Question
1. What tasks are critical to project completion? What tasks will you expedite? 2 How are you measuring system quality, and how does your recommendation
1. What tasks are critical to project completion? What tasks will you expedite?
2 How are you measuring system quality, and how does your recommendation measure up relative to that objective?
3 How much money do you make on the project?
4 What will you give the decision maker to help with the decision?
5 If we can move minimum duration days to lower values, then which values would you like to reduce?
6 If you could control additional tasks by paying more money, which ones would you like to take, and how much would you be willing to pay for control?
System Design (SD) is a small corporation that contracts to manage systems and industrial engineering projects. In this case it must manage the design and construction of a power plant’s data-processing and data-collection system. SD’s role in the project is to hire subcontractors, ensure each task is completed within specification, determine how much labor to assign to each task, and generally ensure the project’s success.
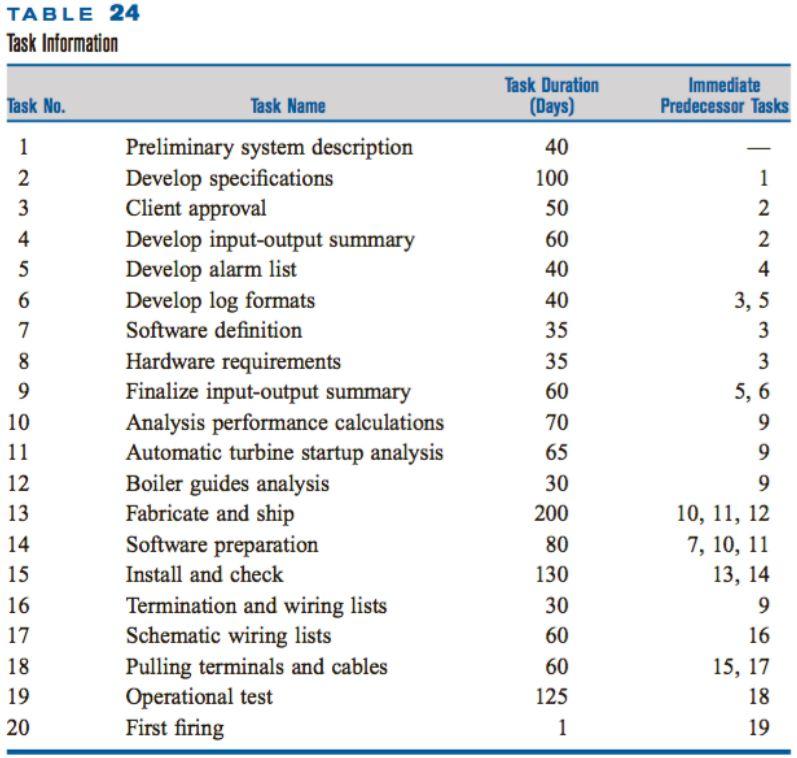
SD is really a subcontractor within the larger project of building the power plant. Table 24 details SD’s plant-construction and data-system-design tasks. SD is directly in charge of tasks 2, 6, 7, 10, 14, 15, and 19. The remaining tasks in Table 24 interact with those in SD’s charge. Assume that the remaining tasks (1) will start whenever their predecessor tasks are complete and (2) will finish exactly after their duration.
