Question: The code needs to be in C, not in C++ Description: You have been tasked to design an application for an engineering firm to measure
The code needs to be in C, not in C++




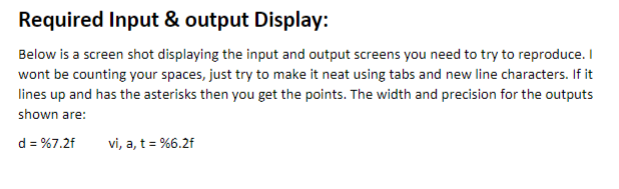
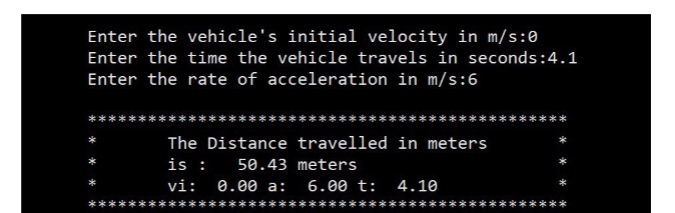

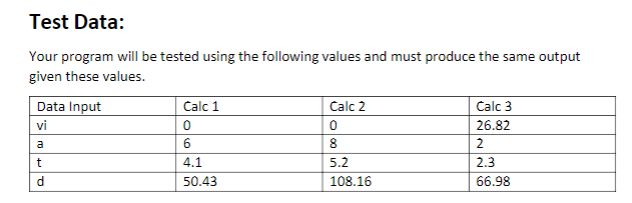
Description: You have been tasked to design an application for an engineering firm to measure the performance of their vehicle designs. The user, an engineer will enter data into your program when prompted and will perform the required calculation and output the answer. The formula used for this project calculates the distance an object will cover in meters given an initial velocity, a rate of acceleration and a time of acceleration or travel. Objectives: Learn to implement a solution to a problem using stepwise refinement. . Use Selection structures. . Declare functions in the C language. . Pass by Reference to functions using pointers. ument your projects. Doc . Use pointers for returning values to calling programs. . Use operator precedence and associativity rules to perform computations. . Display formatted output using input/output statements. . Use format control strings to format text output. . Use C data types. Requirements: 1. Your program must declare three functions using function prototypes 2. The first function should be called "Printinstructions" 3. This function takes no arguments and returns an int or Boolean value, which the caller ca use to determine if the user wishes to quit (entered 'q or 'Q) the program or continue (any other character). This will require an if/else decision in your main function 4. The second function should be called "GetData". 5. This function must use pointers to get the required inputs (time, velocity, and acceleration) from the user and store the values in the caller's local variables in mairn (upward communication). 6. The third function is called "AccelerationDisplacement" This function will take parameters by value from the caller in main and calculate the distance an object will travel given time, initial velocity and acceleration and return the calculated value as a type double to the caller The function should perform the calculation of the formula given. You may use the pow() function pp 191 of the text. 7. 8. 9. The final function is called PrintOutput. 10. This function is called with a value argument and prints the formatted output to the hehered uttbeo he progam hous end gracefully. Formulas: The formula to determine the distance travelled by an accelerating body is shown below. This is a physics kinematics formula. d- displacement (distance) vi initial velocity t time a accelerations Source: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1DKin/Lesson-6/Kinematic-Equations and-Problem-Solving Function Prototypes: int Printinstructions(void) void GetData(float, float, float double AccelerationDisplacement(float vi, float t, float a); void PrintOutput(double result, float vi, float t, float a); Required Input & output Display: Below is a screen shot displaying the input and output screens you need to try to reproduce. I wont be counting your spaces, just try to make it neat using tabs and new line characters. If it lines up and has the asterisks then you get the points. The width and precision for the outputs shown are: d-%7.2f vi, a, t : %6.2f Enter the vehicle's initial velocity in m/s:e Enter the time the vehicle travels in seconds:4.1 Enter the rate of acceleration in m/s:6 The Distance travelled in meters is 50.43 meters vi: 0.00 a 6.00 t: 4.10 Guide & Requirements: The following section supplements the problem in the text to help offer hints and tips to help you succeed. These tips are a pattern of how you will approach programming problems to come 1. Read the entire problem description and requirements before attempting to compose any code Based on the description and requirements outline an algorithm that details in steps how you would solve the calculations procedure of the problem based on the requirements. Map out the logical flow of your solution so you can visualize iteasily Using your steps create pseudocode on the same paper that use some of the important C keywords needed to implement your solution In your source file, use block comments and inline comments to document what steps of your algorithm you are planning to code. This helps give you a sequence of steps to implement in code, which is right in front of you as you work. These comments also help you troubleshoot and document your code so you may work on it incrementally. When you return to your task, it is easy to see where you left off A good practice is to create your empty framework with function prototypes and the main function of main first. Then to add your algorithm steps as comments, from top to bottom in main. Main will be the function, which calls all the other functions to implement the solution. In this way, main is relatively clean and easily readable. Your functions become decoupled from main, making them easier for reuse in other programs. I suggest backing up your work by using the "cp" command to put a copy of your source file into another subdirectory in your osprey directory. One scheme might be to rename the copy as p3.c.bak9 24_18 for instance. This way you know what date it was known good at before you introduced a change. Also, make certain you set your file permissions so that classmates cannot read or copy your projects!!! 