the exercise will be on file i had to take multiple screenshot to show everything
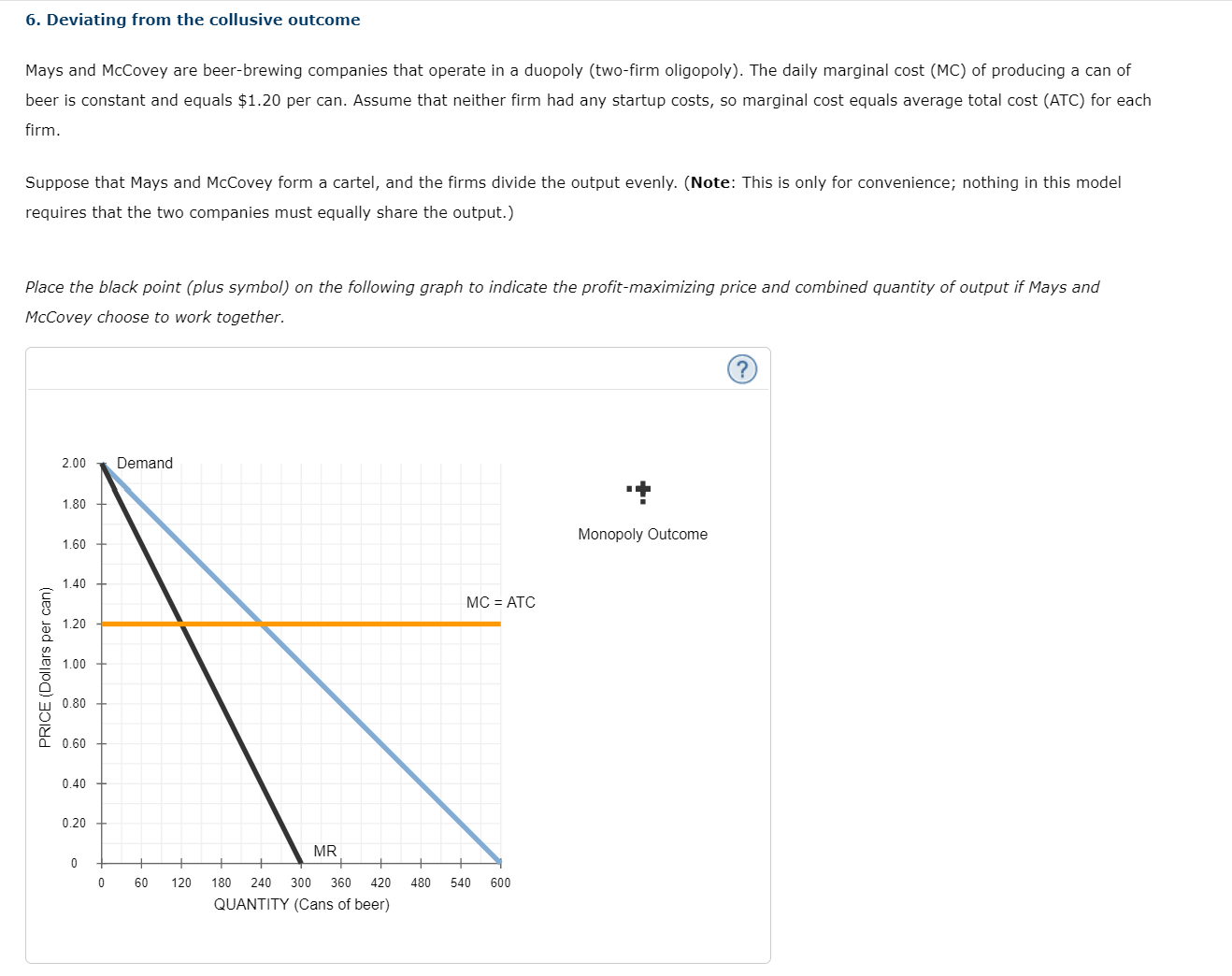
When they act as a protsmaximizing cartel, each company will produce \\:| cans and charge per can. Given this information, each firm earns a daily prot of , so the daily total industry prot in the beer market is . Oligopolists often behave noncooperatively and act in their own selfsinterest even though this decreases total prot in the market. Again, assume the two companies form a cartel and decide to work together. Both rms initially agree to produce half the quantity that maximizes total industry profit. Now, suppose that Mays decides to break the collusion and increase its output by 50%, while McCovey continues to produce the amount set under the collusive agreement. Using the demand curve shown in the previous graph, find the price associated with this new total level of combined output (the price at which this new level of output would be purchased by consumers). Mays's deviation from the collusive agreement causes the price of a can of beer to V to per can. Mays's profit is now , while McCovey's profit is no_ . Therefore, you can conclude that total industry profit 7 when Mays increases its output beyond the collusive quantity. When they act as a protmaximizing cartel, each company will produce: cans and charge per can. Given this information, each firm earns a daily prot of , so the daily total industry prot in the beer market is . Oligopolists often behave noncooperatively and act in their own selfinterest even though this decreases total prot in the market. Again, assume the two companies form a cartel and decide to work together. Both rms initially agree to produce half the quantity that maximizes total industry profit. Now, suppose that Mays decides to break the collusion and increase its output by 50% while McCovey continues to produce the amount set under the decrease collusive agreement. Using the demand curve shown in the previous graph, find th iated with this new total level of combined output [the price at which this new level of output would be purchased by consumers]. increase Mays's deviation from the collusive agreement causes the price of a can of beer to V to per can. Mays's profit is now , while McCovey's profit is now . Therefore, you can conclude that total industry profit V when Mays increases its output beyond the collusive quantity. When they act as a protmaximizing cartel, each company will produce :cans and charge per can. Given this information, each firm earns a daily prot of , so the daily total industry prot in the beer market is . Oligopolists often behave noncooperatively and act in their own selfinterest even though this decreases total prot in the market. Again, assume the two companies form a cartel and decide to work together. Both rms initially agree to produce half the quantity that maximizes total industry profit. Now, suppose that Mays decides to break the collusion and increase its output by 50%, while McCovey continues to produce the amount set under the collusive agreement. Using the demand curve shown in the previous graph, find the price associated with this new total level of combined output (the price at which this new level of output would be purchased by consumers]. decreases increases Mays's deviation from the collusive agreement causes the price of a can of beer to V to per u , while McCovey's profit is now . Therefore, you can conclude that total industry profit V when Mays increases its output beyond the collusive quantity. 6. Deviating from the collusive outcome Mays and Mccovey are beer-brewing companies that operate in a duopoly (two-firm oligopoly). The daily marginal cost (MC) of producing a can of beer is constant and equals $1.20 per can. Assume that neither firm had any startup costs, so marginal cost equals average total cost (ATC) for each firm. Suppose that Mays and Mccovey form a cartel, and the firms divide the output evenly. (Note: This is only for convenience; nothing in this model requires that the two companies must equally share the output.) Place the black point (plus symbol) on the following graph to indicate the profit-maximizing price and combined quantity of output if Mays and Mccovey choose to work together. 2.00 Demand 1.80 + 1.60 Monopoly Outcome PRICE (Dollars per can) 1.40 MC = ATC 1.20 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 MR 60 120 180 240 300 360 420 480 540 600 QUANTITY (Cans of beer)