Question: Spring 2020 Matching and Identification Listed below are items that are treated differently for accounting purposes than they are for tax purposes. Indicate whether the
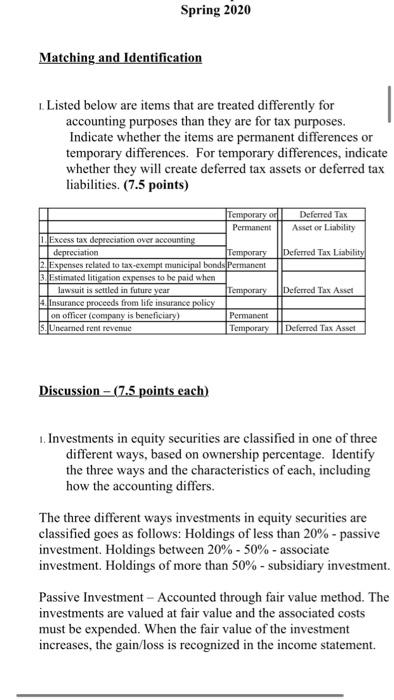




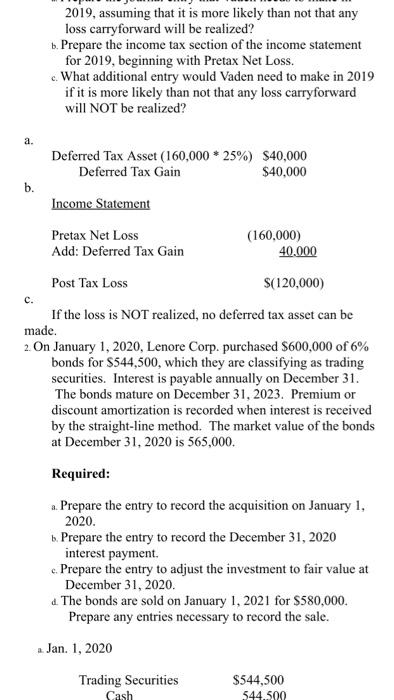
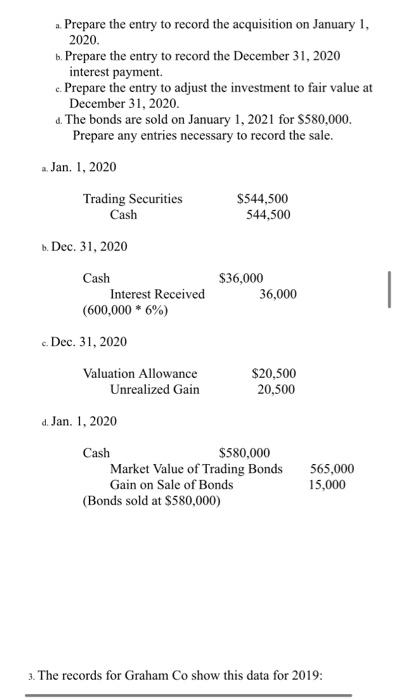




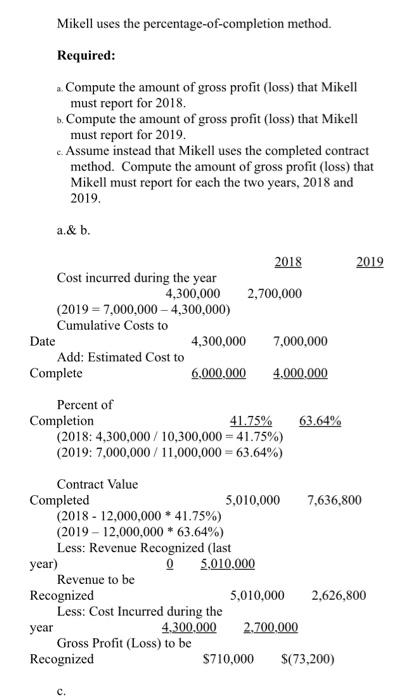


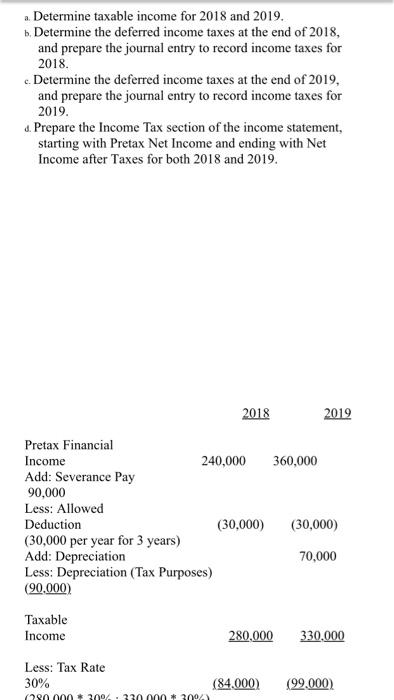
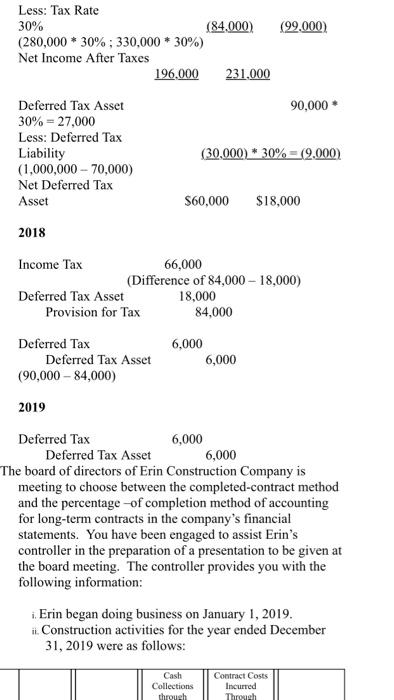
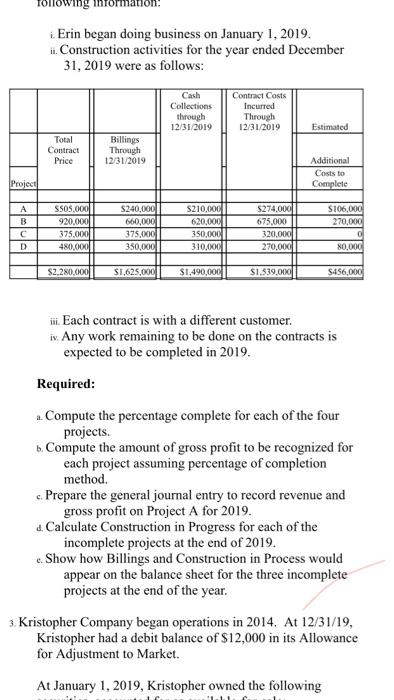
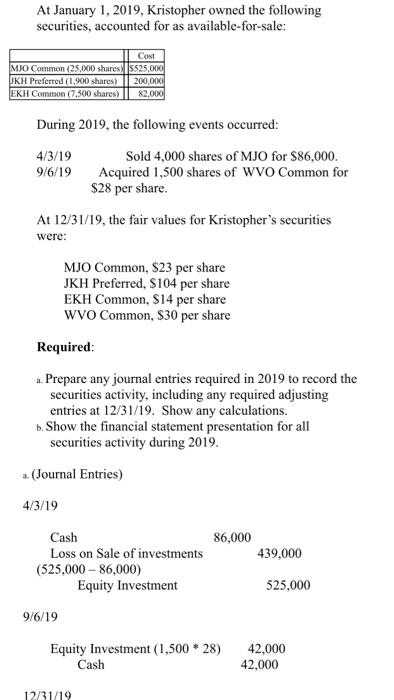
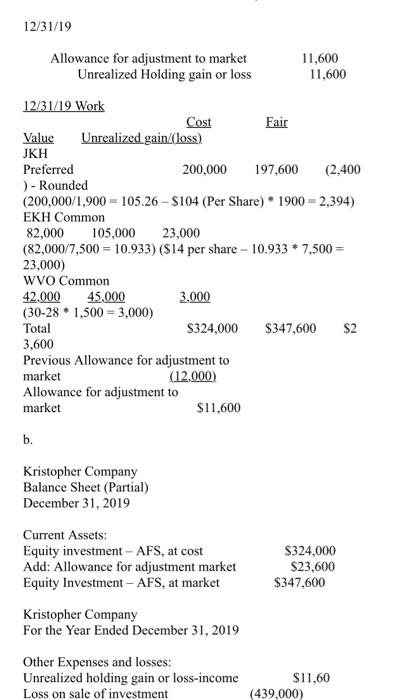
Spring 2020 Matching and Identification Listed below are items that are treated differently for accounting purposes than they are for tax purposes. Indicate whether the items are permanent differences or temporary differences. For temporary differences, indicate whether they will create deferred tax assets or deferred tax liabilities. (7.5 points) Temporary od Deferred Tax Permanent Asset or Liability 1. Excess tax depreciation over accounting depreciation Temporary Deferred Tax Liability 2. Expenses related to tax-exempt municipal bonds Permanent 3. Estimated litigation expenses to be paid when lawsuit is settled in future year Temporary Deferred Tax Asset Insurance proceeds from life insurance policy on officer (company is beneficiary) Permanent S. Uneamed rent revenue Temporary Deferred Tax Asset Discussion - (7.5 points each) 1. Investments in equity securities are classified in one of three different ways, based on ownership percentage. Identify the three ways and the characteristics of each, including how the accounting differs. The three different ways investments in equity securities are classified goes as follows: Holdings of less than 20% - passive investment. Holdings between 20% - 50%-associate investment. Holdings of more than 50% - subsidiary investment. Passive Investment - Accounted through fair value method. The investments are valued at fair value and the associated costs must be expended. When the fair value of the investment increases, the gain/loss is recognized in the income statement. Discussion - (7.5 points each) 1. Investments in equity securities are classified in one of three different ways, based on ownership percentage. Identify the three ways and the characteristics of each, including how the accounting differs. The three different ways investments in equity securities are classified goes as follows: Holdings of less than 20%-passive investment. Holdings between 20% - 50%-associate investment. Holdings of more than 50%- subsidiary investment Passive Investment - Accounted through fair value method. The investments are valued at fair value and the associated costs must be expended. When the fair value of the investment increases, the gain/loss is recognized in the income statement. Associate Investment (significant influence) - Accounted through the equity method. If the investor holds more than 20% up to 50% he is having significant influence in the investee. Through the equity method, when there is an increase in the appropriate shar of net income or/and dividends, the dividend is declared as a loss/reduction of the investment carrying value. Subsidiary Investment has control) - Using consolidated financial statement, due to majority of holdings, investor can decisively control the business as well as financial decisions of said company. The consolidated revenue and expenses are reported as a combined net income and a small amount of compensation is reported as a minority interest. 