Question
Thank you in advance for the help. We are expected to write a the above program in C Language via linux terminal. Here is the
Thank you in advance for the help.

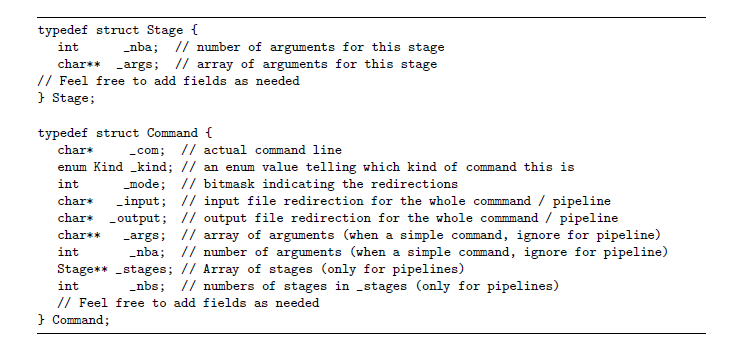
We are expected to write a the above program in C Language via linux terminal.
Here is the shellp.h file:
#ifndef SHELLP_H #define SHELLP_H
enum Kind { noCMD,exitCMD,cdCMD,pwdCMD,linkCMD,rmCMD,basicCMD,pipelineCMD };
typedef struct Stage { int _nba; char** _args; // Feel free to add fields as needed } Stage;
typedef struct Command { char* _com; enum Kind _kind; int _mode; char* _input; char* _output; char** _args; int _nba; Stage** _stages; int _nbs; // Feel free to add fields as needed } Command;
#define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0
// A pipeline "object" contains // 1. An array of nbStages stages // 2. A mode flag to determine whether // - the pipeline input is redirected // - the pipeline output is redirected // Each stage is a structure that encapsulates // - The number of arguments // - Each argument (in string form) // BY DEFAULT THE MAIN PROGRAM CALLS THE PRINT METHOD OF THE COMMAND // OBJECT. So you can see how the pipeline description is represented/stored // Your objective: // * Implement the execute method to create and execute the entire pipeline. // Hint: all the systems calls seen in class will be useful (fork/exec/open/close/pipe/....)
#endif
Here is the shellp.c file:
#include
char *strdup(const char *s);
// Check the bottom of this file to locate the method you must implement. // You do not need to read all provided code, but you are encouraged to // do so if you want to experiment/understand more details about the program.
#define R_NONE 0 /* No redirections */ #define R_INP 1 /* input redirection bit */ #define R_OUTP 2 /* output redirection bit */ #define R_APPD 4 /* append redirection bit */
#define MAXRD 255
Stage* allocStage(int nba,char** args); void freeStage(Stage*); void printStage(Stage*); Command* addCommandStage(Command* c,Stage* s);
int extractRedirect(char* buf,int* len,int* mode,char* input,char* output);
char* skipWS(char* arg); char* cutWord(char* arg); int trimString(char* buf,int len);
Command* allocCommand(char* c) { Command* r = (Command*)calloc(1,sizeof(Command)); r->_com = NULL; r->_kind = noCMD; r->_mode = R_NONE; return r; } void freeCommand(Command* c) { if (c->_com) free(c->_com); if (c->_input) free(c->_input); if (c->_output) free(c->_output); for(int i=0;i _nba;i++) if (c->_args[i]) free(c->_args[i]); free(c->_args); for(int j=0;j
Command* setCommand(Command* c,enum Kind k,char* com) { c->_kind = k; if (c->_com) free(c->_com); c->_com = strdup(com); return c; } Command* setCommandArgs(Command* c,int nb,char** args) { c->_nba = nb + 1; c->_args = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*)*c->_nba); for(int i=0;i
Command* addCommandStage(Command* c,Stage* s) { printf("New stage:"); printStage(s);
c->_stages = realloc(c->_stages,sizeof(Stage*)*(c->_nbs + 1)); c->_nbs += 1; c->_stages[c->_nbs - 1] = s; return c; }
void printCommand(Command* c) { if (c->_mode & R_INP) printf("_input); if (c->_mode & R_OUTP) printf("> [%s] ",c->_output); if (c->_mode & R_APPD) printf(">> [%s] ",c->_output); printf("CORE: %s ",c->_com); for(int i=0;i
Command* makeCommand() { char buffer[1024]; int i = 0; char ch,*ptr; printf("%%");fflush(stdout); while(i
