Question
The 10 description items below belong on the balance sheet. I need help with which categories those items belong. For example, where I would place
The 10 description items below belong on the balance sheet. I need help with which categories those items belong. For example, where I would place the decription for number 1 on the spreadsheet to help balance.
Bramos Printing Company
The Bramos Printing Company was founded in 2000 by Mr. Timken as a one-man-job printing firm in a small southwestern town. Shortly after its founding, the owner decided to concentrate on one specialty line of printing. Because of a high degree of technical proficiency, the company experienced a rapid growth.
However, the company suffered from a competitive disadvantage in that the major market for this specialized output was in a metropolitan area over 300 miles away from the companys plant. For this reason, the owner, in 2012, decided to move nearer his primary market. He also decided to expand and modernize his facilities at the time of the move. After some investigation, an attractive site was found in a suburb of his primary market, and the move was made.
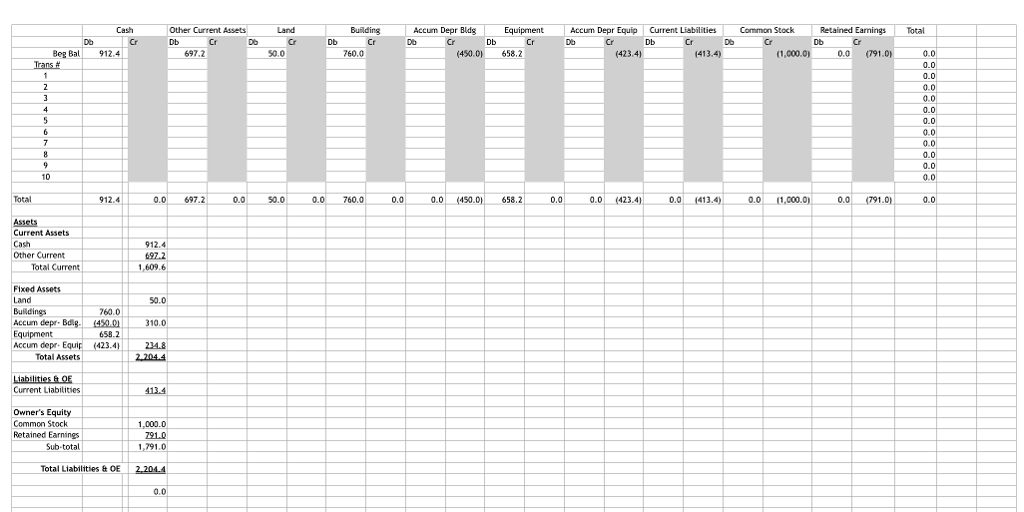
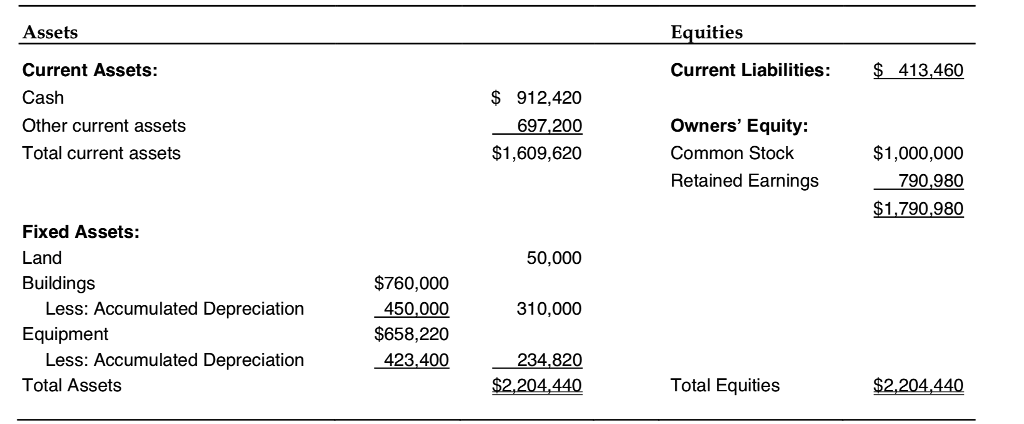
A balance sheet prepared prior to the move is shown in Exhibit 1. The transactions that arose from this move are described in the following paragraphs:
1. The land at the old site together with the building thereon was sold for $350,000. The land had originally cost $50,000. The building appeared on the companys books at a cost of $760,000 and a depreciation allowance of $450,000 had been accumulated on it.
2. Certain equipment was sold for $45,000 cash. This equipment appeared on the books at a cost of $167,000, less accumulated depreciation of $97,000.
3. New bindery equipment was purchased. The invoice cost of this equipment was $200,000. A 2% discount was taken by the Bramos Company, so that only $196,000 was actually paid to the seller. The Bramos Company also paid $800 to a trucker to have this equipment delivered. Installation of this equipment was made by Bramos workmen who worked a total of 40 hours. These men received $15.00 per hour in wages, but their time was ordinarily charged to printing jobs at $40.00 per hour, the difference representing an allowance for overhead ($21.00) and profit ($4.00).
4. The company purchased land for $200,000 in cash.
5. The Bramos Company paid $40,000 to have an old building on the plot of land torn down. In addition, the company paid $20,000 to have permanent drainage facilities installed on the new land.
6. A new strip caster with an invoice cost of $45,000 was purchased. The company paid $30,000 cash and received a trade-in allowance of $15,000 on a used strip caster. The used strip caster could have been sold outright for not more than $12,000. It had cost $30,000 new, and accumulated depreciation on it was $12,000. The design and technology of the new strip caster was dissimilar to that of the used strip caster traded in for the new strip caster.
7. The company erected a building at the new site for $900,000. Of this amount, $700,000 was borrowed on a mortgage.
8. After the equipment had been moved to the new plant, but before operations began there, extensive repairs and replacement of parts were made on a large paper cutter. The cost of this work was $11,000. Prior to this time, no more than $1,000 had been spent in any one year on the maintenance of this paper cutter.
9.Trucking and other costs associated with moving equipment to the new location and installing it there were $14,000.
10. During the moving operation, a piece of equipment costing $30,000 was dropped and damaged. $4,000 was spent to repair it. Mr. Timken believed, however, that the salvage value of this equipment was reduced to $2,000. Up until that time, the equipment was being depreciated at $2,400 per year, representing a 10% rate after deduction of estimated salvage of $6,000. Accumulated depreciation was $9,600.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


