
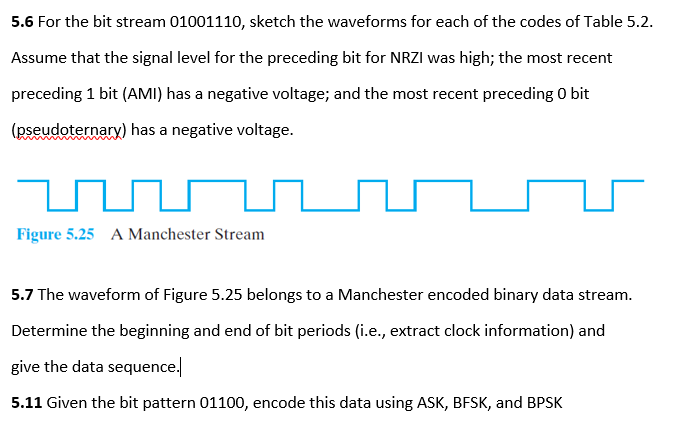
Table 5.2 Definition of Digital Signal Encoding Formats Nonreturn to Zero-Level (NRZ-L) 0 = high level 1 = low level Nonreturn to Zero Inverted (NRZI) 0 = no transition at beginning of interval (one bit time) 1 = transition at beginning of interval Bipolar-AMI 0 = no line signal 1 = positive or negative level, alternating for successive ones Pseudoternary 0 = positive or negative level, alternating for successive zeros 1 = no line signal Manchester 0 = transition from high to low in middle of interval 1 = transition from low to high in middle of interval Differential Manchester Always a transition in middle of interval 0 = transition at beginning of interval 1 = no transition at beginning of interval B8ZS Same as bipolar AMI, except that any string of eight zeros is replaced by a string with two code violations HDB3 Same as bipolar AMI, except that any string of four zeros is replaced by a string with one code violation 5.6 For the bit stream 01001110, sketch the waveforms for each of the codes of Table 5.2. Assume that the signal level for the preceding bit for NRZI was high; the most recent preceding 1 bit (AMI) has a negative voltage; and the most recent preceding O bit (pseudoternary) has a negative voltage. 5.6 For the bit stream 01001110, sketch the waveforms for each of the codes of Table 5.2. Assume that the signal level for the preceding bit for NRZI was high; the most recent preceding 1 bit (AMI) has a negative voltage; and the most recent preceding O bit (pseudoternary) has a negative voltage. Figure 5.25 A Manchester Stream 5.7 The waveform of Figure 5.25 belongs to a Manchester encoded binary data stream. Determine the beginning and end of bit periods (i.e., extract clock information) and give the data sequence. 5.11 Given the bit pattern 01100, encode this data using ASK, BFSK, and BPSK Table 5.2 Definition of Digital Signal Encoding Formats Nonreturn to Zero-Level (NRZ-L) 0 = high level 1 = low level Nonreturn to Zero Inverted (NRZI) 0 = no transition at beginning of interval (one bit time) 1 = transition at beginning of interval Bipolar-AMI 0 = no line signal 1 = positive or negative level, alternating for successive ones Pseudoternary 0 = positive or negative level, alternating for successive zeros 1 = no line signal Manchester 0 = transition from high to low in middle of interval 1 = transition from low to high in middle of interval Differential Manchester Always a transition in middle of interval 0 = transition at beginning of interval 1 = no transition at beginning of interval B8ZS Same as bipolar AMI, except that any string of eight zeros is replaced by a string with two code violations HDB3 Same as bipolar AMI, except that any string of four zeros is replaced by a string with one code violation 5.6 For the bit stream 01001110, sketch the waveforms for each of the codes of Table 5.2. Assume that the signal level for the preceding bit for NRZI was high; the most recent preceding 1 bit (AMI) has a negative voltage; and the most recent preceding O bit (pseudoternary) has a negative voltage. 5.6 For the bit stream 01001110, sketch the waveforms for each of the codes of Table 5.2. Assume that the signal level for the preceding bit for NRZI was high; the most recent preceding 1 bit (AMI) has a negative voltage; and the most recent preceding O bit (pseudoternary) has a negative voltage. Figure 5.25 A Manchester Stream 5.7 The waveform of Figure 5.25 belongs to a Manchester encoded binary data stream. Determine the beginning and end of bit periods (i.e., extract clock information) and give the data sequence. 5.11 Given the bit pattern 01100, encode this data using ASK, BFSK, and BPSK








