Question: Task 1: Cluster Analysis Use the pictures below to answer questions 1, 2, 3 ffffffTime taken to build model (full training data) : 0.01 seccnds
Task 1: Cluster Analysis
Use the pictures below to answer questions 1, 2, 3
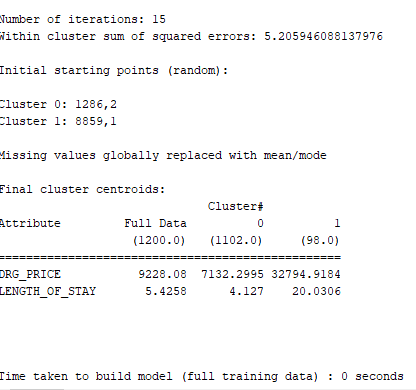

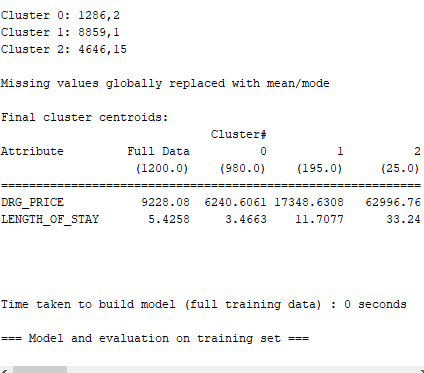

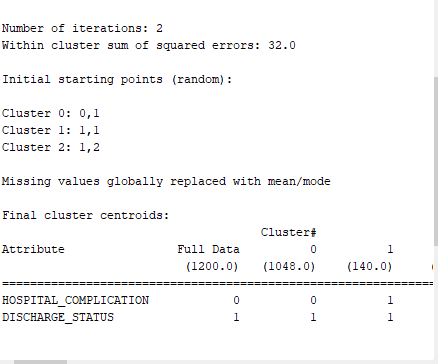
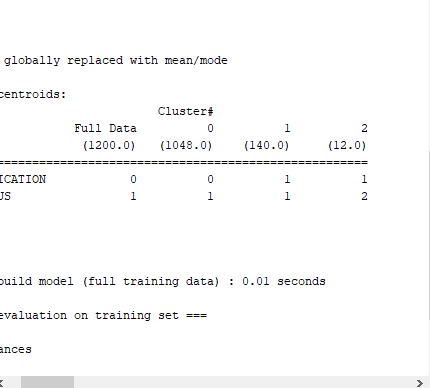