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Test Data: Your program will be tested using the following values and must produce the same output given these values. Calc 1 0 6 4.1 50.43 Calc 3 26.82 2 2.3 66.98 Calc 2 vi 0 8 5.2 108.16 Description: You have been tasked to design an application for an engineering firm to measure the performance of their vehicle designs. The user, an engineer will enter data into your program when prompted and will perform the required calculation and output the answer. The formula used for this project calculates the distance an object will cover in meters given an initial velocity, a rate of acceleration and a time of acceleration or travel. Objectives: Learn to implement a solution to a problem using stepwise refinement. . Use Selection structures. . Declare functions in the C language. . Pass by Reference to functions using pointers. ument your projects. Doc . Use pointers for returning values to calling programs. . Use operator precedence and associativity rules to perform computations. . Display formatted output using input/output statements. . Use format control strings to format text output. . Use C data types. Requirements: 1. Your program must declare three functions using function prototypes 2. The first function should be called "Printinstructions" 3. This function takes no arguments and returns an int or Boolean value, which the caller ca use to determine if the user wishes to quit (entered 'q or 'Q) the program or continue (any other character). This will require an if/else decision in your main function 4. The second function should be called "GetData". 5. This function must use pointers to get the required inputs (time, velocity, and acceleration) from the user and store the values in the caller's local variables in mairn (upward communication). 6. The third function is called "AccelerationDisplacement" This function will take parameters by value from the caller in main and calculate the distance an object will travel given time, initial velocity and acceleration and return the calculated value as a type double to the caller The function should perform the calculation of the formula given. You may use the pow() function pp 191 of the text. 7. 8. 9. The final function is called PrintOutput. 10. This function is called with a value argument and prints the formatted output to the hehered uttbeo he progam hous end gracefully. Formulas: The formula to determine the distance travelled by an accelerating body is shown below. This is a physics kinematics formula. d- displacement (distance) vi initial velocity t time a accelerations Source: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1DKin/Lesson-6/Kinematic-Equations and-Problem-Solving Function Prototypes: int Printinstructions(void) void GetData(float, float, float double AccelerationDisplacement(float vi, float t, float a); void PrintOutput(double result, float vi, float t, float a); Required Input & output Display: Below is a screen shot displaying the input and output screens you need to try to reproduce. I wont be counting your spaces, just try to make it neat using tabs and new line characters. If it lines up and has the asterisks then you get the points. The width and precision for the outputs shown are: d-%7.2f vi, a, t : %6.2f Enter the vehicle's initial velocity in m/s:e Enter the time the vehicle travels in seconds:4.1 Enter the rate of acceleration in m/s:6 The Distance travelled in meters is 50.43 meters vi: 0.00 a 6.00 t: 4.10 Guide & Requirements: The following section supplements the problem in the text to help offer hints and tips to help you succeed. These tips are a pattern of how you will approach programming problems to come 1. Read the entire problem description and requirements before attempting to compose any code Based on the description and requirements outline an algorithm that details in steps how you would solve the calculations procedure of the problem based on the requirements. Map out the logical flow of your solution so you can visualize iteasily Using your steps create pseudocode on the same paper that use some of the important C keywords needed to implement your solution In your source file, use block comments and inline comments to document what steps of your algorithm you are planning to code. This helps give you a sequence of steps to implement in code, which is right in front of you as you work. These comments also help you troubleshoot and document your code so you may work on it incrementally. When you return to your task, it is easy to see where you left off A good practice is to create your empty framework with function prototypes and the main function of main first. Then to add your algorithm steps as comments, from top to bottom in main. Main will be the function, which calls all the other functions to implement the solution. In this way, main is relatively clean and easily readable. Your functions become decoupled from main, making them easier for reuse in other programs. I suggest backing up your work by using the "cp" command to put a copy of your source file into another subdirectory in your osprey directory. One scheme might be to rename the copy as p3.c.bak9 24_18 for instance. This way you know what date it was known good at before you introduced a change. Also, make certain you set your file permissions so that classmates cannot read or copy your projects!!! 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Test Data: Your program will be tested using the following values and must produce the same output given these values. Calc 1 0 6 4.1 50.43 Calc 3 26.82 2 2.3 66.98 Calc 2 vi 0 8 5.2 108.16
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


