Question: Step 1: Inspect the UndoCommand abstract base class The read-only UndoCommand.h file has a declaration for the UndoCommand abstract base class. Access UndoCommand.h by
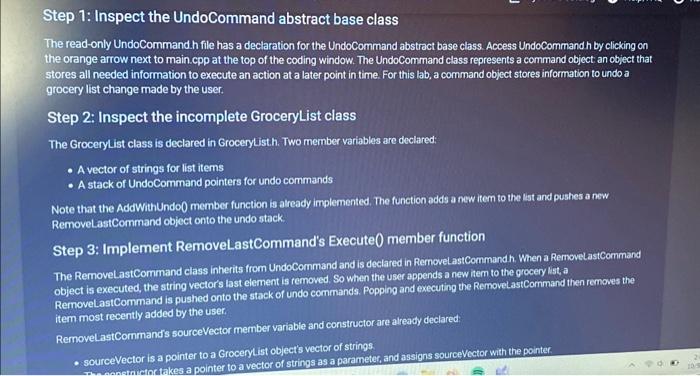

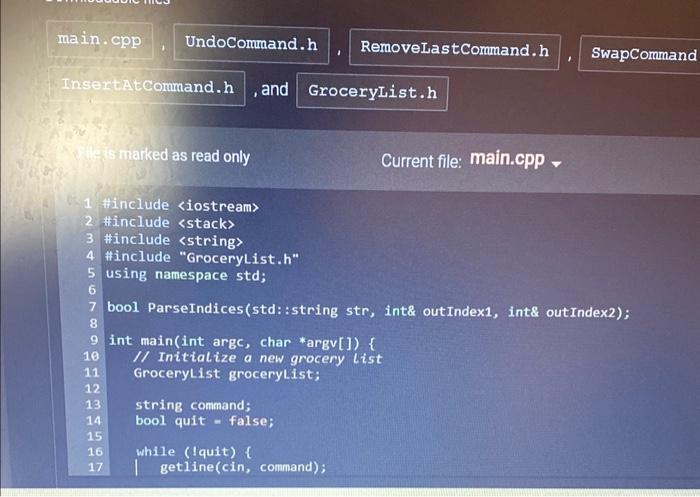
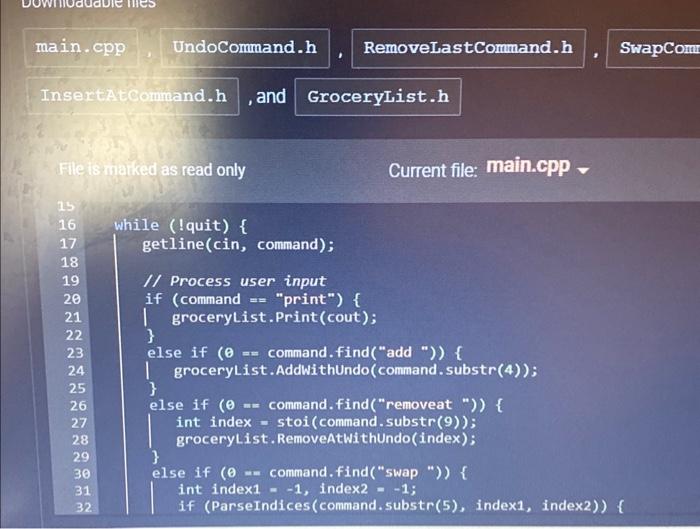
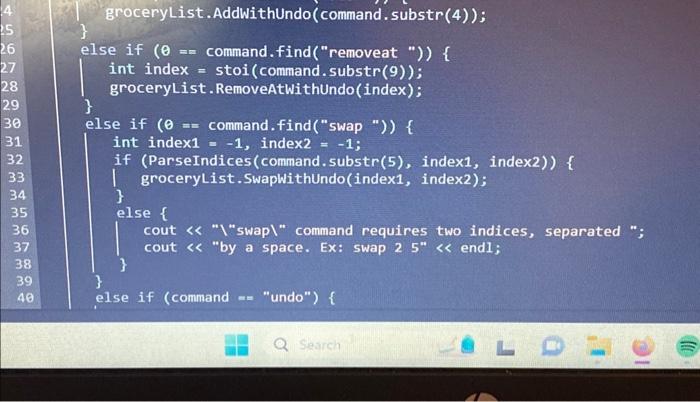
Step 1: Inspect the UndoCommand abstract base class The read-only UndoCommand.h file has a declaration for the UndoCommand abstract base class. Access UndoCommand.h by clicking on the orange arrow next to main.cpp at the top of the coding window. The UndoCommand class represents a command object: an object that stores all needed information to execute an action at a later point in time. For this lab, a command object stores information to undo a grocery list change made by the user. Step 2: Inspect the incomplete GroceryList class The GroceryList class is declared in GroceryList.h. Two member variables are declared: A vector of strings for list items A stack of UndoCommand pointers for undo commands Note that the AddWithUndo) member function is already implemented. The function adds a new item to the list and pushes a new RemoveLastCommand object onto the undo stack. Step 3: Implement RemoveLastCommand's Execute() member function The RemoveLastCommand class inherits from UndoCommand and is declared in RemnovelastCommand. h. When a RemovelastCommand object is executed, the string vector's last element is removed. So when the user appends a new item to the grocery list, a RemoveLastCommand is pushed onto the stack of undo commands. Popping and executing the RemoveLastCommand then removes the item most recently added by the user. RemoveLastCommand's sourceVector member variable and constructor are already declared: sourceVector is a pointer to a GroceryList object's vector of strings. constructor takes a pointer to a vector of strings as a parameter, and assigns sourceVector with the pointer Note that the AddWith Undo member function is already implemented. The function adds a new item to the list and pushes a new RemovelastCommand object onto the undo stack. Step 3: Implement RemoveLastCommand's Execute() member function The RemoveLastCommand class inherits from UndoCommand and is declared in RemovelastCommand.h. When a RemoveLastCommand object is executed, the string vector's last element is removed. So when the user appends a new item to the grocery list, a RemoveLastCommand is pushed onto the stack of undo commands. Popping and executing the RemoveLastCommand then removes the item most recently added by the user. RemoveLastCommand's sourceVector member variable and constructor are already declared: sourceVector is a pointer to a GroceryList object's vector of strings. The constructor takes a pointer to a vector of strings as a parameter, and assigns sourceVector with the pointer. Implement RemoveLastCommand's Execute() member function to