Question
Suppose a typical (representative) corn farm has a short-run production technology which results in the outcome of U-shaped Average Variable Cost (AVC), Average Total Cost
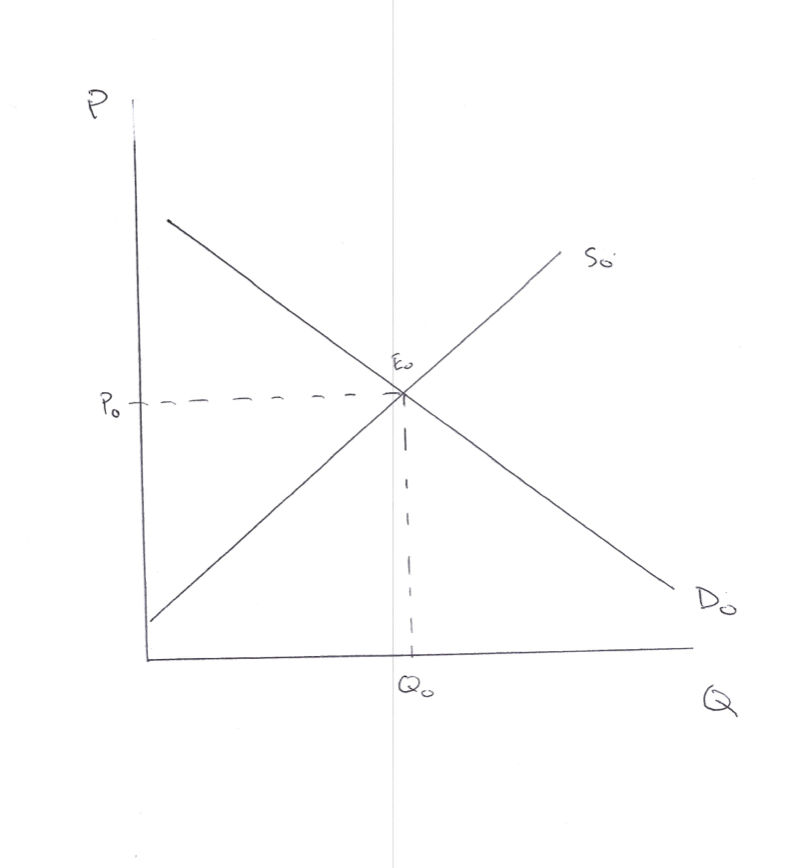
Suppose a typical (representative) corn farm has a short-run production technology which results in the outcome of U-shaped Average Variable Cost (AVC), Average Total Cost (ATC), and Marginal Cost (MC). Further, suppose this firm sells its product in a market where the price of the good is determined by the interaction of market Demand and Supply (such as you depicted in Question #1). Because an individual firm is very small compared to the rest of the market, we treat the market price as the price given to the firm, and the individual firm cannot impact that price. Finally, for the entirety of Questions 3 through 5, assume we are in the Short Run for this firm. In graphing responses to Questions 3 through 5, put $ on the vertical axis and lower-case q (firm output) on the horizontal axis.
1.
In August 2020, the price of corn was theP0you depicted in your answer to Question 1.
- Using the graphs ofAFC0,AVC0,ATC0, andMC0,show this original price,P0, on this graph with$on the vertical axis and lower-caseq(firm output) on the horizontal axis. You should assume that this August 2020 priceP0ishigherthan the minimum point of theATC0you drew on your graph.
- Graphically indicate the profit maximizing outputq0for this typical firm and explain how you determined this output.
- Whydoes it not make sense for the firm to produce either more or less than the profit maximizing outputq0that you've determined? Please explain.
2. Using the same graph with theAFC0,AVC0,ATC0, andMC0,P0andq0:
- Graphically indicate the size of profits or losses (negative profits) at thisP0,q0outcome in August 2020.
- Explain why this graphical representation of profits correctlydepicts the profit made by the firm.
3.
In the March 2021Wall Street Journalstory referenced in Question #1, the author noted that the run up in grain prices of the past 6 months has now caused an increase in the price of farmland. Since farmland is one of the major inputs in production of corn, the higher price for land will increase every farmer's cost. Even if the farmer already owns land they previously purchased at lower prices, they have to recognize that the new higher price of land is their opportunity cost: they could just sell the land and receive the new higher price of land.
- Start with the sameAFC0,AVC0,ATC0, andMC0curves you used in Questions 3 and 4. Now show shifts in any of the cost curves, reflecting the higher cost of land (keeping in mind that this higher cost is independent of how much or how little corn is actually produced) and labeling the changed cost curves with a subscript 1. On the graph with$on the vertical axis and individual firm outputqon the horizontal axis, draw the newP1you determined in Question 2 above. What is the new profit maximizing outputq1for this typical firm?
- Graphically depict the size of profits or losses (negative profits) at the new priceP1. Is the firm making positive or negative profits?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