buffer[i] = 0; ptr = buffer+i-1; while(ptr>=buffer && isspace(*ptr)) ptr--,i--; *++ptr = 0; Command* c = allocCommand(ptr); if(ch==EOF) return setCommand(c,exitCMD,"exit"); else { int mode = R_NONE; char input[1024]; char output[1024]; *input = *output = 0; int len = strlen(buffer); int ok = extractRedirect(buffer,&len,&mode,input,output); c->_mode = mode; c->_input = strdup(input); c->_output = strdup(output); len = trimString(buffer,len); if (ok) { char* sc = skipWS(buffer); char* ec = cutWord(sc); if (strcmp(sc,"cd")==0) { char* a0 = skipWS(ec); char* a1 = cutWord(a0); char* args[1] = {a0}; return setCommandArgs(setCommand(c,cdCMD,sc),1,args); } else if (strcmp(sc,"pwd")==0) { return setCommand(c,pwdCMD,sc); } else if (strcmp(sc,"ln") == 0) { char* a0 = skipWS(ec); char* a1 = skipWS(cutWord(a0)); char* a2 = cutWord(a1); char* args[2] = {a0,a1}; return setCommandArgs(setCommand(c,linkCMD,sc),2,args); } else if (strcmp(sc,"rm") == 0) { char* a0 = skipWS(ec); char* a1 = cutWord(a0); char* args[1] = {a0}; return setCommandArgs(setCommand(c,rmCMD,sc),1,args); } else if (strcmp(sc,"exit") == 0) { return setCommand(c,exitCMD,sc); } else { if (*sc) { if (strchr(ec,'|') != NULL) { // This is a pipeline. char* args[512]; args[0] = sc; char* arg = skipWS(ec); int nba = 1; setCommand(c,pipelineCMD,""); while(arg && *arg) { char* p = *arg == '|' ? arg : 0; if (p) { *p = 0; addCommandStage(c,allocStage(nba,args)); args[0] = arg = skipWS(p+1); arg = cutWord(arg); nba = 1; } else { args[nba++] = arg; arg = skipWS(cutWord(arg)); } } return addCommandStage(c,allocStage(nba,args)); } else { char* args[1024]; args[0] = sc; char* arg = ec; int nba = 1; while(arg && *arg) { args[nba++] = arg; arg = skipWS(cutWord(arg)); assert(nba
#define IS_REDIR(ch) ((ch) == '')
/* The routine extracts any redirects and replaces those parts of the command by whitespaces */
int extractRedirect(char* buf,int* len,int* mode,char* input,char* output) { int i = 0; char* ptr = buf; while(ptr && *ptr) { if (IS_REDIR(*ptr)) { if (ptr[0]== '=MAXRD) { printf("redirect filename too long "); return 0; } input[i++] = *ptr; *ptr++ = ' '; } input[i] = 0; *mode = *mode | R_INP; } } else if (ptr[0]=='>' && ptr[1]=='>') { if (*mode & (R_APPD | R_OUTP)) { printf("Ambiguous output redirect "); return 0; } else { ptr[0] = ' '; ptr[1] = ' '; ptr += 2; i = 0; while(isspace(*ptr)) ptr++; while(isalnum(*ptr) || ispunct(*ptr)) { if (i>=MAXRD) { printf("redirect filename too long "); return 0; } output[i++] = *ptr; *ptr++ = ' '; } output[i] = 0; *mode = *mode | R_APPD; } } else { if (*mode & (R_APPD | R_OUTP)) { printf("Ambiguous output redirect "); return 0; } else { assert(ptr[0]=='>'); *ptr++ = ' '; i = 0; while(isspace(*ptr)) ptr++; while(isalnum(*ptr) || ispunct(*ptr)) { if (i>=MAXRD) { printf("redirect filename too long "); return 0; } output[i++] = *ptr; *ptr++ = ' '; } output[i] = 0; *mode = *mode | R_OUTP; } } } else ptr++; } return 1; }
char* skipWS(char* arg) { while(arg && *arg && isspace(*arg)) arg++; if(arg && *arg=='\"') arg++; return arg; }
char* cutWord(char* arg) { while(arg && *arg && !isspace(*arg)) arg++; if(*(arg-1)=='\"') arg--; if (arg && *arg) *arg++ = 0; return arg; }
int trimString(char* buf,int len) { char* ptr = buf + len - 1; while(ptr>=buf && isspace(*ptr)) ptr--,len--; *++ptr = 0; return len; }
// ================================================================================ // This part of the file contains the PipelineCommand object that you must modify // ================================================================================ Stage* allocStage(int nba,char** args) { Stage* s = (Stage*)calloc(1,sizeof(Stage)); s->_nba = nba + 1; s->_args = (char**)calloc(s->_nba,sizeof(char*)); for(int i=0;i
void freeStage(Stage* s) { for(int i=0;i
void printStage(Stage* s) { printf("\t(%d)[",s->_nba); for(int i=0;i
// ================================================================================ // Write the pipelining logic here. // ================================================================================
