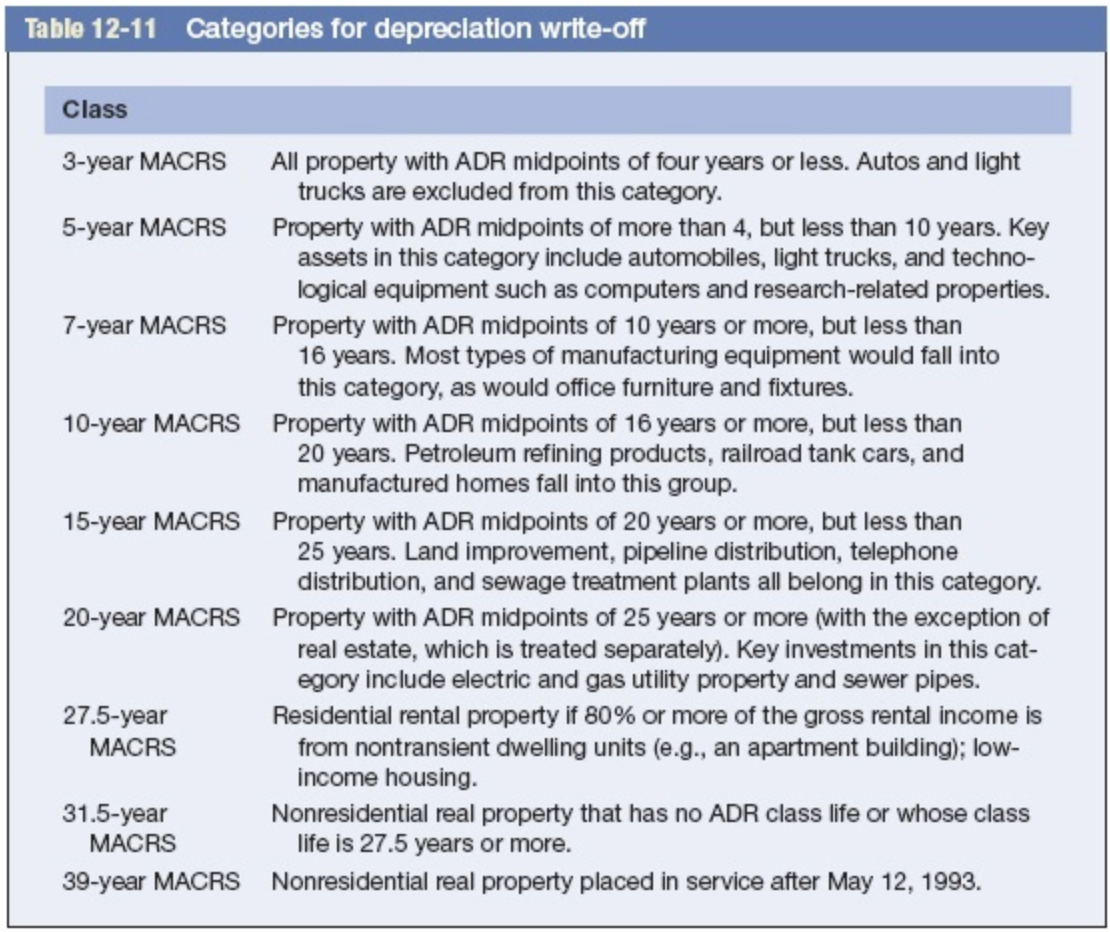
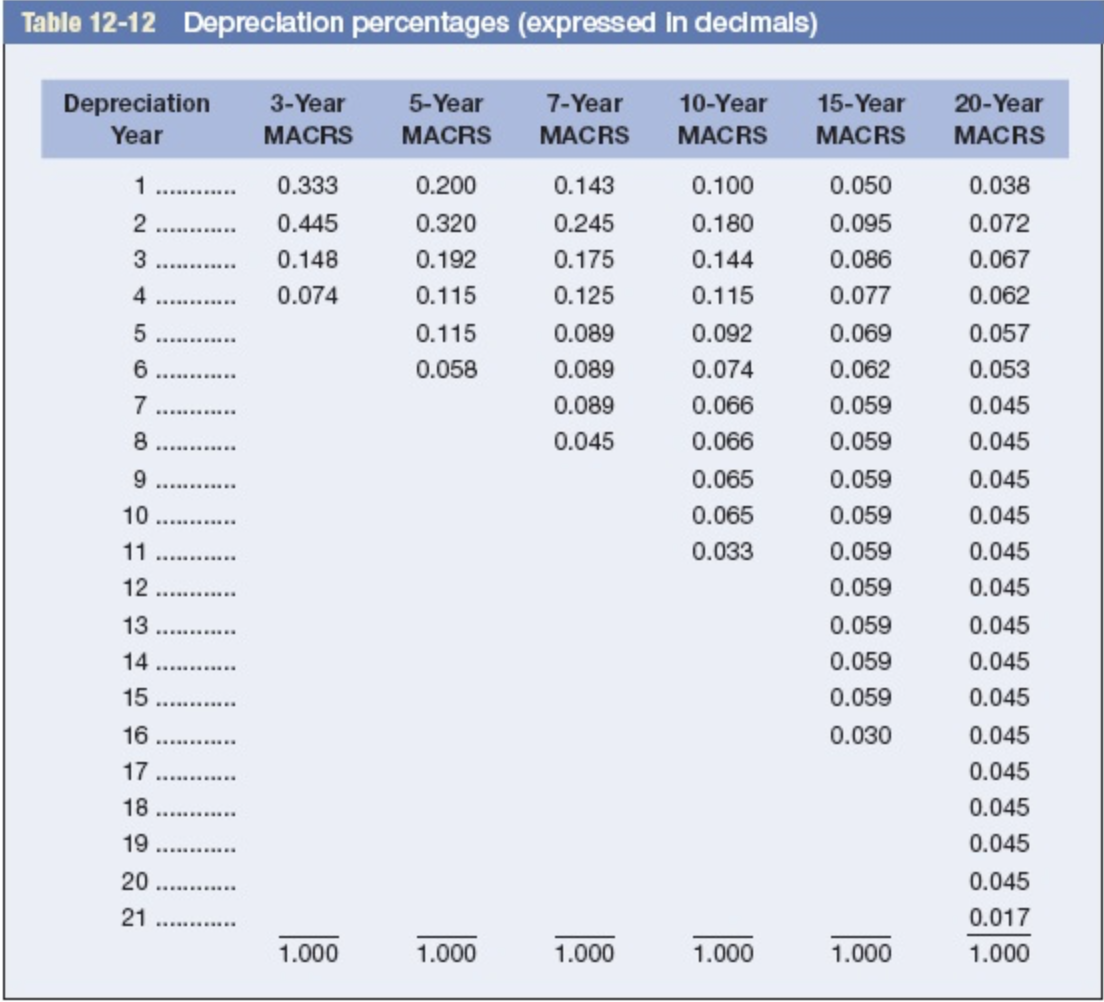
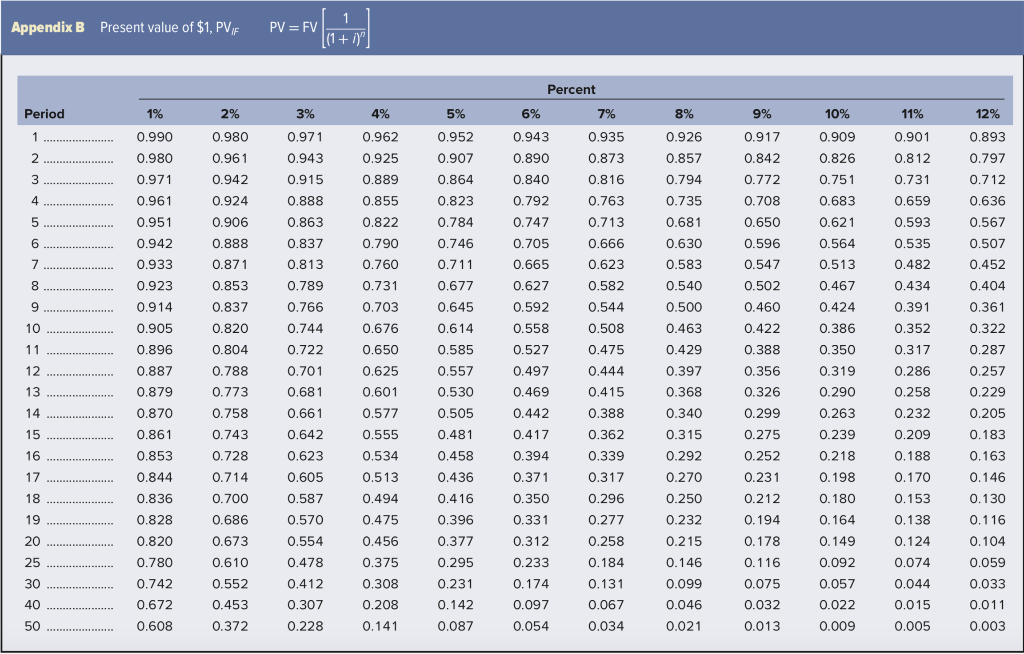
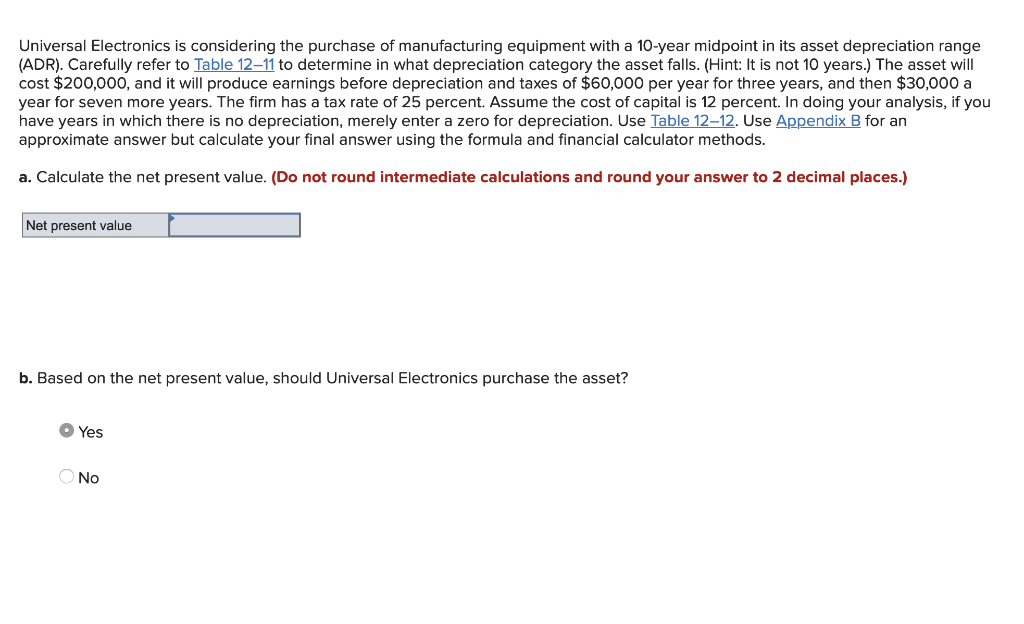
Table 12-11 Categories for depreciation write-off Class 3-year MACRS 5-year MACRS 7-year MACRS 10-year MACRS 15-year MACRS All property with ADR midpoints of four years or less. Autos and light trucks are excluded from this category. Property with ADR midpoints of more than 4, but less than 10 years. Key assets in this category include automobiles, light trucks, and techno- logical equipment such as computers and research-related properties. Property with ADR midpoints of 10 years or more, but less than 16 years. Most types of manufacturing equipment would fall into this category, as would office furniture and fixtures. Property with ADR midpoints of 16 years or more, but less than 20 years. Petroleum refining products, railroad tank cars, and manufactured homes fall into this group. Property with ADR midpoints of 20 years or more, but less than 25 years. Land improvement, pipeline distribution, telephone distribution, and sewage treatment plants all belong in this category. Property with ADR midpoints of 25 years or more (with the exception of real estate, which is treated separately). Key investments in this cat- egory include electric and gas utility property and sewer pipes. Residential rental property if 80% or more of the gross rental income is from nontransient dwelling units (e.g., an apartment building); low- income housing. Nonresidential real property that has no ADR class life or whose class life is 27.5 years or more. Nonresidential real property placed in service after May 12, 1993. 