remove sourceVector's last element. Step 4: Implement GroceryList's ExecuteUndo() member function Implement GroceryList's ExecuteUndo() member function to do the following: Pop an UndoCommand off the undo stack Execute the popped undo command Delete the undo command File main.cpp has code that reads in a list of commands, one per line, that allow for basic testing of basic operations. So after implementing ExecuteUndo), run your program with the following input. main.cpp UndoCommand.h RemoveLastCommand.h InsertAtCommand.h, and GroceryList.h File is marked as read only 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 #include "GroceryList.h" 5 using namespace std; 6 9 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { 10 // Initialize a new grocery List GroceryList groceryList; 11 12 7 bool ParseIndices (std::string str, int& outIndex1, int& out Index2); 8 13 14 15 16 17 Current file: main.cpp- string command; bool quit = false; while (!quit) { | getline (cin, command); SwapCommand main.cpp UndoCommand.h InsertAtCommand.h , and GroceryList.h File is marked as read only 16 15 16 while (!quit) { 789812 20 22 23 24 22 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 getline (cin, command); RemoveLastCommand.h // Process user input if (command == "print") { groceryList.print(cout); | } Current file: main.cpp. else if (0 == command.find("add ")) { | groceryList.AddWithUndo (command.substr(4)); } else if (0 == command.find("removeat ")) { int index stoi (command.substr(9)); groceryList. RemoveAtWithUndo (index); SwapComm } else if (0 command. find("swap ")) { int index1 = -1, index2 = -1; if (ParseIndices (command.substr(5), index1, index2)) { 4 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 groceryList.AddWithUndo (command.substr(4)); else if (0 == command.find("removeat ")) { int index stoi (command.substr(9)); groceryList.RemoveAtWithUndo (index); = } else if (0 command.find("swap ")) { int index1 = -1, index2 = -1; if (ParseIndices (command.substr(5), index1, index2)) { groceryList. SwapWithUndo (index1, index2); } else { cout < < "\"swap\" command requires two indices, separated "; cout < < "by a space. Ex: swap 2 5" < < endl; } } else if (command == "undo") { Q Search n.cpp 7 18 19 50 51 52 53 54 55 56} ertAtCommand.h, and GroceryList.h NY e is marked as read only UndoCommand.h | } else if (command if (0 == groceryList. GetUndoStackSize()) { 1 cout < < "Cannot execute undo because undo stack is empty" < < endl; } else { } } else if (command quit= true; RemoveLastCommand.h SwapCommand.h == Current file: main.cpp- } } return 0; | groceryList.ExecuteUndo(); } "undo") { "quit") { else { cout < < "Unknown command: " < < command < < endl; Q Search LO:
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
C Program to implement include using namespace std Function to perform WRITE X operation void WRITEs... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


