Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Suppose you are given the yields on the following Treasury securities. For simplicity, assume that there is no maturity risk premium. If you want to
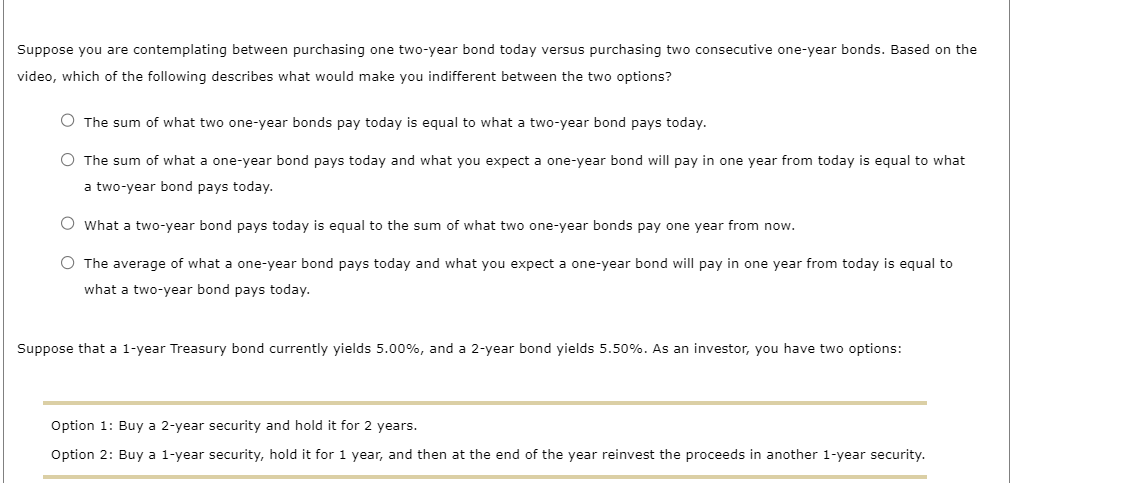

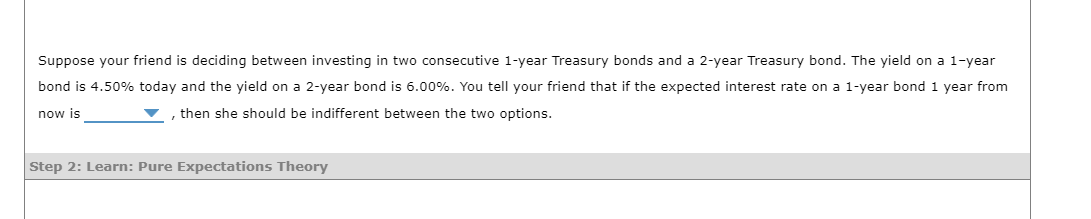

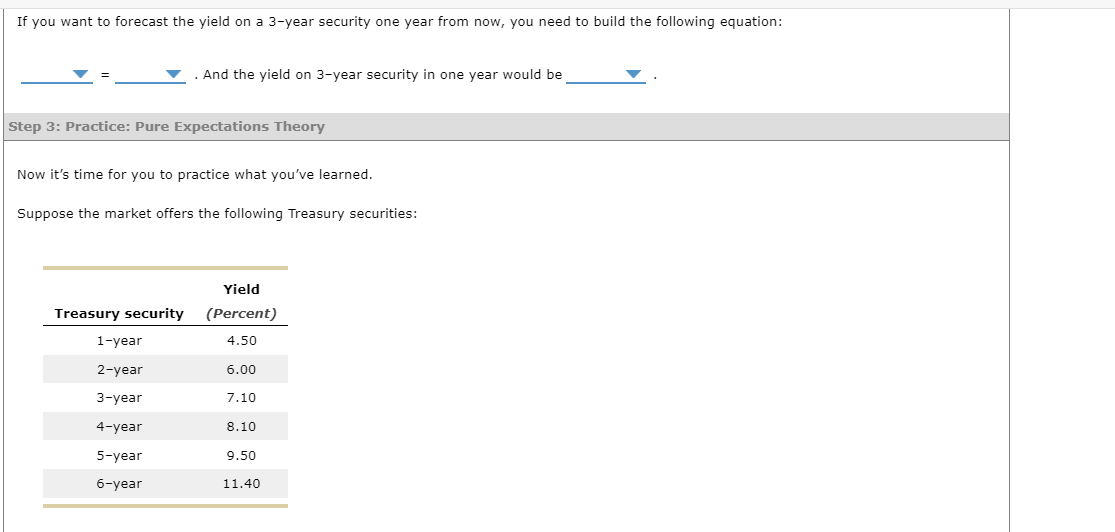
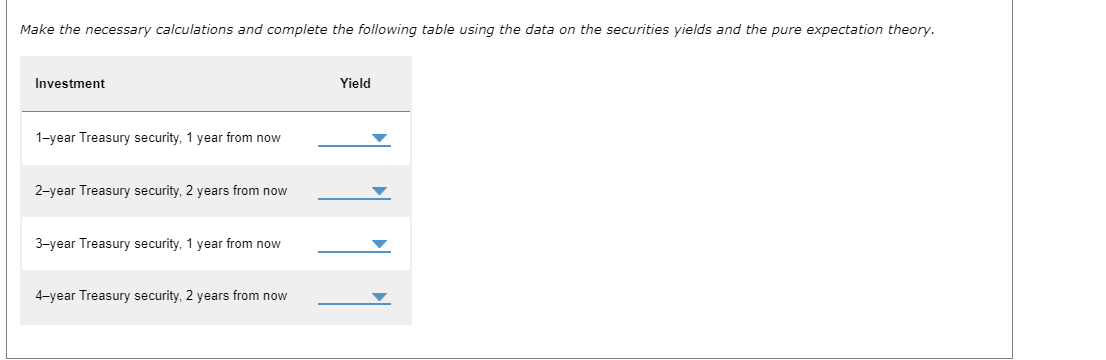 Suppose you are given the yields on the following Treasury securities. For simplicity, assume that there is no maturity risk premium. If you want to forecast the yield on a 1-year security in one year from now, you need to build the following equation: = And the yield on 1-year security in one year would be If you want to forecast the yield on a 1-year security two years from now, you need to build the following equation: = And the yield on 1-year security in two years would be If you want to forecast the yield on a 3-year security one year from now, you need to build the following equation: =. And the yield on 3-year security in one year would be Step 3: Practice: Pure Expectations Theory Now it's time for you to practice what you've learned. Suppose the market offers the following Treasury securities: Suppose your friend is deciding between investing in two consecutive 1-year Treasury bonds and a 2-year Treasury bond. The yield on a 1 -year bond is 4.50% today and the yield on a 2-year bond is 6.00%. You tell your friend that if the expected interest rate on a 1 -year bond 1 year from now is , then she should be indifferent between the two options. Make the necessary calculations and complete the following table using the data on the securities yields and the pure expectation theory. Investment Yield 1-year Treasury security, 1 year from now 2-year Treasury security, 2 years from now 3-year Treasury security, 1 year from now 4-year Treasury security, 2 years from now In two years, Option 1 will yield the following amount per $1 you invested: Yield at the end of year 2=$1(1+0.055)2=$1.113 The pure expectation theory implies that Option 2 should yield the same amount, which can be expressed as follows: Yield at the end of year 2=$1(1+0.05)(1+x)=$1.113, where x stands for the expected interest rate on a 1-year Treasury security 1 year from now. $1(1+0.05)(1+x)$1.05(1+x)(1+x)x=$1.113025=$1.113025=$1.05$1.113025=$1.05$1.1130251