20-year MACRS 27.5-year MACRS 31.5-year MACRS 39-year MACRS Table 12-12 Depreciation percentages (expressed in decimals) Depreciation Year 3-Year MACRS 5-Year 7-Year 10-Year MACRS MACRS MACRS 15-Year MACRS 20-Year MACRS 1 0.200 0.333 0.445 0.148 0.074 0.320 0.192 0.115 0.115 0.058 0.143 0.245 0.175 0.125 0.089 0.089 0.089 0.045 0.100 0.180 0.144 0.115 0.092 0.074 0.066 0.066 0.065 0.065 0.033 7 . 0.050 0.095 0.086 0.077 0.069 0.062 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.030 10 ....... 0.038 0.072 0.067 0.062 0.057 0.053 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.017 1.000 14 ........ 15 ......... 16 ...... 17 ...... 19 . 20 ......... 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 Appendix B Present value of $1, PVF PV = Period 0 1% 0.990 0.980 0.971 0.961 0.951 0.942 0.923 0.914 0.905 0.896 2% 0.980 0.961 0.942 0.924 0.906 0.888 0.871 0.853 0.837 0.820 0.804 0.788 0.773 0.758 0.743 0.728 0.714 0.700 0.686 0.673 0.610 0.552 0.453 0.372 0.887 0.879 0.870 0.861 0.853 0.844 0.836 0.828 0.820 0.780 0.742 0.672 0.608 3% 0.971 0.943 0.915 0.888 0.863 0.837 0.813 0.789 0.766 0.744 0.722 0.701 0.681 0.661 0.642 0.623 0.605 0.587 0.570 0.554 0.478 0.412 0.307 0.228 4% 0.962 0.925 0.889 0.855 0.822 0.790 0.760 0.731 0.703 0.676 0.650 0.625 0.601 0.577 0.555 0.534 0.513 0.494 0.475 0.456 0.375 0.308 0.208 0.141 Percent 5% 6% 7% 0.952 0.943 0.935 0.907 0.890 0.873 0.864 0.840 0.816 0.823 0.792 0.763 0.784 0.747 0.713 0.746 0.705 0.666 0.711 0.665 0.623 0.677 0.627 0.582 0.6450.592 0.544 0.614 0.558 0.508 0.585 0.527 0.475 0.557 0.497 0.444 0.530 0.469 0.415 0.505 0.442 0.388 0.481 0.417 0.362 0.458 0.394 0.339 0.436 0.371 0.317 0.416 0.350 0.296 0.396 0.331 0.277 