THE EXERCISE WILL BE ON FILE PLEASE I HAD TO TAKE MULTIPLE SCREENSHOT TO SHOW EVERYTHING
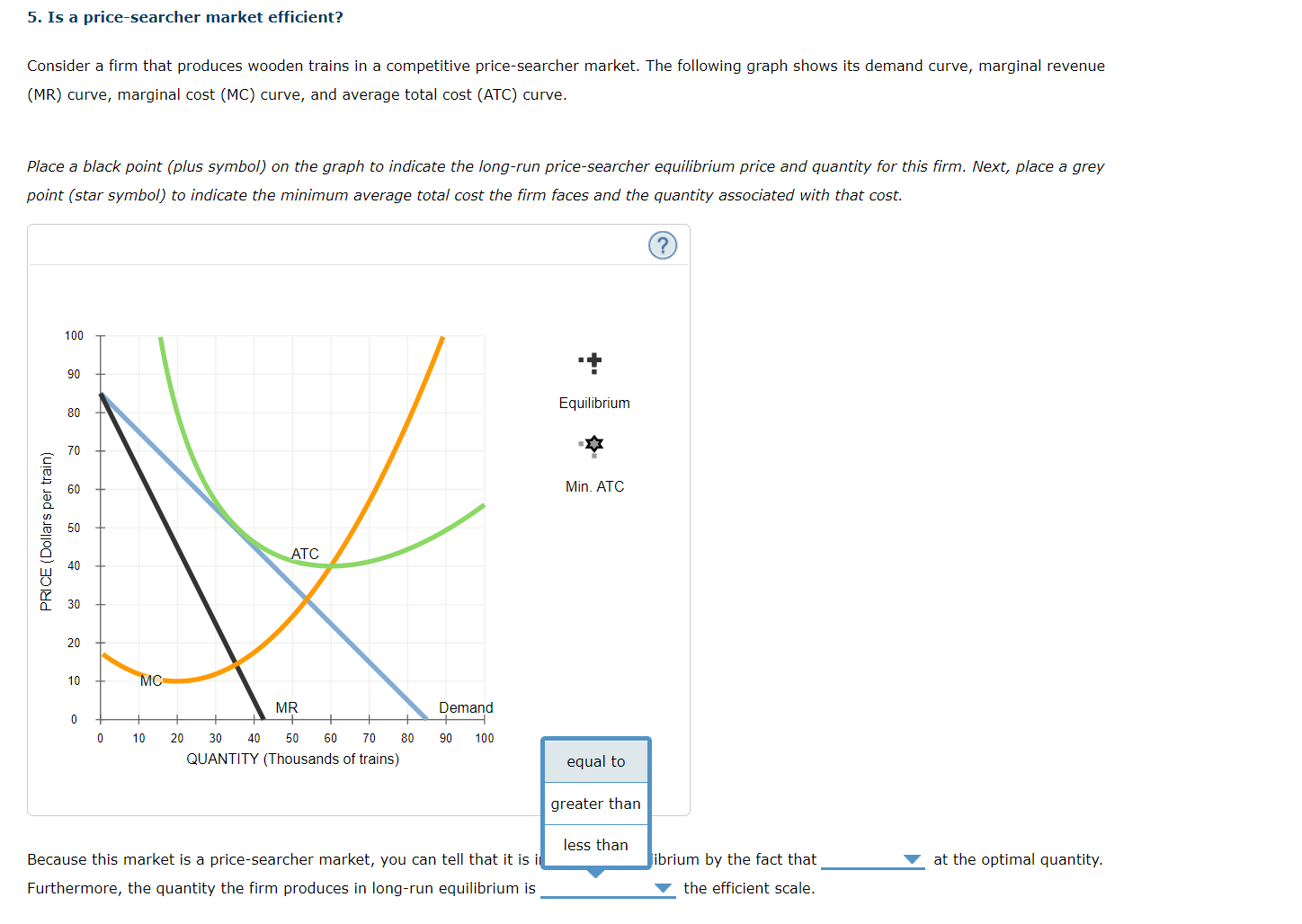
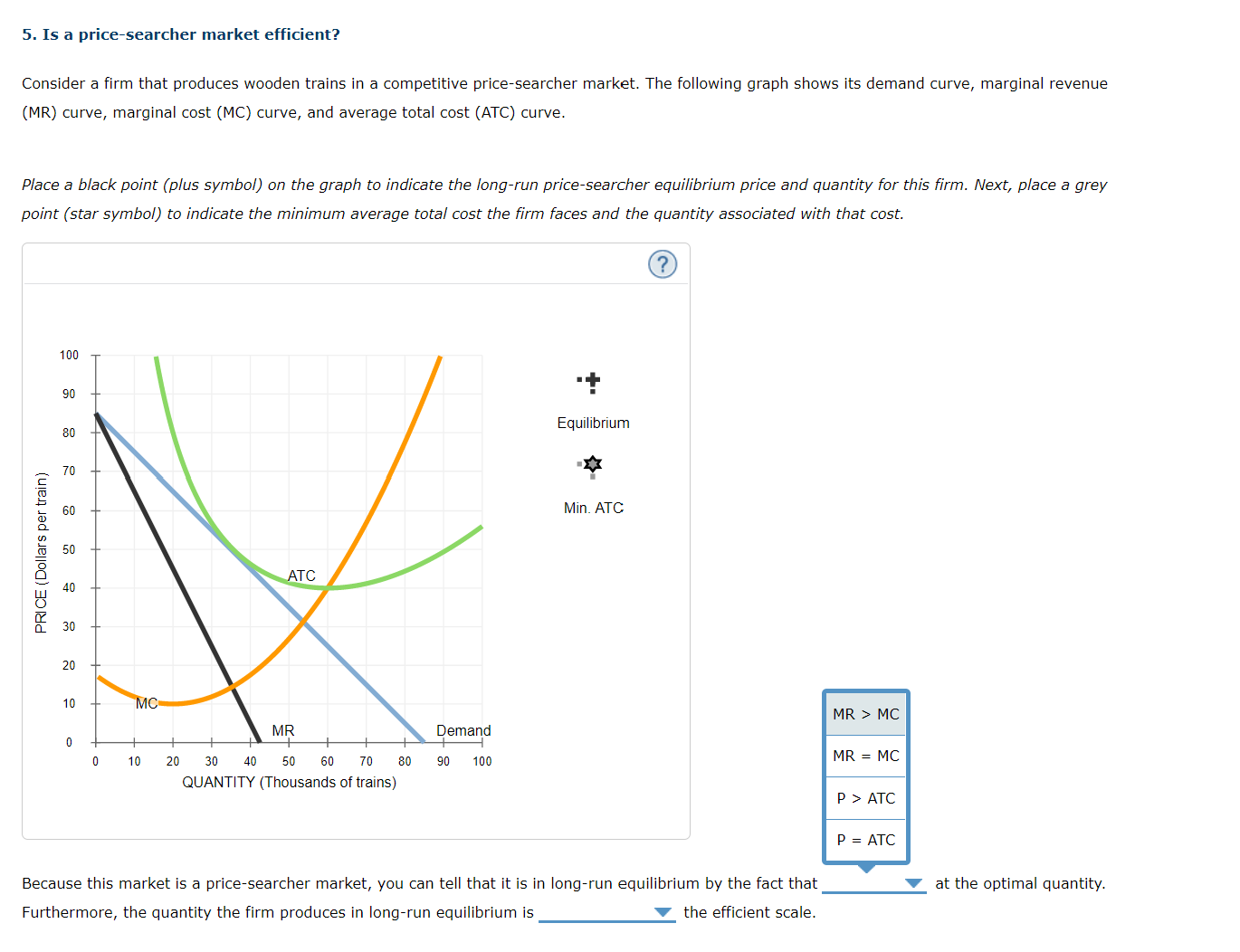
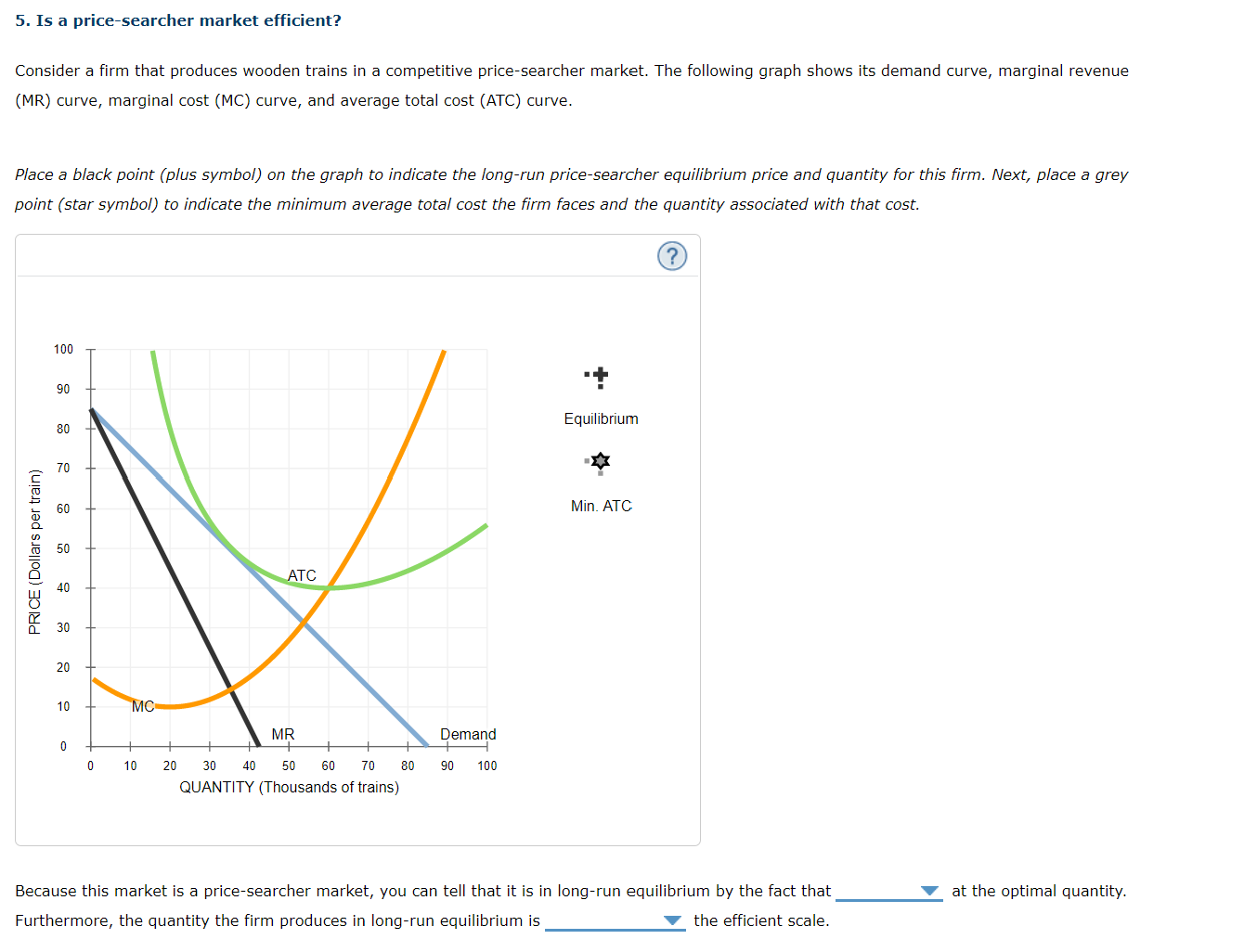
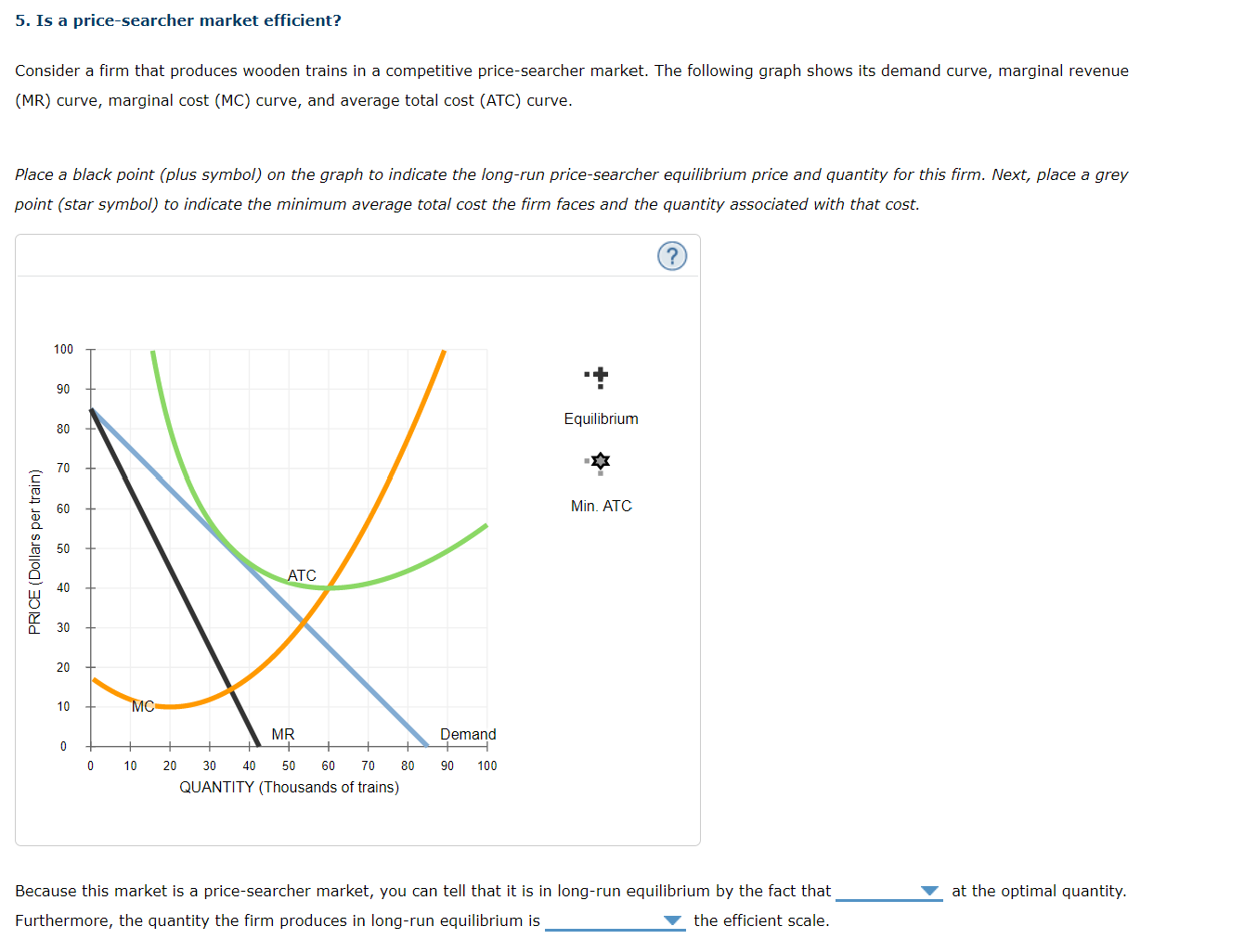
5. Is a price-searcher market efficient? Consider a firm that produces wooden trains in a competitive price-searcher market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run price-searcher equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. 100 90 80 Equilibrium PRICE ( Dollars per train) 70 60 Min. ATC 50 ATC 30 20 MC MR Demand 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 QUANTITY (Thousands of trains) equal to greater than Because this market is a price-searcher market, you can tell that it is less than ibrium by the fact that at the optimal quantity. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is the efficient scale.5. Is a price-searcher market efficient? Consider a firm that produces wooden trains in a competitive price-searcher market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run price-searcher equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. 100 90 80 Equilibrium PRICE ( Dollars per train) 70 Min. ATC 50 40 ATC 30 20 10 MR > MC MR Demand 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 MR = MC QUANTITY (Thousands of trains) P > ATC P = ATC Because this market is a price-searcher market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that at the optimal quantity. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is the efficient scale.5. Is a price-searcher market efficient? Consider a firm that produces wooden trains in a competitive price-searcher market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run price-searcher equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. 100 90 80 Equilibrium PRICE ( Dollars per train) 70 60 Min. ATC 50 40 ATC 30 20 10 MC MR Demand 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 QUANTITY (Thousands of trains) Because this market is a price-searcher market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that at the optimal quantity. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is the efficient scale