). raise AttributeError'Method" + name + " not supported on constrained list!) else: return super().setattribute_(name)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