Suppose you are given the yields on the following Treasury securities. For simplicity, assume that there is no maturity risk premium. If you want to forecast the yield on a 1-year security in one year from now, you need to build the following equation: = And the yield on 1-year security in one year would be If you want to forecast the yield on a 1-year security two years from now, you need to build the following equation: = And the yield on 1-year security in two years would be If you want to forecast the yield on a 3-year security one year from now, you need to build the following equation: =. And the yield on 3-year security in one year would be Step 3: Practice: Pure Expectations Theory Now it's time for you to practice what you've learned. Suppose the market offers the following Treasury securities: Suppose your friend is deciding between investing in two consecutive 1-year Treasury bonds and a 2-year Treasury bond. The yield on a 1 -year bond is 4.50% today and the yield on a 2-year bond is 6.00%. You tell your friend that if the expected interest rate on a 1 -year bond 1 year from now is , then she should be indifferent between the two options. Make the necessary calculations and complete the following table using the data on the securities yields and the pure expectation theory. Investment Yield 1-year Treasury security, 1 year from now 2-year Treasury security, 2 years from now 3-year Treasury security, 1 year from now 4-year Treasury security, 2 years from now In two years, Option 1 will yield the following amount per $1 you invested: Yield at the end of year 2=$1(1+0.055)2=$1.113 The pure expectation theory implies that Option 2 should yield the same amount, which can be expressed as follows: Yield at the end of year 2=$1(1+0.05)(1+x)=$1.113, where x stands for the expected interest rate on a 1-year Treasury security 1 year from now. $1(1+0.05)(1+x)$1.05(1+x)(1+x)x=$1.113025=$1.113025=$1.05$1.113025=$1.05$1.1130251 Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


