Question
Suppose you have a randomized guess calculation for an amplification issue with the end goal that, for any > 0 and any issue occurrence of
Suppose you have a randomized guess calculation for an amplification issue with the end goal that, for any > 0 and any issue occurrence of size n, the calculation returns an answer with cost C to such an extent that Pr[C ? (1 ? 1/) C ? ] ? 1 exp(?1/), where C ? is the expense of the ideal arrangement. Could you at any point utilize your calculation to get a PTAS or FTPAS? Legitimize your response. [6 marks] (b) We think about the accompanying advancement issue. Given an undirected chart G = (V, E) with non-negative edge loads w : E ? R +, we are searching for an task of vertex loads x : V ? R to such an extent that: (I) for each edge {u, v} ? E, x(u) + x(v) ? w({u, v}), (ii) P v?V x(v) is just about as little as could really be expected. (I) Design a 2-estimate calculation for this issue. Additionally examine the running time and demonstrate the upper bound on the estimate proportion. Note: For full denotes, your calculation ought to run in all things considered O(E 2 ) time. Here's a clue: One method for tackling this question is to follow the methodology utilized by the insatiable guess calculation for the VERTEX-COVER issue. [8 marks] (ii) Can this issue be addressed precisely in polynomial-time? Either depict the calculation (counting a defense of its accuracy and why it is polynomial time) or demonstrate that the issue is hard through an appropriate decrease.
(a) Assume you have a randomized estimation calculation for an expansion issue, and your calculation accomplishes an estimation proportion of 2. What can you reason for E[C ? /C], where C ? is the expense of the ideal arrangement, C is the expense of the arrangement of the estimation calculation, and E[.] indicates the assumption? [4 marks] (b) Consider the accompanying streamlining issue on charts: Given an undirected, edge-weighted diagram G = (V, E, w) with w : E ? R +, we need to track down a subset S ? V to such an extent that w(S, V \ S) = P e?E(S,V \S) w(e) (the complete amount of loads over all edges among S and V \ S) is augmented. (I) Design a polynomial-time estimation calculation for this issue. Moreover investigate its running time and demonstrate an upper bound on the guess proportion. [8 marks] (ii) Find a diagram which matches your upper bound on the guess proportion from Part (b)(i) as intently as could be expected. (iii) Consider now the accompanying speculation of the issue. Given a whole number k ? 2, we need to segment V into disjoint subsets S1, S2, . . . , Sk so that we amplify X k i=1 w(Si , V \ Si). Portray an expansion of your calculation in Part (b)(i). What estimation proportion could you at any point demonstrate for this calculation?
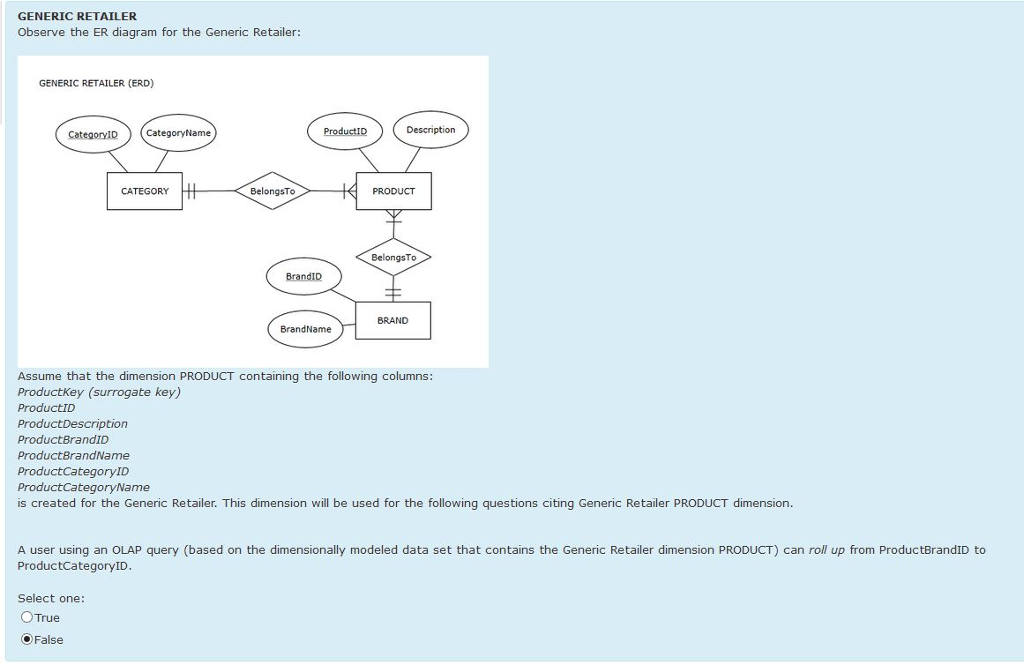

GENERIC RETAILER Observe the ER diagram for the Generic Retailer: GENERIC RETAILER (ERD) CategoryID (CategoryName CATEGORY BelongsTo $742 Select one: True OFalse BrandID ProductID BrandName Description PRODUCT Belongs To BRAND Assume that the dimension PRODUCT containing the following columns: ProductKey (surrogate key) ProductID Product Description ProductBrandID ProductBrandName ProductCategoryID ProductCategoryName is created for the Generic Retailer. This dimension will be used for the following questions citing Generic Retailer PRODUCT dimension. A user using an OLAP query (based on the dimensionally modeled data set that contains the Generic Retailer dimension PRODUCT) can roll up from ProductBrandID to ProductCategoryID.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


