Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The Bienestar Cardiology Clinic has two major activities: diagnostic and treatment. The two activities use four resources: nursing, medical technicians, cardiologists, and equipment. Detailed
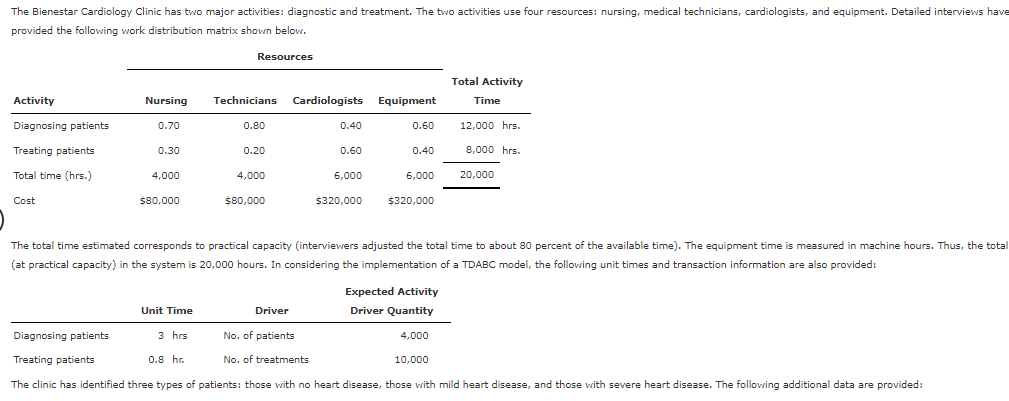
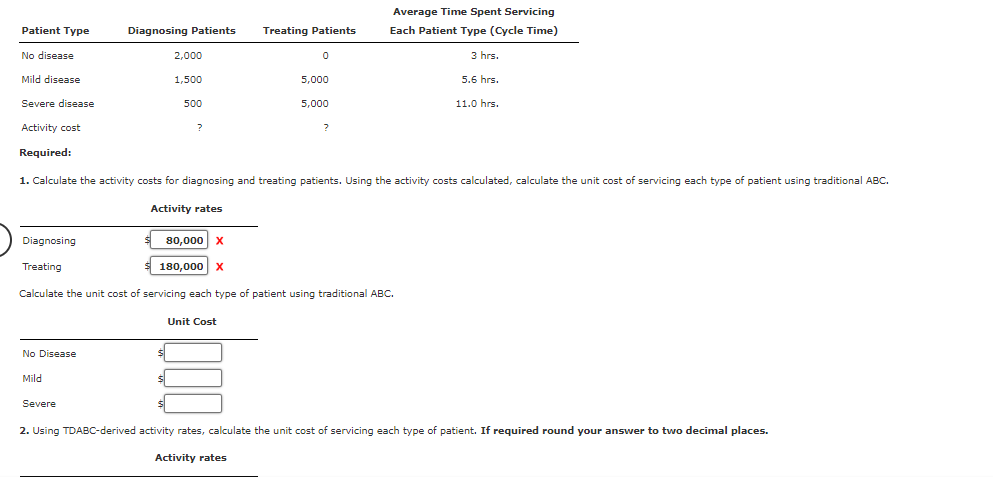

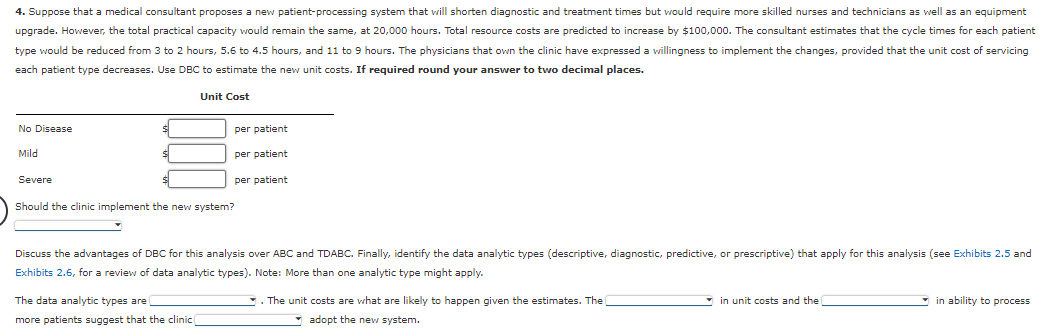
The Bienestar Cardiology Clinic has two major activities: diagnostic and treatment. The two activities use four resources: nursing, medical technicians, cardiologists, and equipment. Detailed interviews have provided the following work distribution matrix shown below. Resources Activity Nursing Technicians Cardiologists Equipment Total Activity Time Diagnosing patients 0.70 0.80 0.40 0.60 12,000 hrs. Treating patients 0.30 0.20 0.60 0.40 8,000 hrs. Total time (hrs.) 4,000 4,000 6,000 6,000 20,000 Cost $80,000 $80,000 $320,000 $320,000 The total time estimated corresponds to practical capacity (interviewers adjusted the total time to about 80 percent of the available time). The equipment time is measured in machine hours. Thus, the total (at practical capacity) in the system is 20,000 hours. In considering the implementation of a TDABC model, the following unit times and transaction information are also provided: Unit Time Driver Expected Activity Driver Quantity Diagnosing patients 3 hrs No. of patients 4,000 Treating patients 0.8 hr. No. of treatments 10,000 The clinic has identified three types of patients: those with no heart disease, those with mild heart disease, and those with severe heart disease. The following additional data are provided: Average Time Spent Servicing Patient Type Diagnosing Patients Treating Patients Each Patient Type (Cycle Time) No disease 2,000 0 3 hrs. Mild disease 1,500 5,000 5.6 hrs. Severe disease 500 5,000 11.0 hrs. Activity cost ? ? Required: 1. Calculate the activity costs for diagnosing and treating patients. Using the activity costs calculated, calculate the unit cost of servicing each type of patient using traditional ABC. Activity rates Diagnosing Treating 80,000 X 180,000 X Calculate the unit cost of servicing each type of patient using traditional ABC. No Disease Unit Cost Mild Severe 2. Using TDABC-derived activity rates, calculate the unit cost of servicing each type of patient. If required round your answer to two decimal places. Activity rates 2. Using TDABC-derived activity rates, calculate the unit cost of servicing each type of patient. If required round