Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The 1 N force upward due to the hand and the 1 N force downward due to gravity sum to a net force of
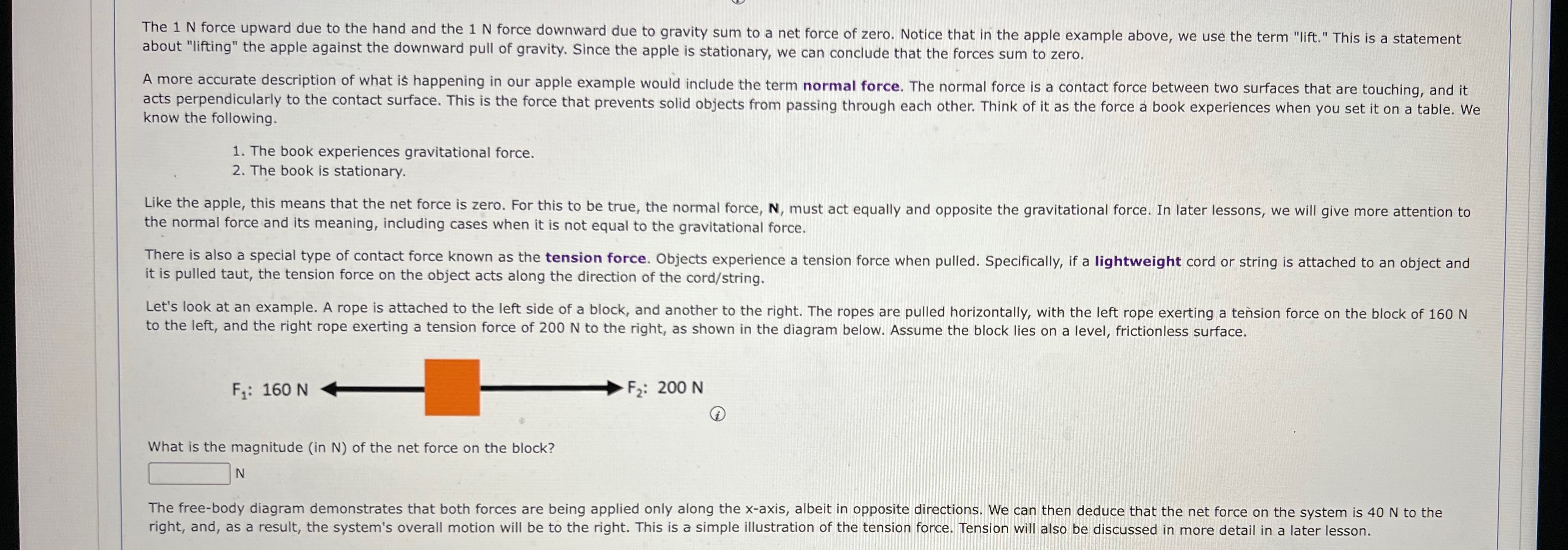
The 1 N force upward due to the hand and the 1 N force downward due to gravity sum to a net force of zero. Notice that in the apple example above, we use the term "lift." This is a statement about "lifting" the apple against the downward pull of gravity. Since the apple is stationary, we can conclude that the forces sum to zero. A more accurate description of what is happening in our apple example would include the term normal force. The normal force is a contact force between two surfaces that are touching, and it acts perpendicularly to the contact surface. This is the force that prevents solid objects from passing through each other. Think of it as the force a book experiences when you set it on a table. We know the following. 1. The book experiences gravitational force. 2. The book is stationary. Like the apple, this means that the net force is zero. For this to be true, the normal force, N, must act equally and opposite the gravitational force. In later lessons, we will give more attention to the normal force and its meaning, including cases when it is not equal to the gravitational force. There is also a special type of contact force known as the tension force. Objects experience a tension force when pulled. Specifically, if a lightweight cord or string is attached to an object and it is pulled taut, the tension force on the object acts along the direction of the cord/string. Let's look at an example. A rope is attached to the left side of a block, and another to the right. The ropes are pulled horizontally, with the left rope exerting a tension force on the block of 160 N to the left, and the right rope exerting a tension force of 200 N to the right, as shown in the diagram below. Assume the block lies on a level, frictionless surface. F: 160 N F2: 200 N What is the magnitude (in N) of the net force on the block? N The free-body diagram demonstrates that both forces are being applied only along the x-axis, albeit in opposite directions. We can then deduce that the net force on the system is 40 N to the right, and, as a result, the system's overall motion will be to the right. This is a simple illustration of the tension force. Tension will also be discussed in more detail in a later lesson.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