0.377 0.312 0.258 0.295 0.233 0.184 0.231 0.174 0.131 .142 0.097 0.067 0.087 0.054 0.034 8% 0.926 0.857 0.794 0.735 0.681 0.630 0.583 0.540 0.500 0.463 0.429 0.397 0.368 0.340 0.315 0.292 0.270 0.250 0.232 0.215 0.146 0.099 0.046 0.021 9% .917 0.842 0.772 0.708 0.650 0.596 0.547 0.502 0.460 0.422 0.388 0.356 0.326 0.299 0.275 0.252 0.231 0.212 0.194 0.178 0.116 0.075 0.032 0.013 10% 0.909 0.826 0.751 0.683 0.621 0.564 0.513 0.467 0.424 0.386 0.350 0.319 0.290 0.263 0.239 0.218 0.198 0.180 0.164 0.149 0.092 0.057 0.022 0.009 11% 0.901 0.812 0.731 0.659 0.593 0.535 0.482 0.434 0.391 0.352 0.317 0.286 0.258 0.232 0.209 0.188 0.170 0.153 0.138 0.124 0.074 0.044 0.015 0.005 12% 0.893 0.797 0.712 0.636 0.567 0.507 0.452 0.404 0.361 0.322 0.287 0.257 0.229 0.205 0.183 0.163 0.146 0.130 0.116 0.104 0.059 0.033 0.011 0.003 0 Universal Electronics is considering the purchase of manufacturing equipment with a 10-year midpoint in its asset depreciation range (ADR). Carefully refer to Table 12-11 to determine in what depreciation category the asset falls. (Hint: It is not 10 years.) The asset will cost $200,000, and it will produce earnings before depreciation and taxes of $60,000 per year for three years, and then $30,000 a year for seven more years. The firm has a tax rate of 25 percent. Assume the cost of capital is 12 percent. In doing your analysis, if you have years in which there is no depreciation, merely enter a zero for depreciation. Use Table 12-12. Use Appendix B for an approximate answer but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. a. Calculate the net present value. