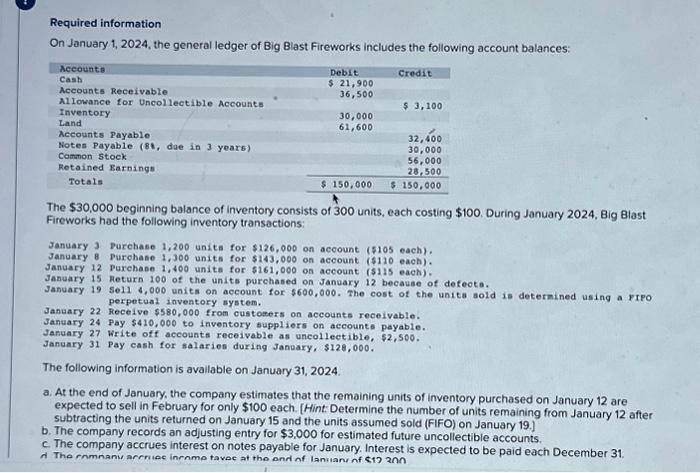
The $30,000 beginning balance of inventory consists of 300 units, each costing $100. During January 2024, Big Blast Fireworks had the following inventory transactions: January 3 Purchase 1,200 units for $126,000 on account ( $105 each). January 8 Purchase 1,300 units for $143,000 on account ( $110 each). January 12 Purchase 1,400 units for $161,000 on account ($115 each). January 15 Return 100 of the units purchased on January 12 because of defects. January 19 sel1 4,000 units on account for $600,000. The cost of the units sold is determined using a FrFo perpetual inventory system. January 22 Receive $80,000 fron custoners on accounts receivable. January 24 Pay $410,000 to inventory suppliers on accounts payable. January 27 Write off accounts receivable as uncollectible, $2,500. Jasuary 31 Pay eash for salaries during January, $128,000. The following information is available on January 31,2024 a. At the end of January, the company estimates that the remaining units of inventory purchased on January 12 are expected to sell in February for only $100 each. [Hint: Determine the number of units remaining from January 12 after subtracting the units returned on January 15 and the units assumed sold (FIFO) on January 19.] b. The company fecords an adjusting entry for $3,000 for estimated future uncollectible accounts. c. The company accrues interest on notes payable for January. Interest is expected to be paid each December 31. d. The company accrues income taxes at the end of January of $12,300. 6. Record closing entries. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Required information On January 1, 2024, the general ledger of Big Blast Fireworks includes the following account balances: The $30,000 beginning balance of inventory consists of 300 units, each costing $100. During January 2024,8ig Biast Fireworks had the following inventory transactions: January 3 Purchase 1,200 units for $126,000 on account ( $105 each). January 8 purchase 1,300 units for $143,000 on account ( $110 each). January 12 purchase 1,400 units for $161,000 on account ( $115 each). January 15 Return 100 of the units purchased on January 12 because of defecta. January 19 Sel1 4,000 units on account for $600,000. The cost ot the units sold is determined using a Y IPO perpetual inventory system. January 22 Recelve $580,000 from customers on accounts receivable. January 24 pay $410,000 to inventory suppliers on accounts payable. January 27 Write off accounts receivable as uncollectible, $2,500. January 31 Pay cash for salaries during Janaary, $128,000. The following information is available on January 31,2024. a. At the end of January, the company estimates that the remaining units of inventory purchased on January 12 are expected to sell in February for only $100 each. [Hint: Determine the number of units remaining from January 12 after subtracting the units returned on January 15 and the units assumed sold (FIFO) on January 19.] b. The company records an adjusting entry for $3,000 for estimated future uncollectible accounts. c. The company accrues interest on notes payable for January. Interest is expected to be paid each December 31. 6. Record closing entries, (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Journal entry worksheet Record the closing entry for revenue accounts. Note: Enter debits before credits