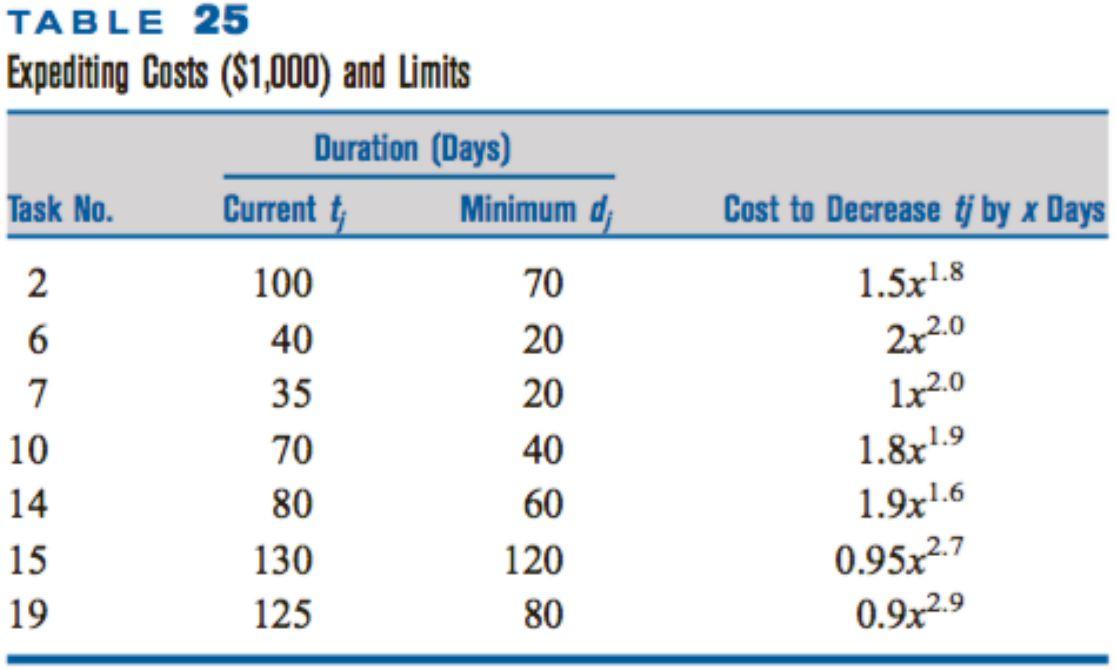
To shorten the seven SD tasks, you must pay additional labor and overhead costs. Table 25 lists the functions you can use to compute the cost of changing each task duration to a new value. (Note: t j is the original duration of task j; d j is the minimum duration of task j.) The table also lists the lowest possible task-duration value. You may not increase the duration of any task.
The revenue that SD obtains from the project depends not only on its tasks but also on when the total project is completed. The project is due at day 900, and SD receives the contract price of $600,000 if the project is done then. If the project is finished x days early, then SD receives a total of $600,000 $15,000x0.7 in revenue. If SD finishes x days late, then it receives $600,000 $20,000x1.4 in revenue.
Expediting tasks can be profitable and necessary to meet deadlines, although employees do not really like it. Task completion quality is a function of the task completion time, and we would like to have a high quality. This may conflict with our objective of maximizing profit. Because quality affects future revenues, it is difficult to estimate the dollar impact of poor quality. If t j is the original duration of task j and x j is the expedited duration time for task j, then quality, measured on a scale of 0–100 (with 100 being the best), can be represented by the function
100 - min [100, (t j - x j ) 2.2 ]
This is only the quality of a task. It is unclear how one might quantify the quality of the project.
Your job is to determine how we should proceed with our tasks.
TABLE 24 Task Information Task Duration Immediate Predecessor Tasks Task No. Task Name (Days) Preliminary system description Develop specifications Client approval Develop input-output summary Develop alarm list Develop log formats Software definition 40 2 100 1 3 50 60 2 40 4 6. 40 3, 5 7 35 3 Hardware requirements Finalize input-output summary Analysis performance calculations Automatic turbine startup analysis 8 35 3 9. 60 5, 6 10 70 11 65 9. Boiler guides analysis Fabricate and ship Software preparation 12 30 9. 13 200 10, 11, 12 14 80 7, 10, 11 15 Install and check 130 13, 14 Termination and wiring lists Schematic wiring lists Pulling terminals and cables Operational test First firing 16 30 9. 17 60 16 18 60 15, 17 19 125 18 20 1 19 1 N 4
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 Tasks that cannot be delayed without affecting the project finish date are the critical tasks In a ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