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Net present value b. Based on the net present value, should Universal Electronics purchase the asset? Yes ONo Table 12-11 Categories for depreciation write-off Class 3-year MACRS 5-year MACRS 7-year MACRS 10-year MACRS 15-year MACRS All property with ADR midpoints of four years or less. Autos and light trucks are excluded from this category. Property with ADR midpoints of more than 4, but less than 10 years. Key assets in this category include automobiles, light trucks, and techno- logical equipment such as computers and research-related properties. Property with ADR midpoints of 10 years or more, but less than 16 years. Most types of manufacturing equipment would fall into this category, as would office furniture and fixtures. Property with ADR midpoints of 16 years or more, but less than 20 years. Petroleum refining products, railroad tank cars, and manufactured homes fall into this group. Property with ADR midpoints of 20 years or more, but less than 25 years. Land improvement, pipeline distribution, telephone distribution, and sewage treatment plants all belong in this category. Property with ADR midpoints of 25 years or more (with the exception of real estate, which is treated separately). Key investments in this cat- egory include electric and gas utility property and sewer pipes. Residential rental property if 80% or more of the gross rental income is from nontransient dwelling units (e.g., an apartment building); low- income housing. Nonresidential real property that has no ADR class life or whose class life is 27.5 years or more. Nonresidential real property placed in service after May 12, 1993. 