int setupCommandPipeline(Command* c) { // TODO: Implement the pipeline commmand. return 1; }
// ================================================================================ // Write the basic command logic here. // ================================================================================
int basicExecute(char* com,int mode,char* input,char* output,char** args) { //TODO: Implement the basic command logic here. return 1; }
int executeCommand(Command* c) { switch(c->_kind) { case cdCMD: { int st = chdir(c->_args[0]); if (st==-1) printf("cd error: [%s] ",strerror(errno)); return TRUE; }break; case pwdCMD: { char buf[1024]; char* ptr = getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf)); if (ptr) printf("cwd: %s ",buf); return TRUE; }break; case exitCMD: return FALSE; case linkCMD: { int rv = link(c->_args[0],c->_args[1]); if (rv!=0) printf("link error [%s] ",strerror(errno)); return TRUE; }break; case rmCMD: { int rv = unlink(c->_args[0]); if (rv!=0) printf("rm error: [%s] ",strerror(errno)); return TRUE; }break; case basicCMD: { return basicExecute(c->_com,c->_mode,c->_input,c->_output,c->_args); }break; case pipelineCMD: { setupCommandPipeline(c); return TRUE; }break; default: printf("oops.... "); return TRUE; } }
int main(int argc,char* argv[]) { int loop = 1; while(loop) { Command* com = makeCommand(); printCommand(com); loop = executeCommand(com); freeCommand(com); } return 0; }
Exercise 1. Basic command (40 points) Consider a simple shell command relying on an external executable. For instance, the cat command (found as the executable /usr/bin/cat) is used to "copy" its standard input to its standard output. Ifgiven an argument, it will instead copy the file whose name is given as argument to its standard output. For instance, the command cat hello.txt sends to the standard output the content of the file named hello.txt. Similarly, the fragment cat hello.txt > foo.txt uses a file redirection to sendthe standardoutput ofcat tothe file namedfoo.txt, effectively creating a copy ofhello.txt in foo.txt. Your first task is to find in shellp.c the function int basicExecute(char* com,int mode,char* input, char* output, char* args) //TODO: Implement this basic command return 1; and implement its body. The interface of the fiunction isquite straightforward and the arguments are described belouw com the fiell name to the binary of the executable to run mode an integer whose bits indicate the kind of file redirections. When equal to R_NONE, there are no redirections. Ifbit R_INP is set, the input is redirected. If bit R_OUTP is set the output is redirected. If bit R_APPD is send, the output is redirected and we should append at the end of the specified file. input an argument which is only defined ifR_ INP is set. output an argument which is only defined ifR OUTP or RAPPD is set. args an array of strings holding the arguments that must be passed to the command com. The first argument is the ececutable path and the last one is NULL The first step is to setup the logic for forking and executing the child process. The second step is to use the mode argument along with input and output to setup the file redirections (if present). [Basic example]The earlier example cat hello.txt > foo.txt is handled by a call to basicExecute where com is the string "fusr/bin/cat, mode is equal to R_OUTP since the output is redirected, input is NULL since we are not redirecting the input andoutput is the name of the target file, ie, footxt". Finally, args is aqwal tPaello .txt , ,NULI.] , an array with two entries representing the argument passed to the cat command
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


