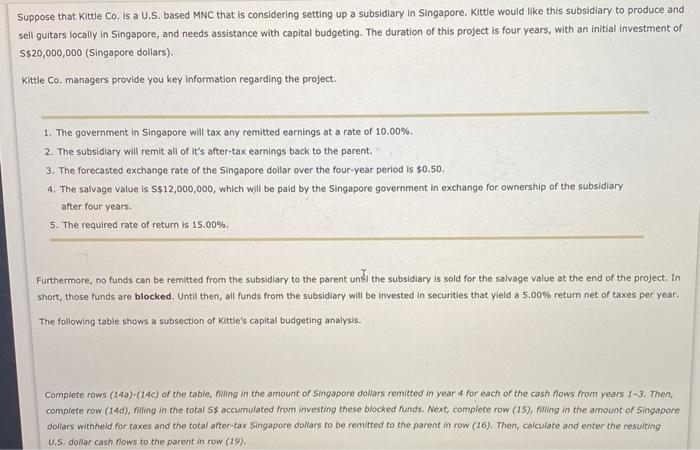
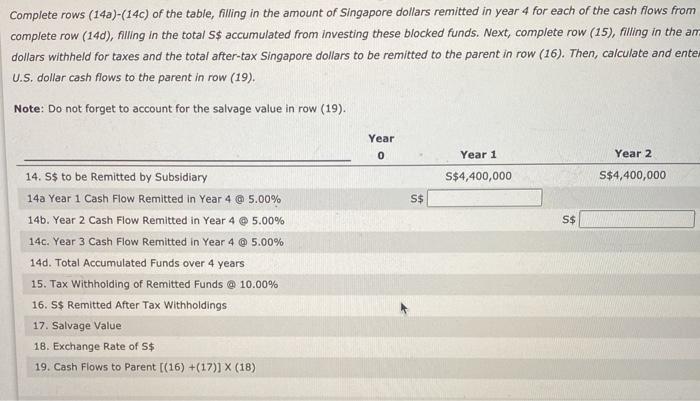
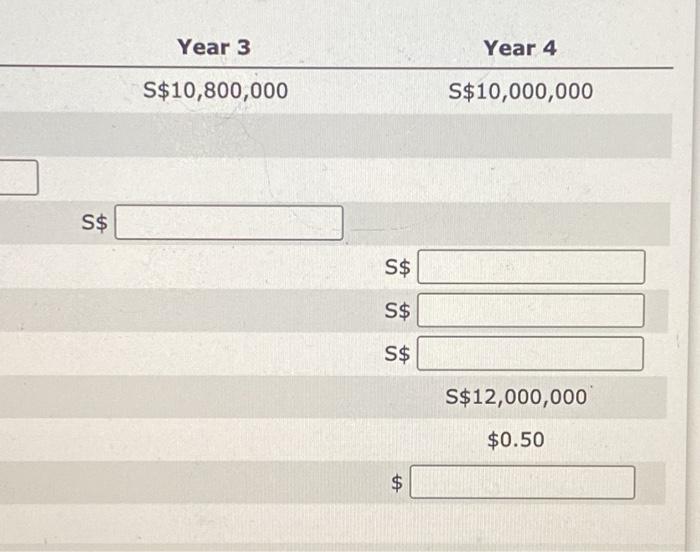
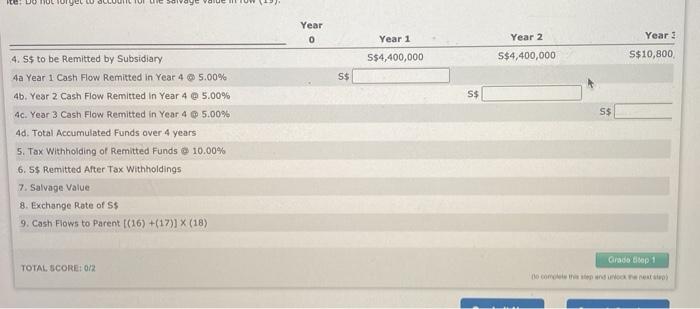
Suppose that Kittle Co. is a U.S. based MNC that is considering setting up a subsidiary in Singapore. Kittle would like this subsidiary to produce and sell guitars locally in Singapore, and needs assistance with capital budgeting. The duration of this project is four years, with an initial investment of S$20,000,000 (Singapore dollars), Kittle Co. managers provide you key Information regarding the project. 1. The government in Singapore will tax any remitted earnings at a rate of 10.00%. 2. The subsidiary will remit all of it's after-tax carnings back to the parent. 3. The forecasted exchange rate of the Singapore dollar over the four-year period is $0.50. 4. The salvage value is S$12,000,000, which will be paid by the Singapore government in exchange for ownership of the subsidiary after four years. 5. The required rate of return is 15.00%. Furthermore, no funds can be remitted from the subsidiary to the parent unill the subsidiary is sold for the salvage value at the end of the project. In short, those funds are blocked. Until then, all funds from the subsidiary will be invested in securities that yield a 5.00% return net of taxes per year, The following table shows a subsection of Kittle's capital budgeting analysis. Complete rows (143)-(14c) of the table, filling in the amount of Singapore dollars remitted in year 4 for each of the cash flows from years 1-3. Then, complete row (140), nilling in the total S$ accumulated from investing these blocked funds. Next, complete row (15), hiling in the amount of Singapore dollars withheld for taxes and the total after-tax Singapore dollars to be remitted to the parent in row (16), Then, calculate and enter the resulting U.S. dollar cash nows to the parent in row (19). Complete rows (14a)-(14c) of the table, filling in the amount of Singapore dollars remitted in year 4 for each of the cash flows from complete row (14d), filling in the total S$ accumulated from investing these blocked funds. Next, complete row (15), filling in the an dollars withheld for taxes and the total after-tax Singapore dollars to be remitted to the parent in row (16). Then, calculate and ente U.S. dollar cash flows to the parent in row (19). Note: Do not forget to account for the salvage value in row (19). Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 S$4,400,000 S$4,400,000 S$ S$ 14. S$ to be Remitted by Subsidiary 14a Year 1 Cash Flow Remitted in Year 4 @ 5.00% 146. Year 2 Cash Flow Remitted in Year 4 @ 5.00% 140. Year 3 Cash Flow Remitted in Year 4 @ 5.00% 14d. Total Accumulated Funds over 4 years 15. Tax Withholding of Remitted Funds @ 10.00% 16. S$ Remitted After Tax Withholdings 17. Salvage Value 18. Exchange Rate of S$ 19. Cash Flows to Parent ((16) +(17)] X (18) Year 3 Year 4 S$10,800,000 S$10,000,000 SS SS SS S$ S$12,000,000 $0.50 $ e o 10 Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 5$4,400,000 S$4,400,000 S$10,800 S$ S$ S$ 4. S$ to be Remitted by Subsidiary 4a Year 1 Cash Flow Remitted in Year 4 5.00% 4b. Year 2 Cash Flow Remitted in Year 4 @ 5.00% 4. Year 3 Cash Flow Remitted in Year 4 @ 5.00% 4d. Total Accumulated Funds over 4 years 5. Tax Withholding of Remitted Funds @ 10.00% 6. S$ Remitted After Tax Withholdings 7. Salvage Value 8. Exchange Rate of S$ 9. Cash Flows to Parent (16) +(17)] X (18) Grado top1 TOTAL SCORE: 0/2