20-year MACRS 27.5-year MACRS 31.5-year MACRS 39-year MACRS Table 12-12 Depreciation percentages (expressed in decimals) Depreciation Year 3-Year MACRS 5-Year 7-Year 10-Year MACRS MACRS MACRS 15-Year MACRS 20-Year MACRS 1 0.200 0.333 0.445 0.148 0.074 0.320 0.192 0.115 0.115 0.058 0.143 0.245 0.175 0.125 0.089 0.089 0.089 0.045 0.100 0.180 0.144 0.115 0.092 0.074 0.066 0.066 0.065 0.065 0.033 7 . 0.050 0.095 0.086 0.077 0.069 0.062 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.059 0.030 10 ....... 0.038 0.072 0.067 0.062 0.057 0.053 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.017 1.000 14 ........ 15 ......... 16 ...... 17 ...... 19 . 20 ......... 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 Appendix B Present value of $1, PVF PV = Period 0 1% 0.990 0.980 0.971 0.961 0.951 0.942 0.923 0.914 0.905 0.896 2% 0.980 0.961 0.942 0.924 0.906 0.888 0.871 0.853 0.837 0.820 0.804 0.788 0.773 0.758 0.743 0.728 0.714 0.700 0.686 0.673 0.610 0.552 0.453 0.372 0.887 0.879 0.870 0.861 0.853 0.844 0.836 0.828 0.820 0.780 0.742 0.672 0.608 3% 0.971 0.943 0.915 0.888 0.863 0.837 0.813 0.789 0.766 0.744 0.722 0.701 0.681 0.661 0.642 0.623 0.605 0.587 0.570 0.554 0.478 0.412 0.307 0.228 4% 0.962 0.925 0.889 0.855 0.822 0.790 0.760 0.731 0.703 0.676 0.650 0.625 0.601 0.577 0.555 0.534 0.513 0.494 0.475 0.456 0.375 0.308 0.208 0.141 Percent 5% 6% 7% 0.952 0.943 0.935 0.907 0.890 0.873 0.864 0.840 0.816 0.823 0.792 0.763 0.784 0.747 0.713 0.746 0.705 0.666 0.711 0.665 0.623 0.677 0.627 0.582 0.6450.592 0.544 0.614 0.558 0.508 0.585 0.527 0.475 0.557 0.497 0.444 0.530 0.469 0.415 0.505 0.442 0.388 0.481 0.417 0.362 0.458 0.394 0.339 0.436 0.371 0.317 0.416 0.350 0.296 0.396 0.331 0.277 0.377 0.312 0.258 0.295 0.233 0.184 0.231 0.174 0.131 .142 0.097 0.067 0.087 0.054 