summarise please I will appreciate
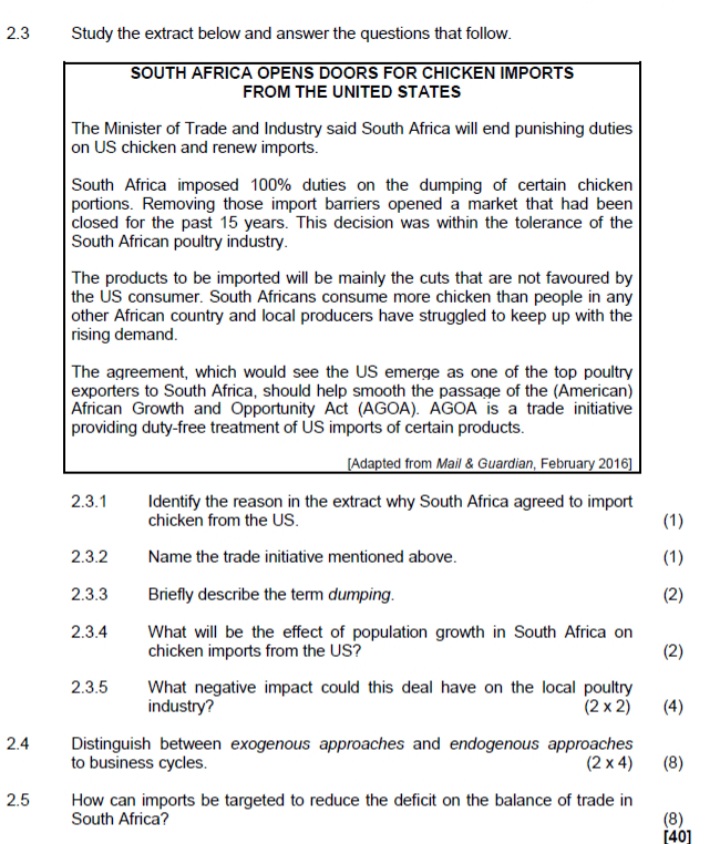
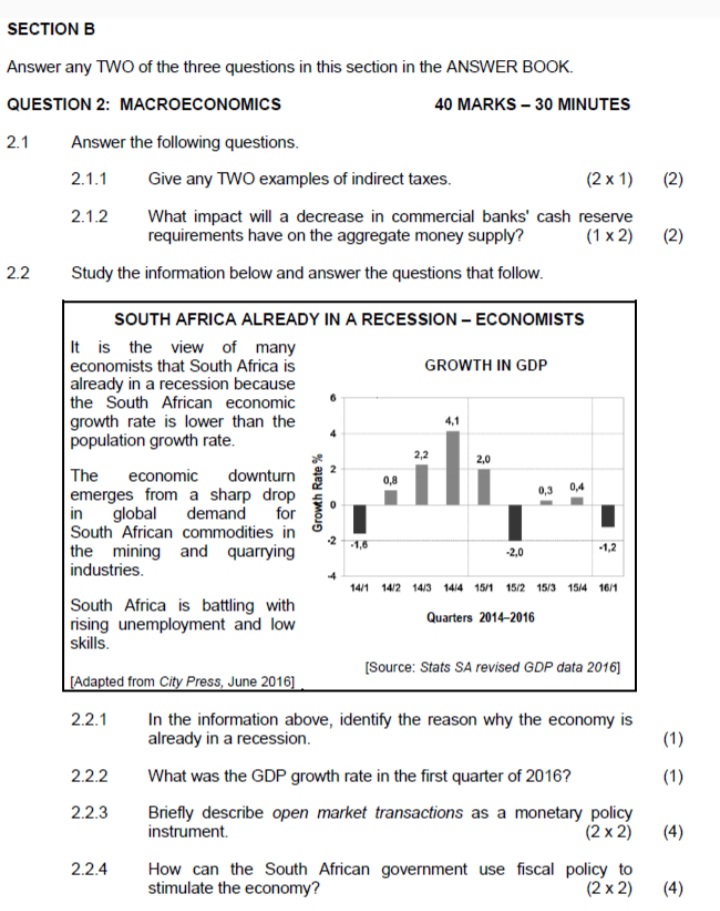
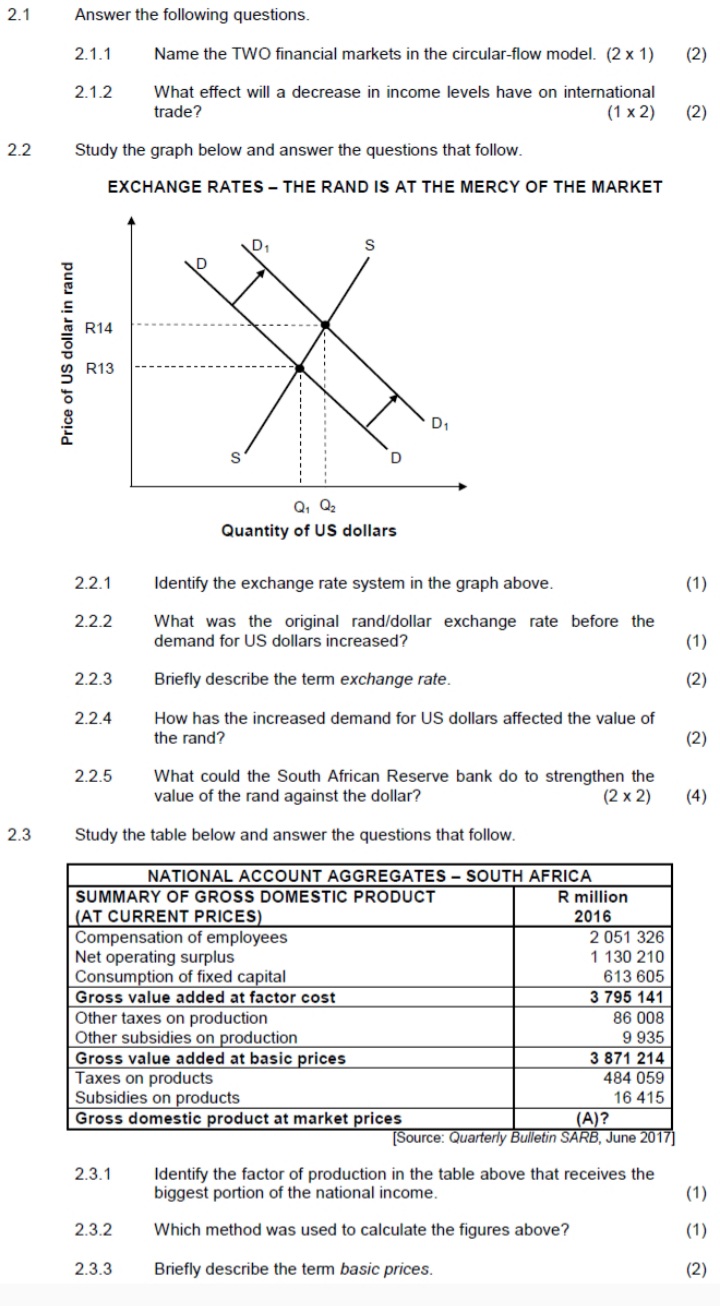
2.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow. SOUTH AFRICA OPENS DOORS FOR CHICKEN IMPORTS FROM THE UNITED STATES The Minister of Trade and Industry said South Africa will end punishing duties on US chicken and renew imports. South Africa imposed 100% duties on the dumping of certain chicken portions. Removing those import barriers opened a market that had been closed for the past 15 years. This decision was within the tolerance of the South African poultry industry. The products to be imported will be mainly the cuts that are not favoured by the US consumer. South Africans consume more chicken than people in any other African country and local producers have struggled to keep up with the rising demand. The agreement, which would see the US emerge as one of the top poultry exporters to South Africa, should help smooth the passage of the (American) African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). AGOA is a trade initiative providing duty-free treatment of US imports of certain products. [Adapted from Mail & Guardian, February 2016] 2.3.1 Identify the reason in the extract why South Africa agreed to import chicken from the US. 2.3.2 Name the trade initiative mentioned above. (1) 2.3.3 Briefly describe the term dumping. (2) 2.3.4 What will be the effect of population growth in South Africa on chicken imports from the US? (2) 2.3.5 What negative impact could this deal have on the local poultry industry? (2 x 2) (4) 2.4 Distinguish between exogenous approaches and endogenous approaches to business cycles. (2 x 4) (8) 2.5 How can imports be targeted to reduce the deficit on the balance of trade in South Africa? (8) [401SECTION B Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of indirect taxes. (2 x 1) (2) 2.1.2 What impact will a decrease in commercial banks' cash reserve requirements have on the aggregate money supply? (1 x 2) (2) 2.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow. SOUTH AFRICA ALREADY IN A RECESSION - ECONOMISTS It is the view of many economists that South Africa is GROWTH IN GDP already in a recession because the South African economic growth rate is lower than the 4.1 population growth rate. 2.0 The economic downturn 2 emerges from a sharp drop 0,3 Growth Rate % in global demand for South African commodities in the mining and quarrying -1.6 20 -1.2 industries. 