Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
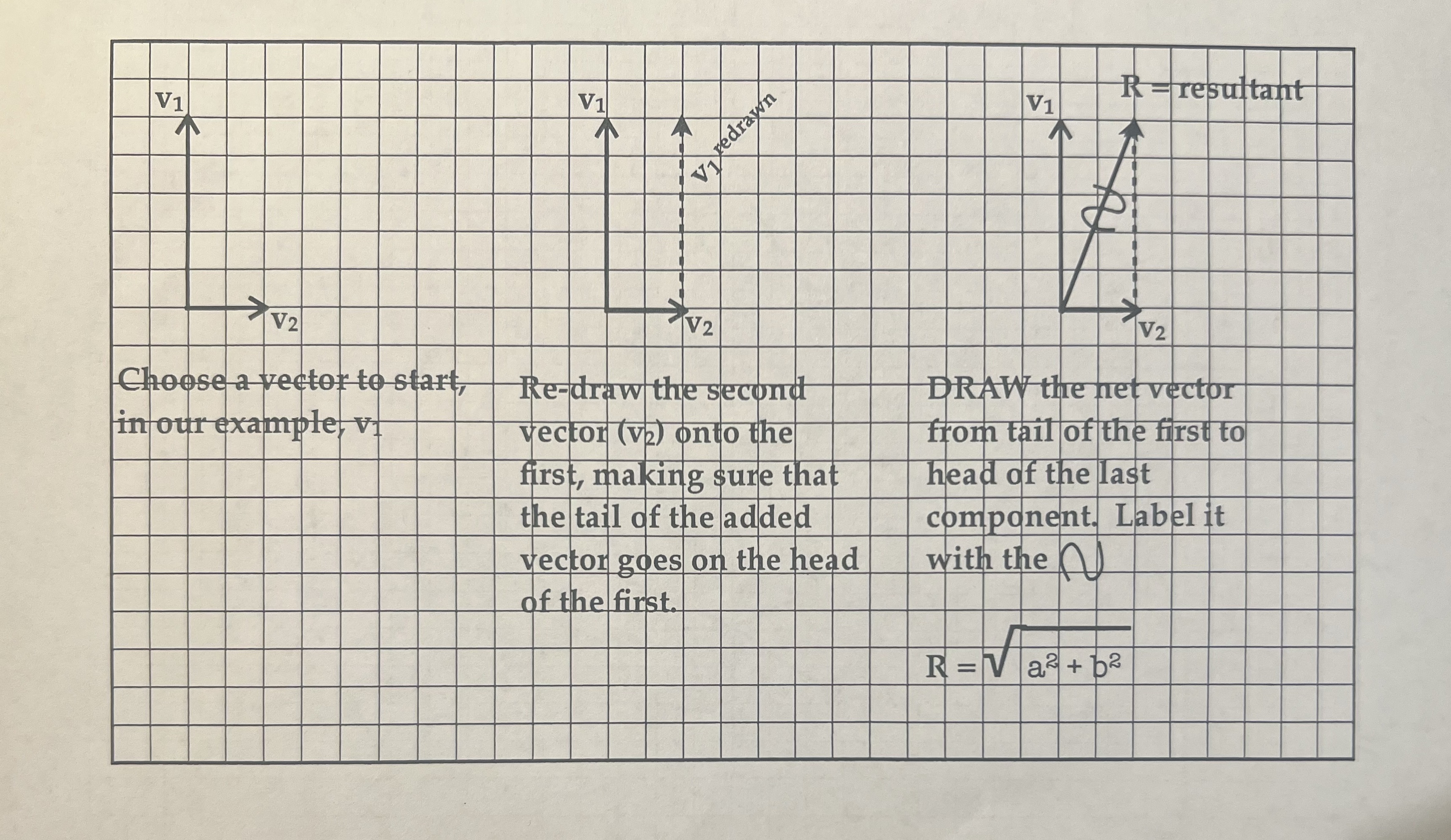
Steps:1) Choose a starting vector: diagonal rather than straight, longer rather than short.2) Redraw the tail of the second vector onto the head of the
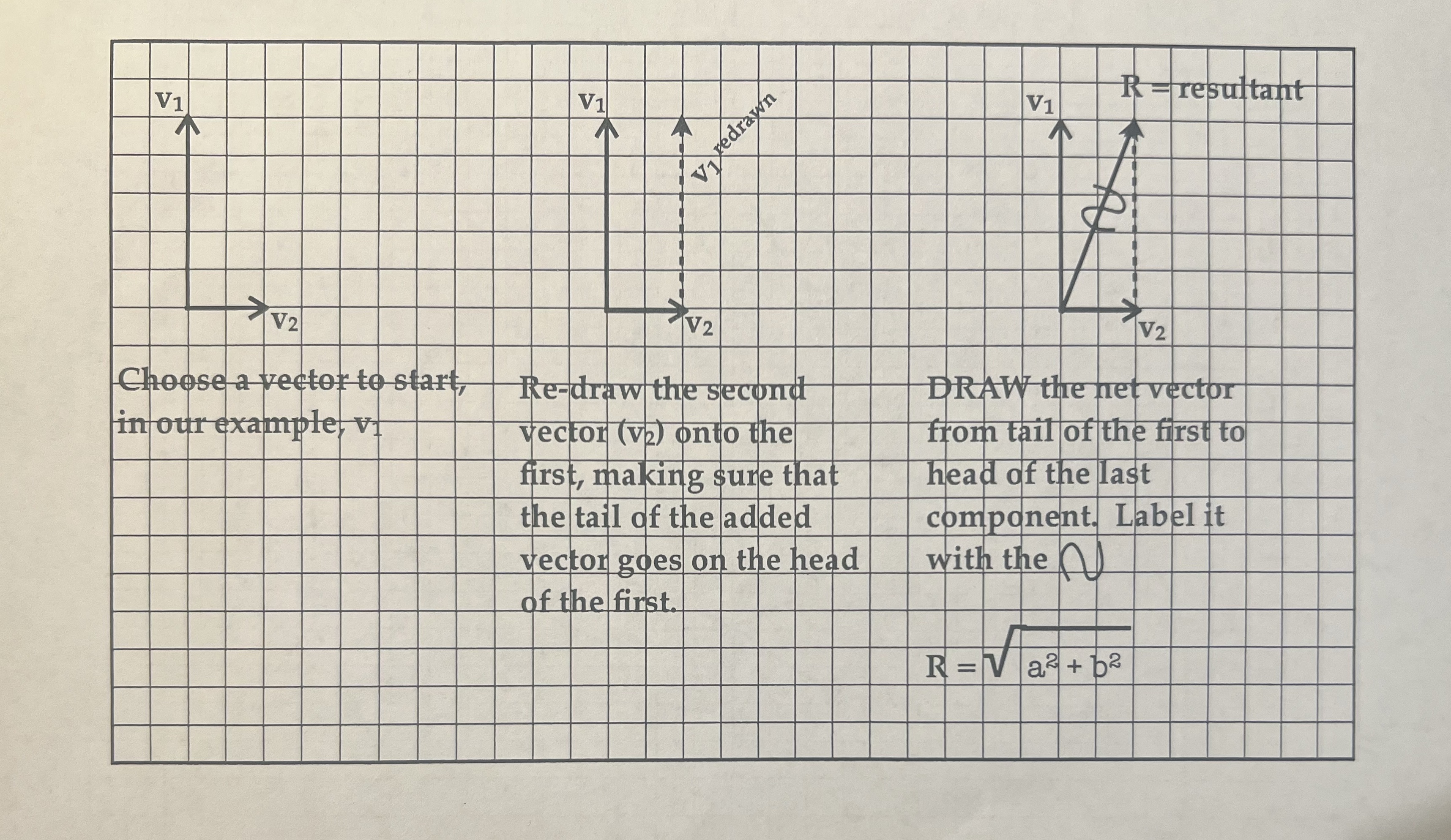
Steps:1) Choose a starting vector: diagonal rather than straight, longer rather than short.2) Redraw the tail of the second vector onto the head of the first vector.3) Repeat Step 2 if you have more vectors, placing the tail of the 3rd vector on the head of the 2nd vector, and so on.4) DRAW the net vector from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.5) LABEL your resultant vector.6) Determine the length of your resultant vector using Pythagorean Theorem.