0.034 8% 0.926 0.857 0.794 0.735 0.681 0.630 0.583 0.540 0.500 0.463 0.429 0.397 0.368 0.340 0.315 0.292 0.270 0.250 0.232 0.215 0.146 0.099 0.046 0.021 9% .917 0.842 0.772 0.708 0.650 0.596 0.547 0.502 0.460 0.422 0.388 0.356 0.326 0.299 0.275 0.252 0.231 0.212 0.194 0.178 0.116 0.075 0.032 0.013 10% 0.909 0.826 0.751 0.683 0.621 0.564 0.513 0.467 0.424 0.386 0.350 0.319 0.290 0.263 0.239 0.218 0.198 0.180 0.164 0.149 0.092 0.057 0.022 0.009 11% 0.901 0.812 0.731 0.659 0.593 0.535 0.482 0.434 0.391 0.352 0.317 0.286 0.258 0.232 0.209 0.188 0.170 0.153 0.138 0.124 0.074 0.044 0.015 0.005 12% 0.893 0.797 0.712 0.636 0.567 0.507 0.452 0.404 0.361 0.322 0.287 0.257 0.229 0.205 0.183 0.163 0.146 0.130 0.116 0.104 0.059 0.033 0.011 0.003 0 Universal Electronics is considering the purchase of manufacturing equipment with a 10-year midpoint in its asset depreciation range (ADR). Carefully refer to Table 12-11 to determine in what depreciation category the asset falls. (Hint: It is not 10 years.) The asset will cost $200,000, and it will produce earnings before depreciation and taxes of $60,000 per year for three years, and then $30,000 a year for seven more years. The firm has a tax rate of 25 percent. Assume the cost of capital is 12 percent. In doing your analysis, if you have years in which there is no depreciation, merely enter a zero for depreciation. Use Table 12-12. Use Appendix B for an approximate answer but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. a. Calculate the net present value. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Net present value b. Based on the net present value, should Universal Electronics purchase the asset? Yes ONo