14/1 14/2 14/3 14/4 15/1 15/2 15/3 15/4 16/1 South Africa is battling with rising unemployment and low Quarters 2014-2016 skills. [Source: Stats SA revised GDP data 2016] [Adapted from City Press, June 2016] 2.2.1 In the information above, identify the reason why the economy is already in a recession. 2.2.2 What was the GDP growth rate in the first quarter of 2016? (1) 2.2.3 Briefly describe open market transactions as a monetary policy instrument. (2 x 2) (4) 2.2.4 How can the South African government use fiscal policy to stimulate the economy? (2 x 2) (4)2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Name the TWO financial markets in the circular-flow model. (2 x 1) (2) 2.1.2 What effect will a decrease in income levels have on international trade? (1 x2) (2) 2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. EXCHANGE RATES - THE RAND IS AT THE MERCY OF THE MARKET D R14 Price of US dollar in rand R13 D Q1 Q2 Quantity of US dollars 2.2.1 Identify the exchange rate system in the graph above. (1) 2.2.2 What was the original rand/dollar exchange rate before the demand for US dollars increased? (1) 2.2.3 Briefly describe the term exchange rate. (2) 2.2.4 How has the increased demand for US dollars affected the value of the rand? (2) 2.2.5 What could the South African Reserve bank do to strengthen the value of the rand against the dollar? (2 x 2) (4) 2.3 Study the table below and answer the questions that follow. NATIONAL ACCOUNT AGGREGATES - SOUTH AFRICA SUMMARY OF GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT R million (AT CURRENT PRICES) 2016 Compensation of employees 2 051 326 Net operating surplus 1 130 210 Consumption of fixed capital 613 605 Gross value added at factor cost 3 795 141 Other taxes on production 86 008 Other subsidies on production 9 935 Gross value added at basic prices 3 871 214 Taxes on products 484 059 Subsidies on products 16 415 Gross domestic product at market prices (A)? [Source: Quarterly Bulletin SARB, June 2017] 2.3.1 Identify the factor of production in the table above that receives the biggest portion of the national income. (1) 2.3.2 Which method was used to calculate the figures above? (1) 2.3.3 Briefly describe the term basic prices. (2)