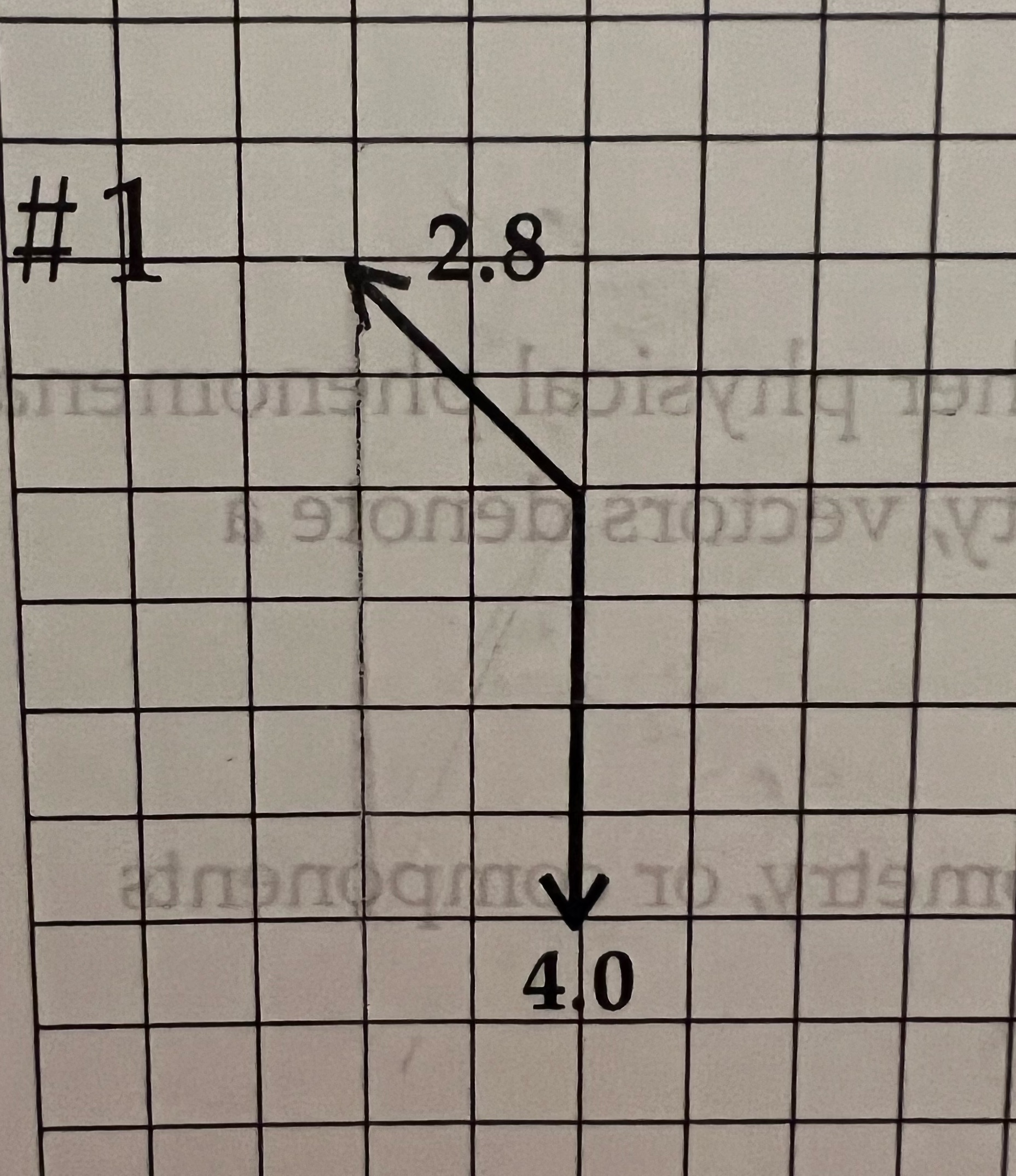
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


