Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The data in the Table II were gathered using a force meter pulling horizontally on a block of wood placed on a level flat
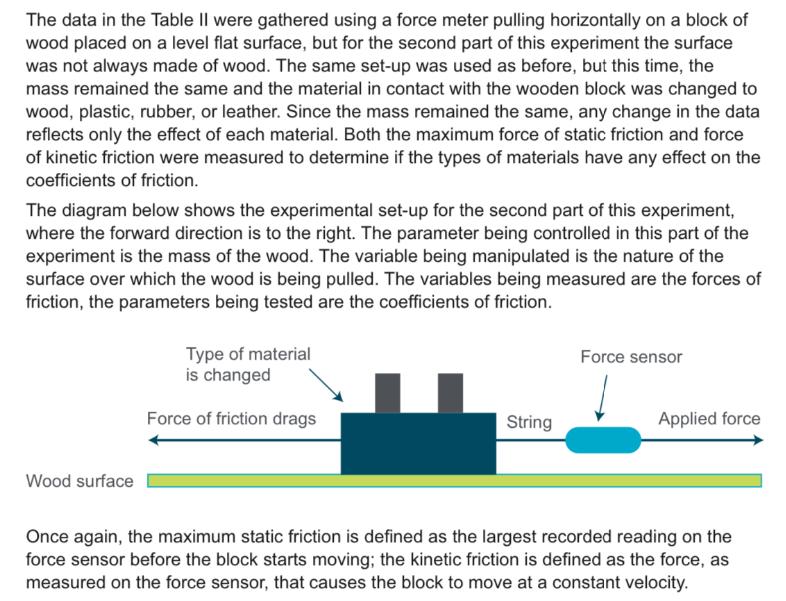
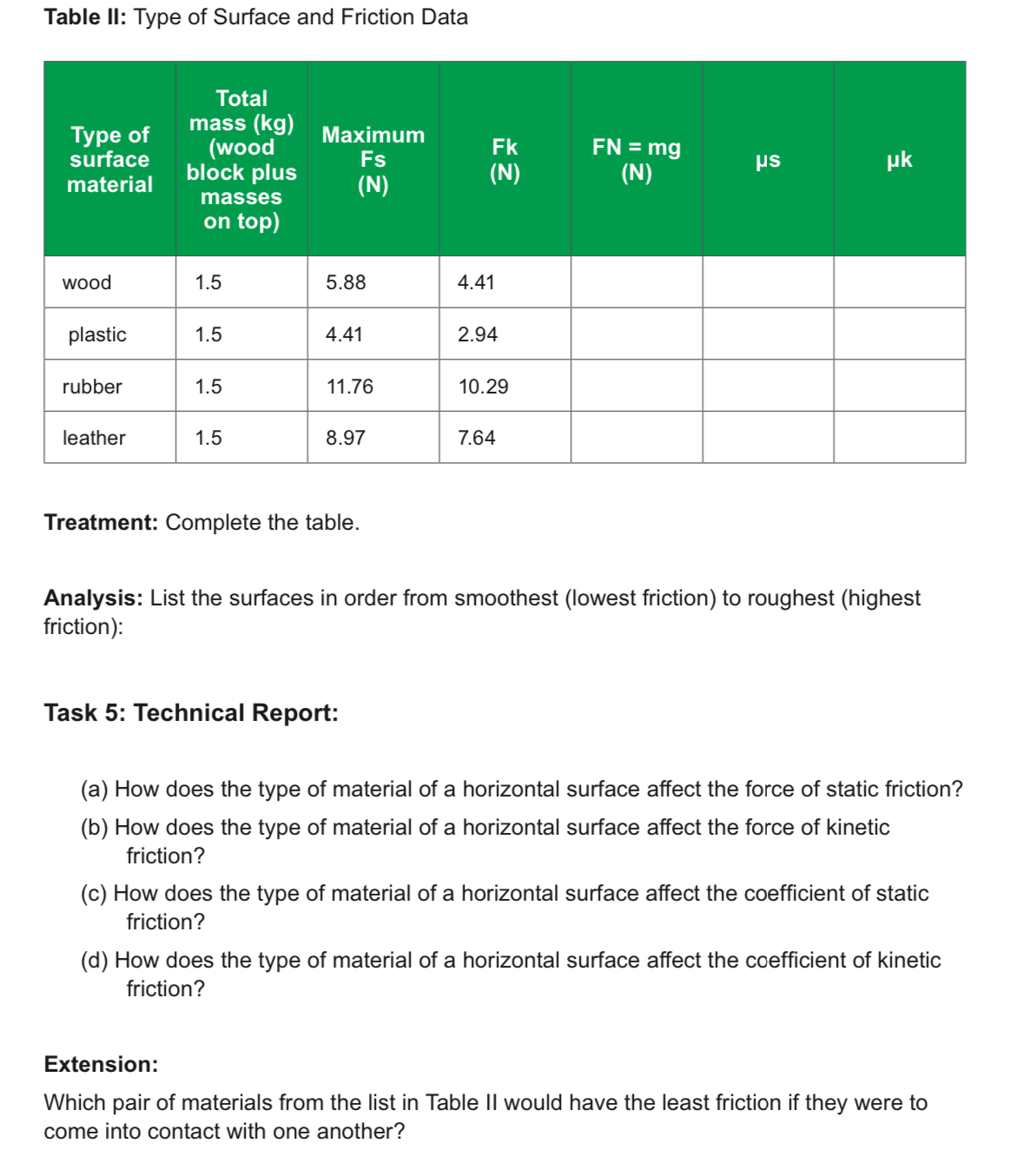
The data in the Table II were gathered using a force meter pulling horizontally on a block of wood placed on a level flat surface, but for the second part of this experiment the surface was not always made of wood. The same set-up was used as before, but this time, the mass remained the same and the material in contact with the wooden block was changed to wood, plastic, rubber, or leather. Since the mass remained the same, any change in the data reflects only the effect of each material. Both the maximum force of static friction and force of kinetic friction were measured to determine if the types of materials have any effect on the coefficients of friction. The diagram below shows the experimental set-up for the second part of this experiment, where the forward direction is to the right. The parameter being controlled in this part of the experiment is the mass of the wood. The variable being manipulated is the nature of the surface over which the wood is being pulled. The variables being measured are the forces of friction, the parameters being tested are the coefficients of friction. Wood surface Type of material is changed Force of friction drags String Force sensor Applied force Once again, the maximum static friction is defined as the largest recorded reading on the force sensor before the block starts moving; the kinetic friction is defined as the force, as measured on the force sensor, that causes the block to move at a constant velocity. Table II: Type of Surface and Friction Data Type of surface Total mass (kg) (wood block plus Maximum Fs IZ Fk FN = mg s S (N) material (N) (N) masses on top) wood 1.5 5.88 4.41 plastic 1.5 4.41 2.94 rubber 1.5 11.76 10.29 leather 1.5 8.97 7.64 HC Treatment: Complete the table. Analysis: List the surfaces in order from smoothest (lowest friction) to roughest (highest friction): Task 5: Technical Report: (a) How does the type of material of a horizontal surface affect the force of static friction? (b) How does the type of material of a horizontal surface affect the force of kinetic friction? (c) How does the type of material of a horizontal surface affect the coefficient of static friction? (d) How does the type of material of a horizontal surface affect the coefficient of kinetic friction? Extension: Which pair of materials from the list in Table II would have the least friction if they were to come into contact with one another?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