\f\f\f\f\f\fTime taken to build model (full training data) : 0.01 seccnds === Model and evaluation on training set === Clustered Instances 0 1048 [ 7%) 1 140 { 12%) 2 12 { 1%) Question 4 : Provide a description for each cluster . cluster o DRG - PRICE : 6240. 6061 LENGTH OF_STAY : 8. 4663 Number of Instances : 980 "Description : . DRG -PRICE : The average cost for patients in this cluster is relatively low , at approx . $6240. 61 . LENGTH_ OF- STAY: These patients have a shorter average hospital stay , around 3. 47 days " Number of Instances : This cluster is the largest, with 980 patient instances , indicating the most patients falls into this category . Cluster | ORG - PRICE : # 17348 . 6303 LENGTH- OF- STAY: 11- 7097 Number of Instances: 195 7 Description : . DRG - PRICE : Patients in this cluster have a moderate average cost of about $ 17 348 . 63 . LENGTH_ OF- STAY : The average stay for these patients is longer. at approx . 11. 71 days . Number of Instances : This cluster includes 195 patients instances, representing a moderate - sized group with higher costs and longer stays compared to cluster 0. . cluster 2 DRG - PRICE : 62 9 96 . 76 LENGTH_ OF- STAY : 33.24 Number of Instances: 25 7 Description : . DRG - PRICE : This cluster has the highest average cost, with patients incurring around $ 62996.76 on average . LENGTH. OF- STAY : Patients in this cluster have the longest hospital stays averaging 33.24 days . . Number of Instances : This is the smallest cluster, containing only 25 patient instances, indicating it represents a rare but significant group of patients with very high costs and long stays . page 1anestion 6 : Provide more information 7 Differences Between Two and Three Clusters 1. Number of clusters: . Two clusters : The dataset is divided into two broad categories . Three clusters : The dataset is divided into three categories , providing a more detailed segmentation . 2 . Cluster Descriptions : . Two clusters : . cluster D: Patients with relatively lower costs and shorter hospital stays . Cluster 1 : patients with higher costs and longer hospital stays . Three clusters : . chester D: Patients with lower costs and shorter hospital stays . Cluster | : Patients with moderate costs and intermediate hospital stays . cluster 2 : patients with the highest costs and longest hospital stays 3. Granularity of Insights : . Two clusters : Provides a basic understanding by dividing patients into low - cost/short- stay and high-cost / long-stay groups . Three clusters : offers a finer level of detail by adding a middle group , highlighting patients with moderate costs and stays . This helps us in understanding intermediate patterns that might be overlooked in a two- cluster model . 4. Resource Allocation: . Two clusters . simplier to manage with only two distinct groups .tasier to allocate resources broadly between two categories . . Three clusters : . Allows for more targeted resource allocation : " Cluster O ( lowest cost , shortest stay ) : General word and standard care . its cluster I ( moderate cost , intermediate stay ) : Enhanced monitoring and specialized treatments. . Cluster 2 (highest cost , longest stay ) : Intensive care units and specialized medical attention . 5. Operational Efficiency . Two clusters Basic categorization that can streamline operational processess but might miss nuances . . Three clusters More detailed segmentation can lead + optimized processes tailored to specific needs of each cluster page 7le . Financial Planning : . Two clusters Provides a broad financial overview for budgeting . three clusters . offers detailed financial insights , allowing for more precise budget planning and financial forecasting . 7 . Quality of care : . Two clusters : Broad focus on patient care strategies for two groups . Three clusters . More specific patient care strategies can be developed, improving overall patient outcomes by addressing the unique needs of each cluster . 7 which grouping is more Useful? Two clusters : . Pros : . simplicity easier to understand and manage . clearer distinction between low-cost / short-stay and high-cost / long- stay patients . . cons : . Oversimplification : May miss intermediate patterns and mances . Three clusters : Pros : . Granularity : offers more detailed insights , capturing intermediate patterns " Better Resource Allocation : More precise targeting of resources Enhanced Understanding : Provides a clearer picture of patient profiles, aiding in more informed decision- making . . Improved care strategies : Tailored strategies for each specific cluster can improve patient outcomes . . Cons : . complexity : Slightly more complex to manage and interpret . Requires more detailed analysis to leverage the full benefits Final Assessment : - Thee three cluster grouping is generally more useful in terms of understanding and differentiating different patient profiles , It provides a more nuanced view , allowing for more precise resuurce allocation , better financial planning , and improved patient care strategies . The additional detail helps in identifying and addressing the needs of patients with moderate costs and intermediate stays , which might be overlooked in a simpler two - cluster model . page 3Question 7 Cluster 0 Number of Instances : 1048 ( 87 2 ) . Hospital - complications : 0 ( NO complication ) . Discharge - STATUS . I ( Discharged healthy ) Description : . Hospital- complications : This cluster represents patients who did not experience any complications during their hospital days " Discharged- status : Allpatients in this cluster where discharged healthy " Implications : The's is the largest cluster, indicating that the majority of patients had a smooth recovery with no implications , reflecting effective hospital care for most patients . Cluster 1 . Number of instances: 140 ( 12 2 ) . Hospital - complications : 1 ( complications occured ) . Discharge - status : I ( Discharged healthy ) Description : . Hospital . complications : patients in this cluster experienced some complications during their hospital stay . . Discharged . status: Despite the complications, these patients were discharged in good health . Implications : This cluster suggests that while some patients faced complications , the hospital was able to manage these issues effectively , resulting in healthy discharges . This group represents patients who needed more intensive care but ultimately recovered well . Cluster 2 * Number of instances: 12 (12 ) . Hospital _ complications : 1 ( complications occured ) . Discharged . Status : 2 ( Discharged in critical condition ) Description : . Hospital - complications : Patients in this cluster experienced complications cluring their hospital stay . . Discharged - status : These patients were discharged in critical condition. suggesting that they did not fully recover by the time of discharged. . Implications for Patient Safety : . High- Risk Group: This small cluster highlights a high-risk group of patients who experienced significant complications and were discharged in a critical state . . Need for Enhanced care : Indicates a need for enhanced monitoring . more intensive care and possibly improved discharge planning to ensure better outcomes. page 4. Follow - Up and Support : Emphasizes the importance of thorough post- discharge follow-up and support for these patients to prevent further deterioration and potential re-admission . . Quality Improvement . Suggests potential areas for quality improvement in hospital procedures and patient care strategies to reduce the number of patients discharged in critical condition . Question 8 : . Effect of Increasing the Number of Clusters 1 . Overfitting . Increasing the number of clusters can lead to overfitting , where the model captures noise and outliers rather than meaningful patterns . Overfitting can result in clusters that are not generalize or practically useful . 2. Less Distinguishable Clusters : . As the number of clusters increases , the clusters may become less distinct and harder to interpret . . Clusters might become too small, providing less statistically significant insights. 3 . Increased complexity : . More clusters increase the complexity of the model , making it more challenging to manage and interpret the results . . It requires more detailed analysis and may not provide additional value . . strategy to choose an Appropriate Number of clusters ( + ) (2 ) In addition to my previous answers which are Elbow method , silhouette score, and Domain knowledge . 4. cross - Validation . use cross- validation to assess The stability and validy of the clusters. . Ensure that the clustering results are consistent across different subsets of the data . 5. Business Context . Align the number of clusters with business goals or research questions. . Ensure that the clusters provide actionable insights that can inform decision - making G . practical considerations . . Balance the trade-off between complexity and interpretability . Avoid over- complicating the model with too many clusters while ensuring that the clustering captures essential patterns and distinctions in the data . page 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


