Question
Suppose the inflation rate is expected to be 6% next year, 4.45% the following year, and 3.35% thereafter. Assume that the real risk-free rate, r*,
Suppose the inflation rate is expected to be 6% next year, 4.45% the following year, and 3.35% thereafter. Assume that the real risk-free rate, r*, will remain at 2.3% and that maturity risk premiums on Treasury securities rise from zero on very short-term bonds (those that mature in a few days) to 0.2% for 1-year securities. Furthermore, maturity risk premiums increase 0.2% for each year to maturity, up to a limit of 1.0% on 5-year or longer-term T-bonds.
a.
Calculate the interest rate on 1-year Treasury securities. Round your answer to two decimal places. %
Calculate the interest rate on 2-year Treasury securities. Round your answer to two decimal places. %
Calculate the interest rate on 3-year Treasury securities. Round your answer to two decimal places. %
Calculate the interest rate on 4-year Treasury securities. Round your answer to two decimal places. %
Calculate the interest rate on 5-year Treasury securities. Round your answer to two decimal places. %
Calculate the interest rate on 10-year Treasury securities. Round your answer to two decimal places. %
Calculate the interest rate on 20-year Treasury securities. Round your answer to two decimal places. %
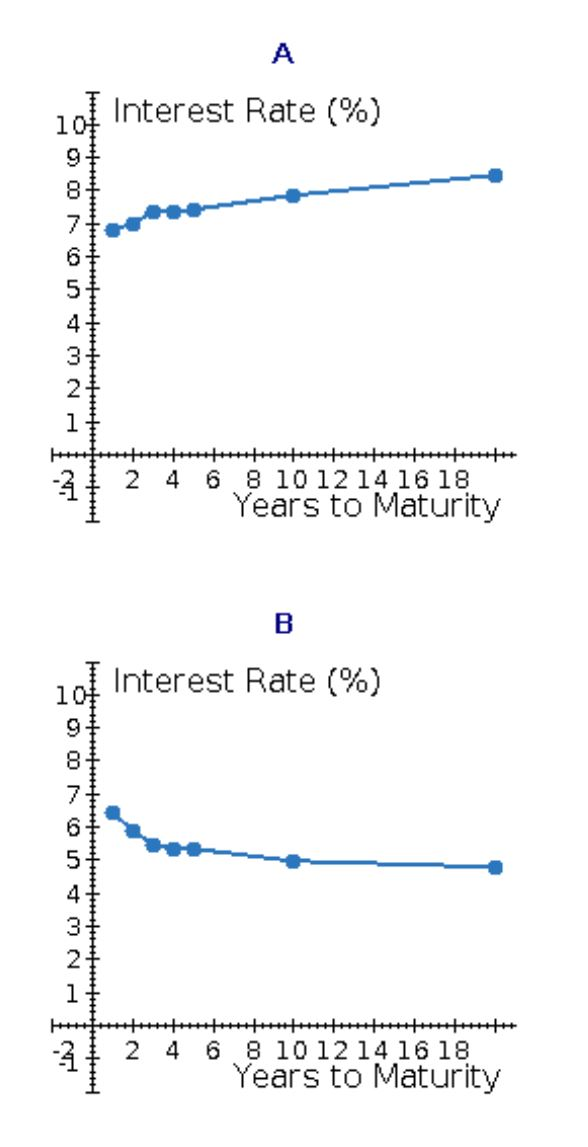
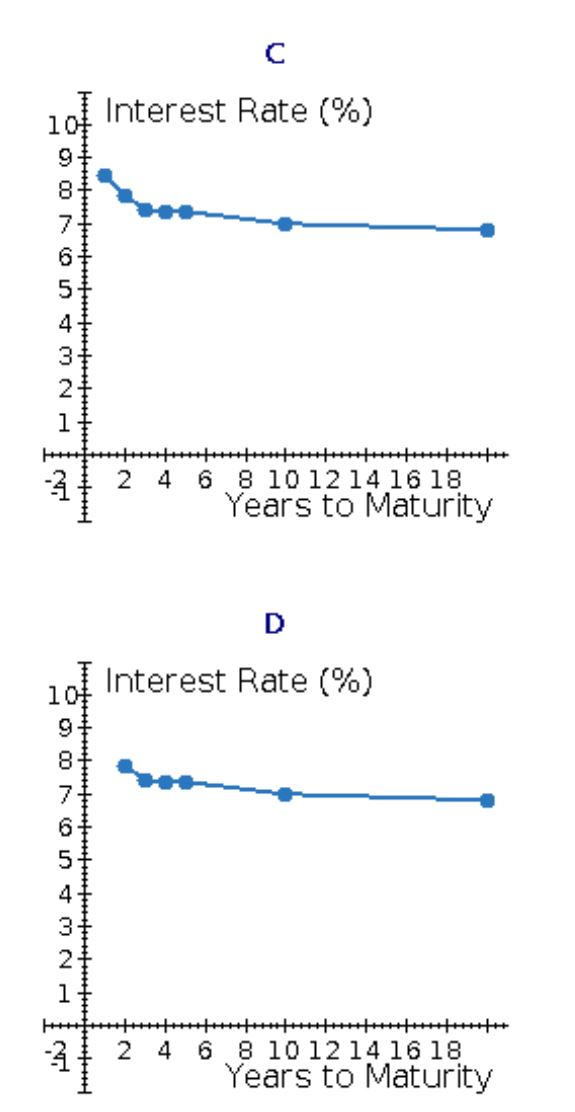
Select the correct sketch is (A, B, C, D).
b.
Suppose a AAA-rated company (which is the highest bond rating a firm can have) had bonds with the same maturities as the Treasury bonds. Estimate what you believe a AAA-rated company's yield curve would look like on the same graph with the Treasury bond yield curve. (Hint: Think about the default risk premium on its long-term versus its short-term bonds.)
The yield risk curve for the AAA-rated corporate bonds will (rise above, fall below, be the same as) the yield curve for the Treasury securities.
c.
What will be the approximate yield curve of a much riskier lower-rated company with a much higher risk of defaulting on its bonds?
The yield risk curve of a much riskier lower-rated company will be (above, below, the same as) the yield curve for the Treasury securities and (above, below, the same as) the yield curve for the AAA-rated corporate bonds.
Interest Rate (%) 101 4 3 2 1 4 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Years to Maturity B Interest Rate (%) 9 8 4 3 2 1 - 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Years to Maturity Interest Rate (%) 101 9 8 7 4 3 2 1 4 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Years to Maturity D Interest Rate (%) 101 9 8 7 6 4 3 2 1 2 ++++++++ 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Years to MaturityStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