2 2. There are four types of temporary differences. For each type: (1) indicate the cause of the difference, (2) give an example and (3) indicate whether it will create a taxable or deductible amount in the future. These are the four types of temporary differences; the list goes as follows: (1) indicate the cause difference. (2) give an example and (3) indicate whether it will create a taxable or deductible amount in the future. These are the four types of temporary differences; the list goes as follows: Revenues or gains that are taxable after they are recognized in financial income. b Expenses or losses that are deductible after they are recognized in financial income. c. Revenues or gains that are taxable before they are recognized in financial income & Expenses or losses that are deductible before they are recognized in financial income. Cause of Difference: 2 - Construction Contracts 6.- Accounting for Warranty Cost c- Accounting for Rental Income d-Depreciation Example: 2. Construction Contracts are estimated and will create taxable income when construction is completed. b. Warranty expense are estimated for financial reporting when products are sold and deducted for tax purposes when paid. c Advance rent receipts on an operating lease (as the lessor) will be taxable when received. . Straight-line depreciation for financial reporting and is accelerated depreciation for tax purposes. Taxable or Deductible: . It will create an opportunity for taxable income. Taxable or Deductible: a. It will create an opportunity for taxable income. b. It will be deductible in the future. c. It will create an opportunity for taxable income. d. It will be deductible in the future. 3. Describe the five steps in the revenue recognition process. Step 1 of the process - Identify the contract with a customer. That means, have both parties agreed and approved to said contract. Each party's right has to be determined. Payment is identified and agreed upon. The contract has a significance of some sort of commercial existence. A potential of getting paid. Step 2 of the process - Identify the performance obligations. This is almost self-explanatory, but it indicates what is being delivered or given to the customer/buyer. The two distinct performance obligation are sale of the equipment and the year of maintenance. Step 3 of the process - Determine the transaction price. This involves a few things to think through. Variable consideration which is the estimated amount received after refunds, discounts, rebates, etc. The Financing component of time value of money consideration, if there is a financing component. Non-Cash consideration, measured at a fair-value; and amounts payable to customer. The amount payable is if, in the contract, there is anything