Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Task 3 Vibration Analysis of A Stepped Euler-Bernoulli Beam (30 points) Figure 4 shows a stepped beam of two uniform segments, which is constrained
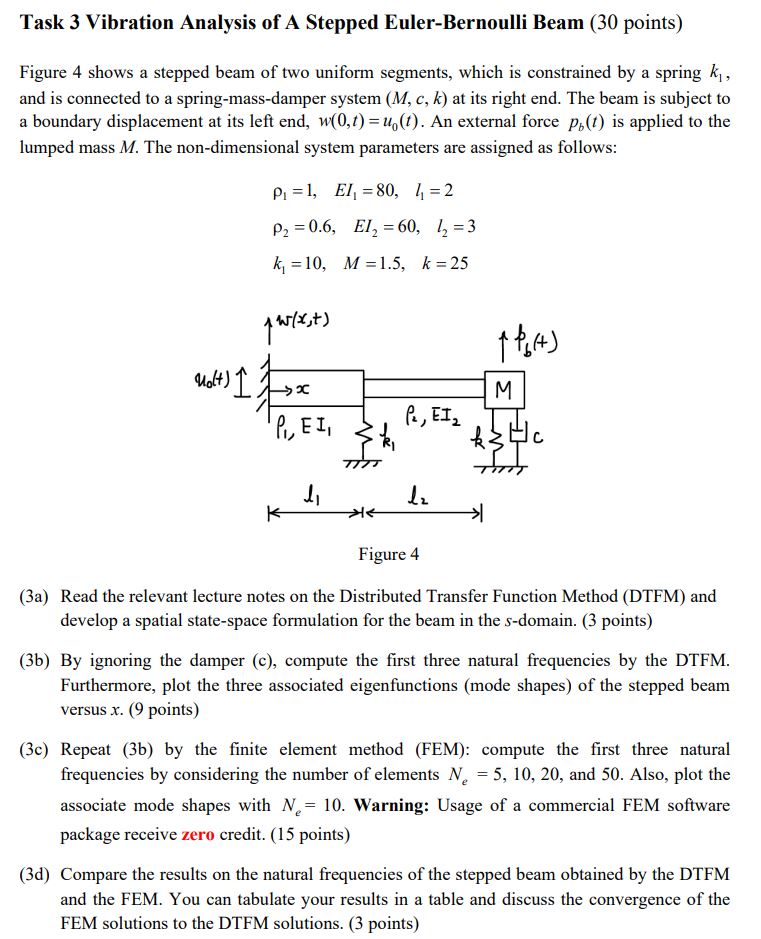
Task 3 Vibration Analysis of A Stepped Euler-Bernoulli Beam (30 points) Figure 4 shows a stepped beam of two uniform segments, which is constrained by a spring k, and is connected to a spring-mass-damper system (M, c, k) at its right end. The beam is subject to a boundary displacement at its left end, w(0,t) = u(t). An external force p,(t) is applied to the lumped mass M. The non-dimensional system parameters are assigned as follows: P = 1, EI = 80, 4 =2 P2 = 0.6, E12=60, 2=3 k =10, M 1.5, k = 25 w(x,t) +64) Molt) 1 ->x M P, EI, P, EI 4, 12 > < Figure 4 (3a) Read the relevant lecture notes on the Distributed Transfer Function Method (DTFM) and develop a spatial state-space formulation for the beam in the s-domain. (3 points) (3b) By ignoring the damper (c), compute the first three natural frequencies by the DTFM. Furthermore, plot the three associated eigenfunctions (mode shapes) of the stepped beam versus x. (9 points) (3c) Repeat (3b) by the finite element method (FEM): compute the first three natural frequencies by considering the number of elements N = 5, 10, 20, and 50. Also, plot the associate mode shapes with N = 10. Warning: Usage of a commercial FEM software package receive zero credit. (15 points) (3d) Compare the results on the natural frequencies of the stepped beam obtained by the DTFM and the FEM. You can tabulate your results in a table and discuss the convergence of the FEM solutions to the DTFM solutions. (3 points)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