your answer to two decimal places. Activity rates Diagnosing Treating Unit Cost No Disease Mild Severe 3. Using DBC, calculate the unit cost of servicing each type of patient. If required round your answer to two decimal places. Unit Cost No Disease Mild Severe per patient per patient per patient 4. Suppose that a medical consultant proposes a new patient-processing system that will shorten diagnostic and treatment times but would require more skilled nurses and technicians as well as an equipment upgrade. However, the total practical capacity would remain the same, at 20,000 hours. Total resource costs are predicted to increase by $100,000. The consultant estimates that the cycle times for each patient type would be reduced from 3 to 2 hours, 5.6 to 4.5 hours, and 11 to 9 hours. The physicians that own the clinic have expressed a willingness to implement the changes, provided that the unit cost of servicing each patient type decreases. Use DBC to estimate the new unit costs. If required round your answer to two decimal places. Unit Cost 4. Suppose that a medical consultant proposes a new patient-processing system that will shorten diagnostic and treatment times but would require more skilled nurses and technicians as well as an equipment upgrade. However, the total practical capacity would remain the same, at 20,000 hours. Total resource costs are predicted to increase by $100,000. The consultant estimates that the cycle times for each patient type would be reduced from 3 to 2 hours, 5.6 to 4.5 hours, and 11 to 9 hours. The physicians that own the clinic have expressed a willingness to implement the changes, provided that the unit cost of servicing each patient type decreases. Use DBC to estimate the new unit costs. If required round your answer to two decimal places. Unit Cost No Disease Mild Severe Should the clinic implement the new system? per patient per patient per patient Discuss the advantages of DBC for this analysis over ABC and TDABC. Finally, identify the data analytic types (descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, or prescriptive) that apply for this analysis (see Exhibits 2.5 and Exhibits 2.6, for a review of data analytic types). Note: More than one analytic type might apply. The data analytic types are more patients suggest that the clinic The unit costs are what are likely to happen given the estimates. The adopt the new system. in unit costs and the in ability to process
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