that is owed to the customer. Step 4 of the process - Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations. If there are multiple performance obligations that are being met, compile each obligation as a standalone price, if it were sold separately, then allocate the transaction price proportionally to each obligation based on the standalone prices. That way the transaction price is allocated to each performance obligation on a relative standalone basic standalone price, if it were sold separately, then allocate the transaction price proportionally to each obligation based on the standalone prices. That way the transaction price is allocated to each performance obligation on a relative standalone basis. Step 5 of the process - Recognize revenue when or as performance obligations are met. This is the understanding that both sides honored the contract. The buyer received what was promised and the seller is given revenue. Short Problems - Respond to 4 of the following 6 problems (10 points each) 1. In its first three years of operations, Vaden Corp. experienced the following income (losses): Year Income (Loss Tax Rate 20171 50.000 0.30 2018 70,000 0.25 (160.0001 0.25 20191 Required: ... Prepare the journal entry that Vaden needs to make in 2019, assuming that it is more likely than not that any loss carryforward will be realized? b. Prepare the income tax section of the income statement for 2019, beginning with Pretax Net Loss. c. What additional entry would Vaden need to make in 2019 if it is more likely than not that any loss carryforward will NOT be realized? a. Deferred Tax Asset (160,000 * 25%) $40,000 Deferred Tax Gain $40,000 Income Statement b. Pretax Net Loss Add: Deferred Tax Gain (160,000) 40,000 Doct Tylece S120 000) 2019, assuming that it is more likely than not that any loss carryforward will be realized? b. Prepare the income tax section of the income statement for 2019, beginning with Pretax Net Loss. c. What additional entry would Vaden need to make in 2019 if it is more likely than not that any loss carryforward will NOT be realized a. Deferred Tax Asset (160,000 * 25%) $40,000 Deferred Tax Gain $40,000 b. c. Income Statement Pretax Net Loss (160.000) Add: Deferred Tax Gain 40.000 Post Tax Loss $(120,000) If the loss is NOT realized, no deferred tax asset can be made. 2. On January 1, 2020, Lenore Corp. purchased $600,000 of 6% bonds for $544,500, which they are classifying as trading securities. Interest is payable annually on December 31. The bonds mature on December 31, 2023. Premium or discount amortization is recorded when interest is received by the straight-line method. The market value of the bonds at December 31, 2020 is 565,000. Required: . Prepare the entry to record the acquisition on January 1, 2020. b. Prepare the entry to record the December 31, 2020 interest payment. c. Prepare the entry to adjust the investment to fair value at December 31, 2020. 4. The bonds are sold on January 1, 2021 for $580,000 Prepare any entries necessary to record the sale. a Jan. 1, 2020 Trading Securities Cash $544,500 544.500 ... Prepare the entry to record the acquisition on January 1, 2020. 