Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Student Exploration: Photosynthesis Lab Directions: Follow the instructions to go through the simulation. Respond to the questions and prompts in the orange boxes. Vocabulary:

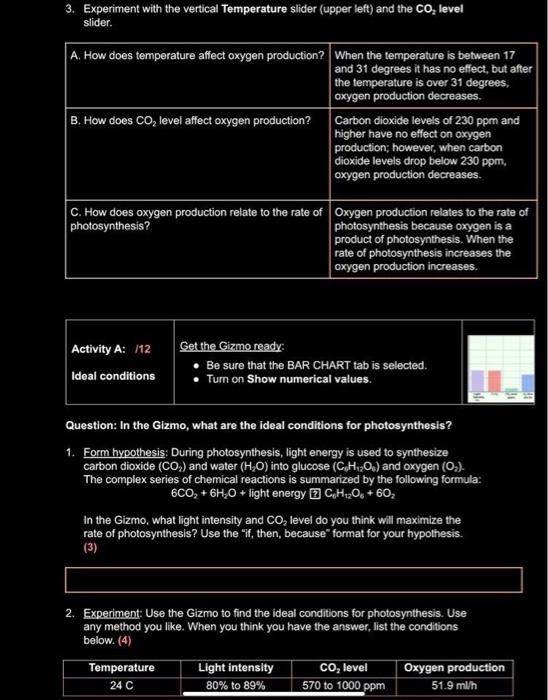


Student Exploration: Photosynthesis Lab Directions: Follow the instructions to go through the simulation. Respond to the questions and prompts in the orange boxes. Vocabulary: carbon dioxide, chlorophyll, glucose, limiting factor, nanometer, photosynthesis, wavelength Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) To survive, what gas do we need to breathe in? Oxygen Where is this gas produced? In plants through the photosynthesis Light intensity co, evel s00 ppm Gizmo Warm-up During photosynthesis, plants use the energy of light to produce glucose (C,H;;0,) from carbon dioxide (CO,), and water (H,0). Glucose is a simple sugar that plants use for energy and as a building block for larger molecules. A by-product of photosynthesis is oxygen. Plants use some of the oxygen they produce, but most of it is released. In the Photosynthesis Lab Gizmo, you can monitor the rate of photosynthesis by measuring oxygen production. 1. Observe the left pane closely. What do you think the bubbles are? I think they are oxygen bubbles. 2. Select the BAR CHART tab. On the graph, notice the Oxygen production bar. Move the Light intensity slider back and forth. How does light intensity affect oxygen production? When the light intensity increases the oxygen production increases too. 3. Experiment with the vertical Temperature slider (upper left) and the CO, level slider. A. How does temperature affect oxygen production? When the temperature is between 17 Land 31 degrees it has no effect, but after antatu 3. Experiment with the vertical Temperature slider (upper left) and the CO, level slider. A. How does temperature affect oxygen production? When the temperature is between 17 and 31 degrees it has no effect, but after the temperature is over 31 degrees, oxygen production decreases. B. How does CO, level affect oxygen production? Carbon dioxide levels of 230 ppm and higher have no effect on oxygen production; however, when carbon dioxide levels drop below 230 ppm, oxygen production decreases. C. How does oxygen production relate to the rate of Oxygen production relates to the rate of photosynthesis? photosynthesis because oxygen is a product of photosynthesis. When the rate of photosynthesis increases the oxygen production increases. Get the Gizmo ready: Activity A: /12 Be sure that the BAR CHART tab is selected. Ideal conditions Turn on Show numerical values. Question: In the Gizmo, what are the ideal conditions for photosynthesis? 1. Form hypothesis: During photosynthesis, light energy is used to synthesize carbon dioxide (CO,) and water (H,O) into glucose (CH,O.) and oxygen (O,). The complex series of chemical reactions is summarized by the following formula: 6CO, + 6H,0 + light energy 7 CH,O, + 6o, In the Gizmo, what light intensity and CO, level do you think will maximize the rate of photosynthesis? Use the "if, then, because" format for your hypothesis. (3) 2. Experiment: Use the Gizmo to find the ideal conditions for photosynthesis. Use any method you like. When you think you have the answer, list the conditions below. (4) Temperature Light intensity CO, level Oxygen production 570 to 1000 ppm 24 C 80% to 89% 51.9 ml/h Temperature Light intensity Co, level Oxygen production 24 C 80% to 89% 570 to 1000 ppm 51.9 ml/h 3. Revise and repeat: One way to test if you've found the ideal conditions is to change each variable slightly from the value that you recorded above. If the oxygen production decreases with each change that you make, it is likely you have found the ideal conditions. If a small change causes oxygen production to increase, continue to experiment. If necessary, revise your numbers in the tablie above. 4. Think and discuss: Thnk about the process of finding the ideal conditions A. Why would it be hard to find the ideal light intensity if the temperature were very hot or cold? (1) A. Because photosynthesis will not ta place if the temperature is too high, it will become too cold and denatured, causing cells to stop working. B. Why would it be hard to find the ideal CO, level if the light intensity were very low? (1) B. Because there is essentially little oxygen production when the light intensity is low. C. Would every plant have these same data for ideal conditions? Explain.(2) C. Get the Gizmo ready: Activity B: /11 Select the COLOR tab and the BAR CHART tab. Set the Temperature to 24C, the Light intensity to 90%, and the CO, level to 1,000 ppm. Colored light Introduction: Plants use a green pigment called chlorophyll to absorb light and convert its energy into a form that the plant can use. Chlorophyll gives plants their green color. Question: What color of light is the best for photosynthesis? 1. Observe: The color of a light wave is determined by its wavelength. On the COLOR tab, slowly drag the Light wavelength slider back and forth and observe the effect on oxygen production. How does the color of light affect the rate of photosynthesis? It makes it go faster 2. Form hypothesis: Which color of light do you think will maximize the rate of photosynthesis? (3) Activity C: 11 Get the Gizmo ready: Select the WHITE tab and the BAR CHART tab. Limiting factors Turn on Show numerical values. Introduction: Photosynthesis requires light, water, and CO, to work. When one of these factors is in short supply, it is called a limiting factor. Temperature can also be a limiting factor when it is too hot or too cold for photosynthesis to work well. Question: What is the effect of limiting factors on photosynthesis? 1. Observe: Set Temperature to 24'C, Light intensity to 50%, and CO, level to 200 ppm. (3) A. Move the Temperature slider up and down. Were you able to increase oxygen production? (Return the slider to 24C when finished.) There is no increase in oxygen production while moving the temperature slider. B. Move the Light intensity slider back and forth. Were you able to increase oxygen production? (Return the slider to 50% when finished.) C. Move the Co, level slider back and forth. Were you able to increase oxygen production? (Return the slider to 200 ppm when finished.) 2. Analyze: In this situation, what was the limiting factor? (1) How do you know? (1) 3. Challenge: In each of the situations below, use the Gizmo to find the limiting factor. (3) Temperature Light intensity Co, level Limiting factor 25C 60% 700 ppm 200 ppm 400 ppm 15C 20% 30C 50% 4. Think and discuss: Suppose you were a farmer trying to grow plants in a greenhouse. Give two reasons for why would it be important to know what the limiting factor is. (3)
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.38 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
However I can provide you with some information and help answer your questions based on the informat...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