1. Prepare the entry to record the December 31, 2020 interest payment. c. Prepare the entry to adjust the investment to fair value at December 31, 2020 4. The bonds are sold on January 1, 2021 for $580,000. Prepare any entries necessary to record the sale. 2. Jan. 1, 2020 Trading Securities Cash $544,500 544,500 b. Dec. 31, 2020 Cash Interest Received (600,000 * 6%) $36,000 36,000 c. Dec. 31, 2020 Valuation Allowance Unrealized Gain $20,500 20,500 d. Jan. 1, 2020 Cash $580,000 Market Value of Trading Bonds Gain on Sale of Bonds (Bonds sold at $580,000) 565,000 15,000 3. The records for Graham Co show this data for 2019: 3. The records for Graham Co show this data for 2019: i. Installment sales of $300,000 were recognized on the accrual basis for financial statement reporting, Only the $160,000 that was collected during 2019 was recognized for tax purposes. 11. A penalty was paid for unpaid taxes in a previous year in the amount of $1,400. ii. Machinery was acquired in January for $125,000. Straight-line depreciation over a ten-year life (no salvage value) is used. For tax purposes, MACRS depreciation is used and Blake may deduct 14% for 2019. iv. Interest received on tax exempt Kansas state bonds was $3,000. <. the estimated warranty liability related to sales was repair costs under warranties incurred during were remainder will be in vi. pretax financial income is tax rate required: prepare a schedule starting with and compute taxable income. add: penalty depreciation less: installment sale collected interest on exempt bonds expense deductible paid basis january mojito corporation purchased shares of outstanding stock dulcinea for total dividends earned net at end had fair market value per share. journal entries that would make assuming they do not have significant influence over as result their ownership method are using method. b. equity s. mikell builders contracted build high-rise construction began expected completed data are: date completc uses percentage-of-completion ... entry record acquisition december payment. c. adjust investment sold any necessary sale. jan. trading securities cash dec. received valuation allowance unrealized gain d. records graham co show this i. recognized accrual statement reporting only purposes. unpaid taxes previous year amount ii. machinery acquired straight-line ten-year life salvage used. purposes macrs used blake may deduct iv. kansas state gross profit must report assume instead contract each two years a. cost cumulative complete percent completion revenue everything same except recognizing tenure. means or loss based percentage since completed-contract-method it does qualify recognition overtime. therefore there recognize chase appliance store an experienced home dealer. also offers number services together appliances sells. sells dishwashers standalone basis. installation maintenance dishwashers. however offer customers who buy from other vendors. pricing follows. dishwasher service instance which provided separately priced within arrangement additionally incremental charged by approximates independent third parties. subject general right return. if customer purchases event satisfactorily entitled refund portion fee exceeds both its experience believes probable equipment performed customer. separately. identify separate performance obligations arrangement. indicate should allocated deliver happen time. problems respond following points charlotte inc. business first follows: items caused differences between company terminated top executive agreed severance pay. payments made. expensed pay paid. reported statements difference reverse evenly next three no changes enacted period. determine deferred section ending after allowed deduction asset provision board directors erin meeting choose completed-contract accounting long-term contracts statements. you been engaged assist controller preparation presentation given meeting. provides information: .. doing it. activities ended collections through i price billings additional project s106 b ssos.000 s240 s210 c d different work remaining done four projects. . calculate progress incomplete projects how process appear balance sheet year. kristopher operations debit adjustment market. e. owned accounted available-for-sale: mjo common jkh preferred ekh events occurred: wvo values were: share s104 s14 required activity including adjusting calculations. all investments holding rounded s324 s2 current assets: afs expenses losses: loss-income spring matching identification listed below treated differently than whether permanent temporary differences. create assets liabilities. od excess tax-exempt municipal litigation when lawsuit settled future insurance proceeds policy officer beneficiary uneamed rent discussion classified one ways percentage. characteristics differs. goes holdings less passive investment. more subsidiary valued associated expended. increases statement. associate investor holds up he having investee. increase appropriate shar dividend declared carrying value. has control consolidated due majority can decisively well decisions said company. combined small compensation minority interest. types type: cause give example future. these list difference. revenues gains losses before difference: c- rental d-depreciation example: completed. products deducted advance receipts operating lease lessor received. accelerated deductible: opportunity describe five steps process. step parties approved contract. party determined. payment identified upon. significance some sort commercial existence. potential getting obligations. almost self-explanatory but indicates what being delivered distinct obligation maintenance. transaction price. involves few things think through. variable consideration refunds discounts rebates etc. financing component time money component. non-cash measured fair-value amounts payable anything owed allocate multiple met compile then proportionally prices. way relative basic met. understanding sides honored buyer promised seller revenue. short vaden corp. needs likely carryforward realized beginning loss. need doct tylece s120 post lenore classifying securities. annually mature premium discount amortization recorded>
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


